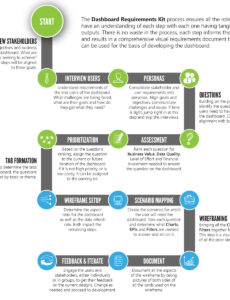
In the complex landscape of modern project development, managing a multitude of requirements, design specifications, test cases, and deployment considerations can feel like navigating a labyrinth. Without a clear path connecting each piece, projects can quickly veer off course, leading to budget overruns, missed deadlines, and ultimately, stakeholder dissatisfaction. This is where a robust system for tracking project elements becomes not just helpful, but absolutely essential.
Imagine a tool that provides a crystal-clear lineage for every single requirement, from its initial conception to its final implementation and verification. Such a tool ensures that nothing is overlooked, every change is understood, and the project remains aligned with its original objectives. This foundational element is precisely what a Requirements Traceability Matrix Example Template offers, serving as the connective tissue that binds all project artifacts together and promotes transparency and control across the entire development lifecycle.
Why a Requirements Traceability Matrix is Indispensable
Successful project delivery hinges on clarity and accountability. A well-constructed traceability matrix acts as a living document that systematically links requirements to other project elements, such as design documents, code modules, test cases, and even business objectives. This comprehensive mapping provides invaluable insights, allowing teams to understand the ripple effect of any proposed change before it’s implemented.
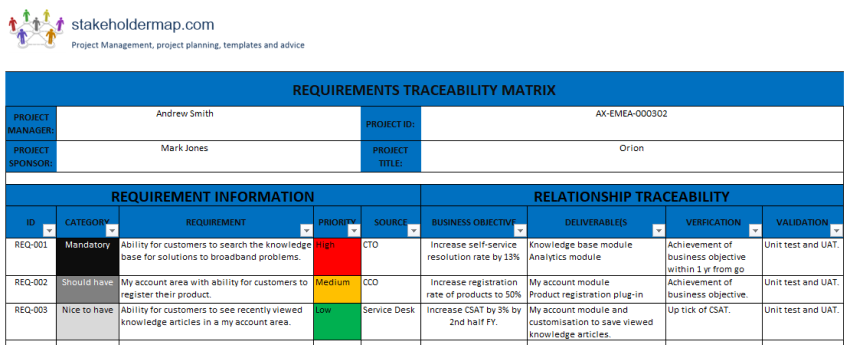
Beyond just tracking, a requirements traceability matrix significantly mitigates risks. It helps identify orphaned requirements that aren’t being addressed or test cases that don’t cover specific functionalities, preventing critical gaps in development. Furthermore, it improves communication among diverse project teams, ensuring everyone operates from a unified understanding of what needs to be built and why. This level of interconnectedness is vital for ensuring project integrity and meeting regulatory compliance where applicable.
What is a Requirements Traceability Matrix?
At its core, a requirements traceability matrix is a document, often in a table format, that establishes a many-to-many relationship between various project artifacts. It serves as a visual and systematic record of the connections between high-level business requirements, detailed functional requirements, technical specifications, and validation methods. This matrix provides a complete audit trail, demonstrating that every requirement has been considered, designed for, developed, and thoroughly tested.
The power of a traceability matrix lies in its ability to offer both forward and backward traceability. Forward traceability ensures that every requirement is ultimately delivered through the project’s outputs. Conversely, backward traceability confirms that every output can be linked back to a specific requirement, preventing scope creep and unnecessary work. This dual perspective is crucial for maintaining focus and ensuring the final product meets its intended purpose.
Key Components of a Robust Traceability Matrix
While the specific columns in a traceability matrix can vary based on project needs and organizational standards, certain core elements are almost universally beneficial. These components help create a comprehensive and useful document that supports all phases of a project. They provide the necessary detail to ensure that requirements are clearly understood and thoroughly validated throughout their lifecycle.
Here are some essential components typically found in an effective traceability matrix:
- **Requirement ID:** A unique identifier for each specific requirement, allowing for easy reference.
- **Requirement Description:** A clear, concise statement outlining what the requirement entails.
- **Requirement Type:** Categorization (e.g., functional, non-functional, business, security).
- **Source:** Who or what originated the requirement (e.g., stakeholder, user story, regulatory document).
- **Priority:** The importance or criticality of the requirement (e.g., high, medium, low).
- **Status:** The current state of the requirement (e.g., proposed, approved, in progress, tested, deployed).
- **Design Specification:** Links to design documents or architectural components that address the requirement.
- **Development Component/Module:** Identifies the specific code or module implementing the requirement.
- **Test Case ID(s):** References to the test cases created to verify the requirement’s implementation.
- **Test Status:** The outcome of testing related to the requirement (e.g., passed, failed, blocked).
- **Verification Method:** How the requirement will be validated (e.g., inspection, demonstration, test).
- **Owner:** The individual or team responsible for the requirement.
- **Version/Change Log:** To track modifications to the requirement over time.
How to Effectively Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix
Implementing and maintaining a requirements traceability matrix goes beyond simply filling out a table; it’s an ongoing process that integrates into the project’s workflow. To maximize its benefits, teams should approach its usage strategically. This involves establishing clear guidelines and regularly updating the document to reflect the project’s current state.
Firstly, begin establishing requirement links early in the project lifecycle, ideally as soon as requirements are defined. Proactive linkage prevents significant rework later and ensures that design and development efforts are directly aligned with established needs. Secondly, assign clear ownership for updating the matrix to specific individuals or roles, ensuring consistency and accuracy. Regular reviews with stakeholders are also critical for validating the ongoing relevance and accuracy of the linked items.
For larger, more complex projects, consider leveraging specialized requirements management tools rather than basic spreadsheets. These tools offer enhanced automation, version control, and collaboration features, making the management of extensive traceability data much more efficient. Whether using a simple spreadsheet or advanced software, the commitment to keeping the traceability document current is paramount for its continued value.
Choosing and Customizing Your Traceability Solution
The choice of tool for managing your project traceability can significantly impact its usability and effectiveness. For smaller projects with fewer requirements, a well-structured spreadsheet application like Excel or Google Sheets can serve as an adequate Requirements Traceability Matrix Example Template. These tools are readily accessible and allow for a high degree of customization without significant investment. You can easily define columns, apply filters, and use basic formulas to manage the data.
However, as projects grow in complexity, the limitations of spreadsheets become apparent. Manual updates can be prone to errors, collaboration can be cumbersome, and version control challenging. In such cases, dedicated Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) tools or specialized requirements management software become invaluable. Products like Jira, Azure DevOps, IBM DOORS, or Jama Connect offer integrated solutions for linking requirements to epics, user stories, tasks, code commits, and test results, providing a seamless and automated approach to maintaining comprehensive project traceability. When selecting a tool, consider factors like team size, project complexity, integration needs with existing systems, and budget to find the best fit.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While the benefits of maintaining a detailed requirements traceability matrix are clear, teams often encounter challenges in its implementation and upkeep. One common hurdle is the initial effort required to set up the matrix and establish all the necessary links. This can feel like a significant overhead, especially for teams unfamiliar with the practice. Overcome this by starting with a simpler version, focusing on critical links first, and gradually expanding its scope as the team becomes more proficient.
Another frequent challenge is keeping the traceability matrix updated as requirements evolve and project components change. Outdated information renders the matrix useless. To combat this, embed traceability updates into the standard change management process. Whenever a requirement or a related artifact changes, the traceability document must also be updated as part of the approval workflow. Additionally, ensure that team members understand the value of an accurate traceability matrix, fostering a culture where its maintenance is seen as an integral part of quality assurance and project control, rather than an optional chore.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between forward and backward traceability?
Forward traceability shows that every requirement is covered by a design, implemented in code, and verified by a test case, ensuring all initial requirements are met. Backward traceability links design elements, code, and test cases back to specific requirements, confirming that no extra features (scope creep) are developed and that all work has a legitimate origin.
Can a small project benefit from an RTM?
Absolutely. Even small projects benefit from a basic traceability matrix. It helps clarify scope, prevents miscommunication, and ensures that the final product addresses the core needs. For smaller efforts, a simplified template in a spreadsheet might be perfectly sufficient.
What tools are best for managing a traceability matrix?
For simple projects, a spreadsheet (Excel, Google Sheets) works well. For more complex endeavors, dedicated ALM tools like Jira, Azure DevOps, IBM DOORS, Jama Connect, or Siemens Polarion are highly recommended. These tools offer advanced linking capabilities, version control, and reporting features.
How often should the traceability matrix be updated?
The traceability matrix should be a living document, updated whenever there are changes to requirements, design specifications, test cases, or any other linked artifact. This often means updates occur throughout the development lifecycle, particularly during requirements refinement, design phases, and testing cycles. Regular reviews (e.g., weekly or bi-weekly) should also be scheduled to ensure its accuracy.
Ultimately, adopting a well-defined requirements traceability strategy is a proactive step towards greater project success. It transforms complex relationships into clear, manageable pathways, offering unparalleled visibility into the entire development process. By understanding the intricate connections between requirements, design, development, and testing, teams can make informed decisions, minimize risks, and deliver solutions that truly meet user and business needs.
Embracing the principles behind a robust traceability matrix empowers teams to navigate project complexities with confidence. It fosters a disciplined approach to project management, ensuring that every effort contributes directly to the project’s objectives. Start by exploring a Requirements Traceability Matrix Example Template today, and witness firsthand how this foundational practice can elevate your project delivery to new heights of clarity, control, and consistency.