In the complex landscape of modern business and technology, data is often heralded as the new oil – a vital resource that fuels innovation, drives decisions, and shapes strategy. Yet, just like crude oil, raw data needs refinement. Before it can be effectively used, it must be properly identified, understood, and meticulously collected. This critical initial phase, often overlooked or rushed, is where many projects stumble, leading to costly rework, missed deadlines, and ultimately, solutions that fail to meet their intended purpose.
Imagine embarking on a construction project without a detailed blueprint, or trying to bake a cake without knowing the ingredients. The outcome would be, at best, uncertain, and at worst, a complete disaster. The same principle applies to any initiative reliant on data. Without a clear, comprehensive understanding of what data is needed, why it’s needed, where it comes from, and how it will be used, even the most brilliant ideas can falter. This is precisely where a robust Data Requirements Gathering Template steps in, acting as your essential architectural plan for data.
The Unseen Power of Structured Data Needs
Many organizations underestimate the profound impact that well-defined data requirements have on project success. It’s not merely about ticking boxes; it’s about establishing a shared understanding among all stakeholders – business users, analysts, developers, and project managers. When everyone is on the same page regarding the data needed, the project gains clarity, scope creep is minimized, and the risk of building the wrong solution is drastically reduced.
A structured approach to identifying information needs brings discipline to an often chaotic process. It moves data collection from an ad-hoc, reactive activity to a proactive, strategic endeavor. By systematically detailing every piece of data, its source, its format, and its purpose, teams can build a solid foundation for robust systems, accurate analyses, and truly impactful business intelligence. This foresight not only saves time and money but also fosters greater confidence in the project’s ultimate delivery.
Why a Data Requirements Gathering Framework is Non-Negotiable
Implementing a consistent data requirements gathering process offers a multitude of benefits that resonate across the entire project lifecycle and beyond. It’s an investment that pays dividends in efficiency, accuracy, and stakeholder satisfaction.
Firstly, it significantly improves communication. By providing a common framework, it bridges the gap between technical and non-technical team members, ensuring everyone speaks the same language when it comes to data. Secondly, it drastically reduces rework. Clear, documented data needs mean developers build the right features the first time, preventing expensive modifications later on. Thirdly, it enhances data quality. When requirements specify data formats, validation rules, and sources, the data collected is inherently cleaner and more reliable. This, in turn, leads to more trustworthy analytics and better-informed decisions. Finally, it mitigates project risk by identifying potential data gaps, integration challenges, or compliance issues early in the process, allowing for proactive solutions rather than reactive damage control.
Core Components of an Effective Data Needs Blueprint
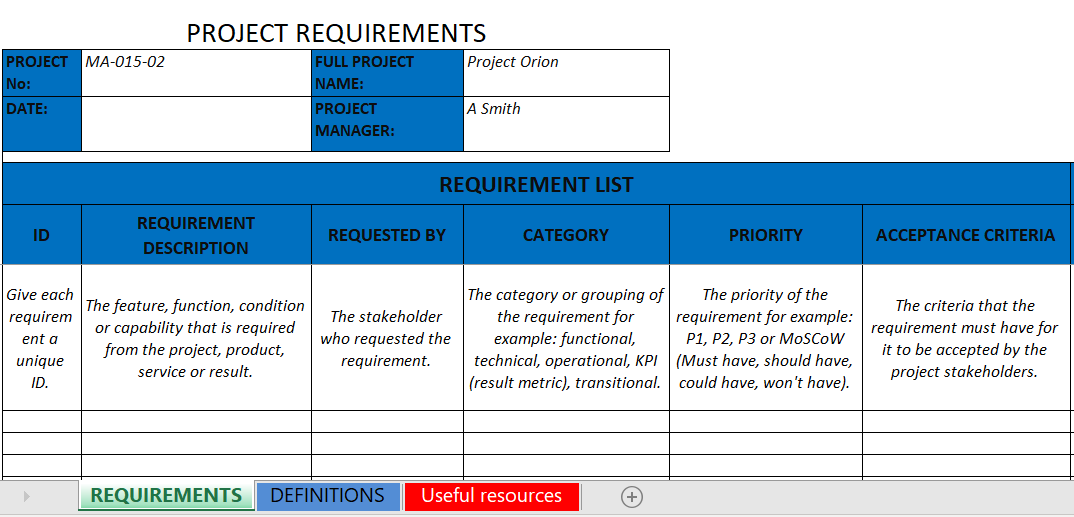
While the specifics of any information gathering worksheet will vary based on project scope and industry, a comprehensive structure generally includes several key sections designed to capture all essential details. These components work together to form a holistic view of your data landscape.
Here are the fundamental elements you should expect to find in a powerful data collection blueprint:
- Project Overview and Scope: Briefly describes the project, its objectives, and how this data requirement effort fits within the larger initiative. Defines the boundaries of the data being discussed.
- Stakeholder Identification: Lists all individuals or groups involved in defining, providing, or using the data. Includes their roles and contact information for clarity.
- Business Requirements: Outlines the overarching business needs and problems the data is intended to solve. Links data directly to strategic goals.
- Data Elements and Definitions: This is the heart of the document. For each required data element, it specifies:
- Name: The common name of the data field (e.g., CustomerID, OrderDate).
- Description: A clear, concise explanation of what the data represents.
- Source: Where the data originates (e.g., CRM system, external API, user input).
- Data Type: The format of the data (e.g., String, Integer, Date, Boolean).
- Length/Format: Specific constraints like maximum characters, decimal places, or date format (e.g., MM/DD/YYYY).
- Validation Rules: Criteria for ensuring data quality (e.g., must be numeric, must be unique, within a certain range).
- Required/Optional: Indicates if the data element is mandatory for a record.
- Privacy/Security Classification: Identifies if the data contains sensitive information (e.g., PII, PHI) and what security measures apply.
- Non-Functional Data Requirements: Addresses aspects like data volume, latency, retention policies, and performance expectations.
- Reporting and Analytics Requirements: Details specific reports, dashboards, or analytical views that will utilize the gathered data.
- Data Flow and Integration: Describes how data moves between systems and any necessary transformations.
- Approval and Sign-off: A section for key stakeholders to formally approve the documented requirements, signifying their agreement and commitment.
Practical Steps for Leveraging Your Data Collection Blueprint
Having a well-designed information gathering worksheet is only half the battle; knowing how to effectively use it is the other. The process of filling out a **Data Requirements Gathering Template** is highly interactive and iterative.
Begin by preparing thoroughly. Understand the project’s overall goals and identify the key stakeholders who possess the necessary data knowledge. Schedule dedicated sessions for requirements elicitation, whether through interviews, workshops, or group discussions. During these sessions, use the template as a guide, systematically going through each section and prompting stakeholders for detailed input. Don’t be afraid to ask "why" multiple times to uncover the true underlying needs. Once initial requirements are captured, validate them rigorously. Review the documented data elements with stakeholders to ensure accuracy, completeness, and alignment with business objectives. This iterative review and feedback loop is crucial for refining your data specification guide and preventing misunderstandings. Finally, ensure your requirements management resource is version controlled and accessible to all relevant team members throughout the project life cycle.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Requirements Elicitation
Even with the best tools, the process of defining business data requirements can be fraught with challenges. Being aware of common pitfalls can help teams navigate these complexities more effectively. One frequent issue is **ambiguity or vagueness**. Requirements like “the system needs to handle customer data” are practically useless. Instead, push for specific details: “the system needs to store customer name (first, last), email address (validated format), and phone number (10 digits, numeric only).”
Another pitfall is lack of stakeholder engagement. If key business users aren’t actively involved, the documented project data needs may not accurately reflect reality. Ensure you involve the right people at the right time. Furthermore, assuming prior knowledge can lead to gaps. Never assume that a technical team understands the business context or that business users understand technical limitations. Use the data acquisition strategy as a bridge to clarify these differences. Lastly, scope creep is a persistent threat. While flexibility is important, continuously re-evaluating the scope and documenting any changes in the information architecture plan is vital to keep the project on track and prevent an ever-expanding list of data requirements.
Customizing Your Information Gathering Worksheet
While a general data specification guide provides an excellent starting point, its true power comes from its adaptability. No two projects, or even two organizations, are exactly alike, so a rigid, one-size-fits-all approach rarely succeeds. The beauty of a robust data requirements gathering template lies in its flexibility to be tailored to specific needs.
Consider the complexity of your project. A small internal reporting tool will likely require a less exhaustive template than a large-scale data warehouse or a customer-facing application dealing with sensitive personal information. Think about the industry and compliance regulations. Healthcare projects, for instance, will need to incorporate specific sections for HIPAA compliance, while financial services might require FINRA-related data points. The maturity of your organization in data governance also plays a role; a company new to structured data processes might benefit from more detailed guidance, while a mature organization might streamline certain sections. Feel free to add, remove, or rephrase sections to best fit your unique environment and ensure the template serves as a truly useful data modeling foundation, rather than a bureaucratic hurdle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary benefit of using a Data Requirements Gathering Template?
The primary benefit is improved project clarity and reduced risk. By standardizing the process of identifying, documenting, and validating data needs, it ensures all stakeholders have a shared understanding, minimizes misinterpretations, and reduces the likelihood of costly rework later in the project lifecycle. It acts as a comprehensive checklist to ensure no critical data point is overlooked.
Who should be involved in filling out a data collection blueprint?
A diverse group of stakeholders should be involved. This typically includes business users and subject matter experts who understand the data’s context and purpose, data analysts or business analysts who can translate business needs into technical specifications, and technical leads or developers who understand the system’s capabilities and limitations. Project managers facilitate the process.
How often should data requirements be reviewed and updated?
Data requirements should be treated as living documents, especially in agile environments. They should be reviewed at key project milestones, whenever there are significant changes in business processes, system capabilities, or regulatory landscapes. Continuous feedback loops and periodic validation with stakeholders ensure the data needs remain relevant and accurate throughout the project’s evolution.
Can a single template work for all types of data projects?
While a foundational Data Requirements Gathering Template provides an excellent starting point, it’s generally best practice to customize it for specific project types (e.g., transactional systems, analytics platforms, data migrations) and industry regulations. The core structure remains, but specific fields, validation rules, and compliance considerations will often need to be adapted to ensure it perfectly aligns with the project’s unique demands.
In an era where data drives every decision, having a clear, structured approach to defining your data needs is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. Embracing a robust data requirements gathering framework empowers teams to build solutions that are not only technically sound but also truly address the underlying business challenges. It transforms ambiguous ideas into concrete data specifications, fostering efficiency and confidence from conception to deployment.
By proactively utilizing a well-crafted data requirements gathering template, organizations can lay the groundwork for successful projects, avoid common pitfalls, and ensure their most valuable asset – data – is collected, managed, and leveraged to its fullest potential. Don’t leave your data needs to chance; equip your team with the right tools to build a future powered by precision and insight.


