In the fast-paced world of Agile development, where change is constant and iterations are rapid, maintaining clarity on "why" a feature exists and "how" it’s being addressed can be a significant challenge. Teams often find themselves juggling evolving user stories, new tests, and bug reports, all while striving to deliver value quickly. This constant flux underscores the critical need for a structured approach to connect the dots between stakeholder needs and delivered solutions.
Enter the requirements traceability matrix: a powerful tool that, when adapted for Agile, becomes an indispensable asset for ensuring transparency, managing scope, and validating quality. It’s not about imposing rigid bureaucracy but rather about empowering teams with the insights needed to make informed decisions and build the right product efficiently. Understanding and utilizing an effective Agile Requirements Traceability Matrix Template can transform how your team navigates complexity, ensuring every piece of work aligns with strategic goals.
Why Traceability Matters in Agile
While Agile methodologies emphasize flexibility and responding to change, this doesn’t diminish the need for understanding the lineage of requirements. Quite the opposite, rapid iterations and continuous delivery heighten the importance of knowing how a user story, for instance, connects to a specific business goal, development task, or test case. Without this clear lineage, it’s easy for features to drift from their original intent or for critical requirements to be overlooked.
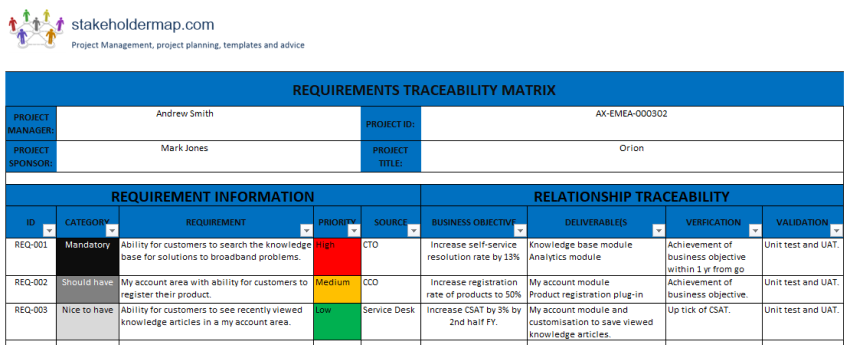
Effective requirements traceability provides a foundational layer of understanding for the entire development team and stakeholders alike. It offers a clear, verifiable path from a high-level business objective down to the individual lines of code or test results. This transparency is crucial for impact analysis, validating successful implementation, and demonstrating compliance in regulated industries. It serves as a living document that evolves with the product, reflecting changes and ensuring alignment at every stage.
What is an Agile Requirements Traceability Matrix?
At its core, a requirements traceability matrix is a document that links requirements to other artifacts in the development lifecycle. In an Agile context, this matrix isn’t a static, weighty tome created once and forgotten. Instead, it’s a dynamic, lightweight artifact that provides a continuous, two-way mapping between different elements such as user stories, acceptance criteria, development tasks, test cases, and even defects. Its purpose is to show the relationships and dependencies between these items, ensuring that all requirements are accounted for and tested.
This Agile traceability matrix serves as a powerful communication tool, enhancing collaboration within the scrum team and with stakeholders. It helps answer critical questions like: Which user stories are impacted if a particular technical component changes? Which tests validate a specific acceptance criterion? Has every requirement been fully implemented and verified? By providing these answers, it reduces miscommunication, prevents scope creep, and ultimately contributes to the delivery of a higher-quality product.
Key Elements of an Effective Traceability Matrix
A well-structured traceability matrix provides a clear, comprehensive view of your project’s progress and requirement coverage. While its specific contents may vary based on project needs and team practices, certain core elements are universally beneficial. These elements create the links necessary to understand the full lifecycle of a requirement, from conception to validation.
Here are the essential components typically found in a robust requirements mapping tool for Agile teams:
- **Requirement ID:** A unique identifier for each user story, epic, or feature. This ensures clear referencing.
- **Requirement Description:** A concise summary of the requirement, detailing its purpose and desired outcome.
- **Source/Stakeholder:** Who requested this requirement? This helps in understanding context and facilitates clarification.
- **Related Epics/Features:** Links to higher-level business objectives or larger features this requirement supports.
- **Development Tasks/Components:** The specific engineering tasks or system components designed to implement the requirement.
- **Test Cases/Scenarios:** The test cases created to verify that the requirement has been met correctly.
- **Test Results:** The outcome of executing the associated test cases (e.g., **Pass**, Fail, Blocked).
- **Defects/Bugs:** Any defects or bugs identified that are linked back to this requirement.
- **Status:** The current lifecycle status of the requirement (e.g., **New**, In Progress, Done, Verified).
- **Iteration/Sprint:** The sprint or iteration in which the requirement is being addressed or was completed.
By meticulously tracking these connections, teams can gain invaluable insights into their progress, potential risks, and overall product quality.
How to Implement and Use Your Traceability Matrix
Implementing a requirements traceability matrix in an Agile environment doesn’t require a heavy upfront investment; it’s an ongoing practice that integrates into your existing workflow. The goal is to make it a natural extension of your daily activities, not an additional burden. Start by identifying the key artifacts you want to link. For most Agile teams, this means connecting user stories to tasks, and then to test cases.
Begin by defining your linking strategy. Will you link every user story directly to every sub-task and test? Or will you focus on linking epics to user stories, and then user stories to acceptance tests? The level of granularity should be practical and provide sufficient value without becoming overly complex. Leverage your existing Agile tools – many project management platforms like Jira, Azure DevOps, or Trello offer built-in features for linking work items. Establish clear conventions for naming and numbering requirements to maintain consistency. During sprint planning, discuss how traceability will be maintained for new items. Encourage team members to update the matrix or relevant fields as they work, making it a shared responsibility. Regular reviews during sprint reviews or retrospectives can also ensure the matrix remains current and useful.
Benefits of Adopting a Traceability Approach
Embracing a systematic approach to managing requirements, even in Agile, yields a multitude of advantages that extend beyond mere documentation. The proactive linking of development artifacts ensures a higher degree of control and understanding throughout the product lifecycle. This improved visibility translates directly into better decision-making and a more efficient development process.
The benefits of a well-maintained requirements mapping solution include:
- Enhanced Visibility and Transparency: Provides a clear, real-time view of the progress of each requirement, making it easy to identify bottlenecks or unmet criteria.
- Improved Impact Analysis: Quickly determine which features or tests will be affected by a change to a specific requirement, reducing risks and preventing unintended consequences.
- Better Quality Assurance: Ensures that every requirement has associated test cases, guaranteeing comprehensive test coverage and validation.
- Effective Scope Management: Helps prevent scope creep by clearly defining the boundaries of each requirement and its associated work.
- Easier Compliance and Auditing: For regulated industries, a robust traceability record is invaluable for demonstrating adherence to standards and passing audits.
- Reduced Risk of Defects: By linking requirements to tests, teams can identify gaps in testing early, leading to fewer defects in production.
- Stronger Stakeholder Confidence: Clear traceability fosters trust by showing stakeholders exactly how their requirements are being addressed and validated.
Customizing Your Matrix for Different Agile Contexts
The beauty of an Agile development artifact like a traceability matrix lies in its adaptability. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution, and your requirements management approach should be tailored to fit your team’s specific needs, project complexity, and regulatory landscape. A small startup building a minimum viable product might opt for a very lean matrix, perhaps just linking user stories to high-level acceptance criteria and a few key tests. Their focus would be on speed and immediate feedback, so an overly detailed solution would be counterproductive.
Conversely, a large enterprise developing a critical system in a highly regulated environment (e.g., medical devices, finance) would require a much more granular and formal traceability solution. They might link not only user stories to tests but also to specific regulations, risk assessments, design documents, and even code modules. The key is to find the right balance between comprehensive coverage and overhead. Regularly review your traceability process in retrospectives. Is it providing value? Is it too cumbersome? Adjust the level of detail, the tools used, and the linking strategy to ensure it continuously supports your team’s efficiency and effectiveness without becoming a bureaucratic burden.
Tools and Best Practices for Managing Traceability
While a simple spreadsheet can serve as an initial Agile Requirements Traceability Matrix Template, modern Agile teams often benefit from integrated tools that automate much of the linking and reporting. Project management platforms, application lifecycle management (ALM) suites, and dedicated requirements management tools offer features designed to streamline traceability. These tools can automatically link different work items, generate reports, and provide real-time status updates, significantly reducing manual effort.
When selecting tools or establishing best practices, consider these points:
- **Leverage Existing Platforms:** Utilize features within your current Agile project management tool (e.g., Jira, Azure DevOps, Trello, Rally) for linking and tracking work items.
- **Define Clear Naming Conventions:** Standardize how requirements, tasks, and tests are named and identified to ensure consistency.
- **Automate Where Possible:** Use integrations or scripts to automatically establish links or update statuses between related artifacts.
- **Involve the Whole Team:** Ensure developers, testers, and product owners understand the importance of traceability and contribute to its maintenance.
- **Regularly Review and Refine:** Periodically check the accuracy and completeness of your traceability links, especially during sprint reviews or quality gates.
- **Focus on Value, Not Volume:** Traceability should provide actionable insights, not just a mountain of data. Link only what truly adds value to your project.
- **Maintain Bi-directional Traceability:** Ensure you can trace from a requirement to its implementation/tests, and also from a test/implementation back to its originating requirement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between a traditional RTM and an Agile RTM?
The primary difference lies in their nature and application. A traditional Requirements Traceability Matrix is often a static, comprehensive document created upfront and updated periodically, focusing on formal contractual requirements. An Agile traceability matrix is dynamic, lightweight, and continuously evolved throughout sprints, focusing on user stories, acceptance criteria, and their rapid implementation and validation within an iterative development cycle. It emphasizes immediate relevance and continuous feedback over exhaustive upfront documentation.
Do I really need a traceability matrix in a truly Agile environment?
While strict, formal documentation might seem counter-Agile, a form of requirements mapping is highly beneficial. It’s not about bureaucracy, but about clarity, risk mitigation, and quality assurance. Agile teams benefit from understanding dependencies, ensuring comprehensive testing, and verifying that delivered features align with business value. A well-implemented, lightweight traceability solution enhances transparency and decision-making without hindering agility.
Can a spreadsheet work as an Agile traceability matrix template?
Yes, a spreadsheet can absolutely serve as an effective starting point for an Agile traceability matrix, especially for smaller teams or less complex projects. It’s a low-cost, flexible option that allows teams to customize columns and linking methods. However, as projects scale or complexity increases, specialized project management or ALM tools often become more efficient due to their ability to automate linking, generate reports, and integrate with other development tools.
How often should an Agile requirements traceability matrix be updated?
An Agile requirements traceability matrix should be updated continuously and organically as work progresses. Ideally, links are created or updated as new user stories are defined, tasks are created, test cases are written, and defects are identified. It’s a living document that reflects the current state of development, making it valuable for sprint reviews, retrospectives, and daily stand-ups to provide a clear, up-to-date picture of requirement coverage and status.
The journey through Agile development is one of continuous discovery and adaptation. While the emphasis remains on working software over comprehensive documentation, the strategic application of tools like an Agile Requirements Traceability Matrix Template offers an invaluable framework for maintaining clarity and control. It’s not about stifling creativity or slowing down progress, but about illuminating the path from concept to delivered value, ensuring every effort contributes meaningfully to the product’s success.
By embracing the principles of continuous traceability, teams can navigate the complexities of evolving requirements with greater confidence. This structured approach fosters a deeper understanding of interdependencies, enhances the quality of deliverables, and ultimately empowers teams to build products that truly meet user needs and business objectives. Make traceability an integrated part of your Agile practice, and watch your team’s efficiency and product quality soar.


