In the intricate dance of modern project management, where countless moving parts coalesce into a finished product, clarity and control are paramount. Projects, whether developing cutting-edge software, constructing a new facility, or launching a complex marketing campaign, are built upon a foundation of requirements. These requirements define what needs to be delivered, why it’s important, and how it will be validated. The challenge, however, lies not just in defining these requirements but in ensuring they are consistently met, tracked, and validated throughout the entire project lifecycle.
This is precisely where a robust framework for tracking and linking requirements becomes indispensable. Without a clear mechanism to connect initial needs to final delivery, projects risk scope creep, missed features, costly reworks, and ultimately, stakeholder dissatisfaction. The ability to demonstrate that every single requirement has been addressed, tested, and implemented is not just good practice; it’s a cornerstone of successful project execution.
The Indispensable Role of Requirement Traceability
Requirement traceability is the ability to describe and follow the life of a requirement, in both a forward and backward direction, from its origins, through its development and specification, to its deployment and use, and through periods of refactoring and iteration. It’s about creating a verifiable audit trail for every piece of functionality or feature. This meticulous linking ensures that no requirement is overlooked, misunderstood, or dropped during the often-complex journey from concept to reality.
At its core, traceability provides visibility into the relationships between various project artifacts. It connects business objectives to user stories, user stories to design specifications, design specifications to code modules, and code modules to test cases. This comprehensive mapping not only aids in project execution but also plays a critical role in regulatory compliance, quality assurance, and risk management across diverse industries. The insights gained from a well-maintained traceability system are invaluable for any team striving for excellence and accountability.
Why a Traceability Matrix is Your Project’s North Star
A well-structured requirement traceability matrix serves as a definitive guide, illuminating the path from initial stakeholder needs to the final delivered solution. It’s more than just a document; it’s a living tool that empowers teams to navigate project complexities with confidence. The benefits extend far beyond simple tracking, touching every facet of project success.
First, a comprehensive traceability matrix significantly enhances clarity and alignment. By explicitly linking requirements to their sources, designs, and tests, it ensures that every team member understands what needs to be built and why. This shared understanding minimizes misinterpretations and fosters cohesive effort across development, testing, and business analysis functions. Second, it is a formidable tool for risk management and change control. When a requirement changes, the matrix instantly highlights all dependent artifacts, allowing project managers to assess the impact of the change accurately. This proactive approach prevents unforeseen issues, manages scope creep effectively, and mitigates potential project delays or cost overruns.
Furthermore, an effective requirement traceability matrix is crucial for quality assurance. It ensures that every requirement has corresponding test cases, confirming that the developed solution meets the specified criteria. This direct link between requirements and testing leads to more thorough validation and verification processes, ultimately delivering a higher quality product. Finally, for stakeholder communication, the matrix offers a transparent and objective view of project progress, demonstrating exactly how requirements are being addressed. This fosters trust and keeps all parties informed, providing a robust answer to the question: "Are we building the right thing?"
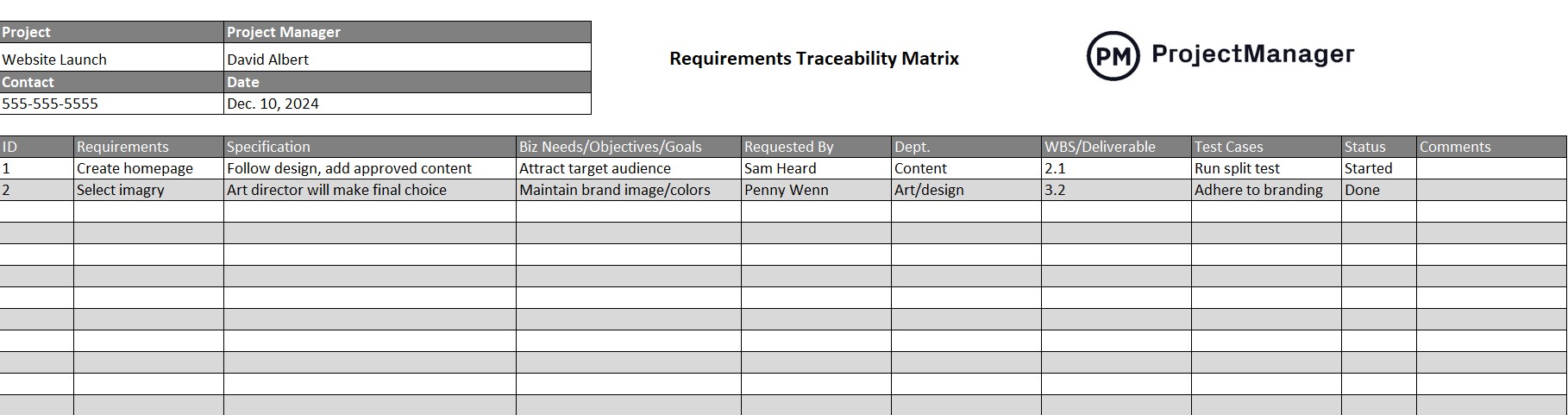
Key Elements of an Effective Requirement Traceability Matrix
While the specific columns and details within a traceability matrix can vary based on project scale and type, a truly effective matrix will incorporate several core elements to provide comprehensive visibility. When reviewing a Sample Requirement Traceability Matrix Template, look for these foundational components that ensure robust tracking and linkage:
- Requirement ID: A unique identifier for each individual requirement, allowing for easy reference.
- Requirement Description: A clear, concise summary of the requirement, explaining what it entails.
- Requirement Source: Identifies where the requirement originated (e.g., stakeholder interview, regulatory document, user story).
- Status: The current state of the requirement (e.g., drafted, approved, in development, in testing, implemented, deferred).
- Priority: Indicates the relative importance or urgency of the requirement (e.g., critical, high, medium, low).
- Design/Technical Specifications: Links to specific design documents, architecture diagrams, or technical specifications that address the requirement.
- Test Cases/Scenarios: References to the test cases designed to validate that the requirement has been correctly implemented.
- Implementation Status: Tracks the progress of the requirement’s development or implementation.
- Verification Status: Confirms whether the requirement has been successfully verified through testing or other quality assurance activities.
- Parent/Child Requirements: Establishes hierarchical relationships, showing how high-level requirements break down into more detailed ones.
- Change Log: A record of any modifications made to the requirement, including who made the change and when.
- Owner: The person or team responsible for the requirement’s successful delivery.
How to Leverage a Traceability Matrix for Project Success
Implementing and utilizing a traceability matrix effectively transforms it from a static document into a dynamic tool that drives project success. Its utility spans the entire project lifecycle, providing continuous value and insights. For example, during the **initial project planning phase**, the matrix helps in refining requirements, identifying dependencies, and creating a realistic project roadmap. Populating the matrix early with all known requirements establishes a baseline for future work.
As development progresses, the matrix becomes invaluable for tracking progress and managing dependencies. Project managers can quickly see which requirements are in progress, which are blocked, and which have been completed. This granular visibility allows for proactive resource allocation and timely intervention if delays occur. During the testing and quality assurance phase, the matrix ensures comprehensive test coverage. QA teams can directly link test results back to specific requirements, ensuring every feature is validated against its original specification. This systematic approach reduces the risk of defects and enhances the overall quality of the delivered product.
Crucially, a robust requirement traceability matrix is a cornerstone of effective change management. When new requirements emerge or existing ones need modification, the matrix helps assess the ripple effect across design, development, and testing. This impact analysis enables informed decision-making, minimizing disruption and controlling scope. Finally, at project closure, the matrix provides a definitive record that all agreed-upon requirements have been met, serving as a powerful validation tool for stakeholders and a valuable artifact for future reference and audits.
Best Practices for Implementing and Maintaining Your Matrix
To truly harness the power of a traceability matrix, mere creation isn’t enough; diligent implementation and consistent maintenance are key. First and foremost, **start early and integrate it into your project workflow from day one.** Retrofitting a traceability matrix late in the project is far more challenging and less effective. Define your traceability strategy during project initiation, clearly outlining what will be traced and how.
Keep it updated regularly. The matrix is a living document and must reflect the current state of requirements. Any changes to requirements, designs, code, or test cases should trigger an update to the matrix. Assign clear ownership for different sections to ensure accountability. Furthermore, involve your entire project team. Business analysts define requirements, developers implement them, and testers validate them. Each role contributes to and benefits from the matrix, making team-wide adoption crucial for its success. Conduct regular reviews with key stakeholders to ensure its accuracy and relevance.
Consider automating where possible. While a spreadsheet can be a good starting point for smaller projects, dedicated requirement management tools or project lifecycle management (PLM) systems offer automated linking, reporting, and version control, significantly reducing manual effort and potential errors for larger, more complex endeavors. Finally, tailor your matrix to the project’s needs. Not every project requires the same level of granularity. Customize the columns and linkages to fit the specific complexity, regulatory environment, and stakeholder expectations of your project. A streamlined, relevant matrix is always more effective than an overly complex one that becomes a burden to maintain.
Customizing Your Traceability Solution
While a general Sample Requirement Traceability Matrix Template provides an excellent starting point, the true power of traceability lies in its adaptability. No two projects are exactly alike, and therefore, the ideal traceability solution will always be a customized fit. Consider the nature of your project: a software development project might emphasize links between user stories, epics, features, and test cases, while a construction project might focus on regulatory requirements, engineering specifications, and inspection reports.
The depth and breadth of your traceability links should also be proportionate to your project’s scale and criticality. For smaller, less complex projects, a simpler spreadsheet-based matrix might suffice, focusing on core requirements and their corresponding tests. However, for large-scale, mission-critical projects or those in highly regulated industries, a more robust, integrated tool is often necessary. These specialized tools can automate linkages, provide real-time dashboards, and integrate seamlessly with other project management and development systems. The key is to select or adapt a template that addresses your specific needs without becoming an overly burdensome administrative task. Your traceability solution should enhance, not hinder, project velocity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a requirement traceability matrix?
The primary purpose of a requirement traceability matrix is to establish a clear, verifiable link between project requirements and other artifacts like design documents, code modules, and test cases. It ensures that all requirements are addressed, validated, and managed throughout the project lifecycle, providing full visibility and control.
Who typically uses a requirement traceability matrix?
A wide range of project roles benefit from and contribute to the traceability matrix. This includes project managers (for oversight and risk management), business analysts (for requirement clarity), QA leads and testers (for test coverage and validation), developers (for understanding implementation context), and stakeholders or compliance officers (for verification and audit trails).
Can a simple spreadsheet serve as a traceability matrix?
Yes, for smaller, less complex projects, a simple spreadsheet can be an effective way to create and manage a traceability matrix. It allows for manual linking and tracking. However, for larger projects with numerous requirements and frequent changes, specialized requirement management software or project lifecycle management tools offer superior automation, version control, and integration capabilities.
How often should the traceability matrix be updated?
The traceability matrix should be a living document, updated continuously throughout the project lifecycle. Key triggers for updates include changes to requirements, finalization of design specifications, completion of development tasks, execution of test cases, and any major project milestones. Regular, consistent updates ensure its accuracy and value.
What’s the difference between forward and backward traceability?
Forward traceability tracks requirements from their origin to later project phases (e.g., from a business requirement to a design document, then to code, and finally to test cases). It ensures that all requirements are implemented. Backward traceability, conversely, traces from later phases back to the original requirements (e.g., from a test case back to the specific requirement it validates). This ensures that all work contributes to an approved requirement and prevents “gold plating” or scope creep.
Embracing the principles of requirement traceability is more than just adopting a new document; it’s about instilling a discipline of clarity, accountability, and quality throughout your project endeavors. A well-designed and consistently maintained traceability matrix acts as the backbone for effective project communication, a powerful safeguard against common pitfalls, and a vital enabler for delivering solutions that truly meet their intended purpose. It transforms abstract needs into concrete, verifiable outcomes.
The initial investment in setting up a comprehensive traceability solution, even if it’s based on a basic Sample Requirement Traceability Matrix Template, pays dividends throughout the project. It saves time, reduces rework, manages risks, and ultimately leads to higher stakeholder satisfaction. By providing an unambiguous map from idea to implementation, it empowers teams to navigate complexities, adapt to changes, and maintain focus on what truly matters.
Don’t let your project requirements become an uncharted territory. Take the initiative to integrate robust requirement traceability into your workflow. Whether you start with a simple spreadsheet or opt for a sophisticated software solution, the act of linking and tracking your requirements will elevate your project management practices, boost team efficiency, and significantly increase your chances of delivering successful, high-quality outcomes every single time.


