In the fast-paced world of product development, where innovation is constant and customer expectations are ever-evolving, clarity and strategic alignment are not just advantages—they are absolute necessities. Without a foundational understanding of what the market truly demands, product teams can easily stray off course, investing valuable resources into features that miss the mark or products that fail to resonate. This is where a robust framework for defining market needs becomes indispensable, guiding every decision from conception to launch.
Imagine a world where product teams, engineering, marketing, and sales are all marching to the beat of the same drum, driven by a shared, crystal-clear vision of the problem they’re solving and the market they’re serving. This synergy isn’t born from serendipity; it emerges from meticulous planning and effective communication, encapsulated perfectly within a well-structured document designed to articulate market requirements. Leveraging a proven Market Requirement Document Template can transform ambiguity into actionable insights, ensuring every effort contributes to building products customers genuinely want and need.
What is a Market Requirements Document, and Why Does it Matter?
A Market Requirements Document (MRD) is a comprehensive strategic document that outlines the market needs for a product or service. It defines the “what” and “why” from the perspective of the target market, rather than dictating the “how” of technical implementation. This crucial document serves as a bridge between market opportunity and product development, ensuring that new offerings are aligned with customer pain points and business objectives.
The significance of a strong market requirements document cannot be overstated. It acts as the North Star for product teams, providing a singular source of truth for all stakeholders. Without it, product development risks becoming an endless cycle of subjective decisions, feature creep, and ultimately, products that struggle to find their place in the market. An MRD grounds the entire product lifecycle in objective market realities, fostering a shared understanding and reducing costly misalignments.
The Undeniable Benefits of a Well-Crafted MRD
Adopting a disciplined approach to defining market requirements brings a wealth of advantages that permeate every aspect of product development and business strategy. From enhanced communication to accelerated market entry, the ripple effects are profoundly positive.
- Clarity and Alignment: An MRD ensures that everyone involved, from executive leadership to engineering teams, shares a common understanding of the market problem, target audience, and product vision. This unified perspective minimizes confusion and drives collaborative effort towards a singular goal.
- Risk Reduction: By thoroughly documenting market needs and validating them against customer insights, an MRD helps mitigate the risk of building unwanted features or entire products that fail to achieve product-market fit. It focuses resources on high-impact initiatives.
- Faster Time to Market: With clear, agreed-upon requirements, development teams can work more efficiently, reducing rework and bottlenecks. This streamlined process allows products to move from concept to customer much more quickly, capitalizing on market windows.
- Better Product-Market Fit: The core purpose of an MRD is to ensure that the product directly addresses genuine market problems. By keeping market needs at the forefront, organizations can develop solutions that resonate deeply with their target audience, leading to higher adoption and satisfaction.
- Strategic Decision Making: An MRD provides the data-driven foundation needed for sound strategic choices. It helps prioritize features, allocate resources effectively, and make informed trade-offs, all based on documented market evidence.
- Resource Optimization: When requirements are vague, teams often spend time and money on speculative features. A robust market definition document ensures that resources—time, budget, and talent—are invested only in areas that promise the highest return based on identified market opportunities.
Key Elements of an Effective Market Requirements Document
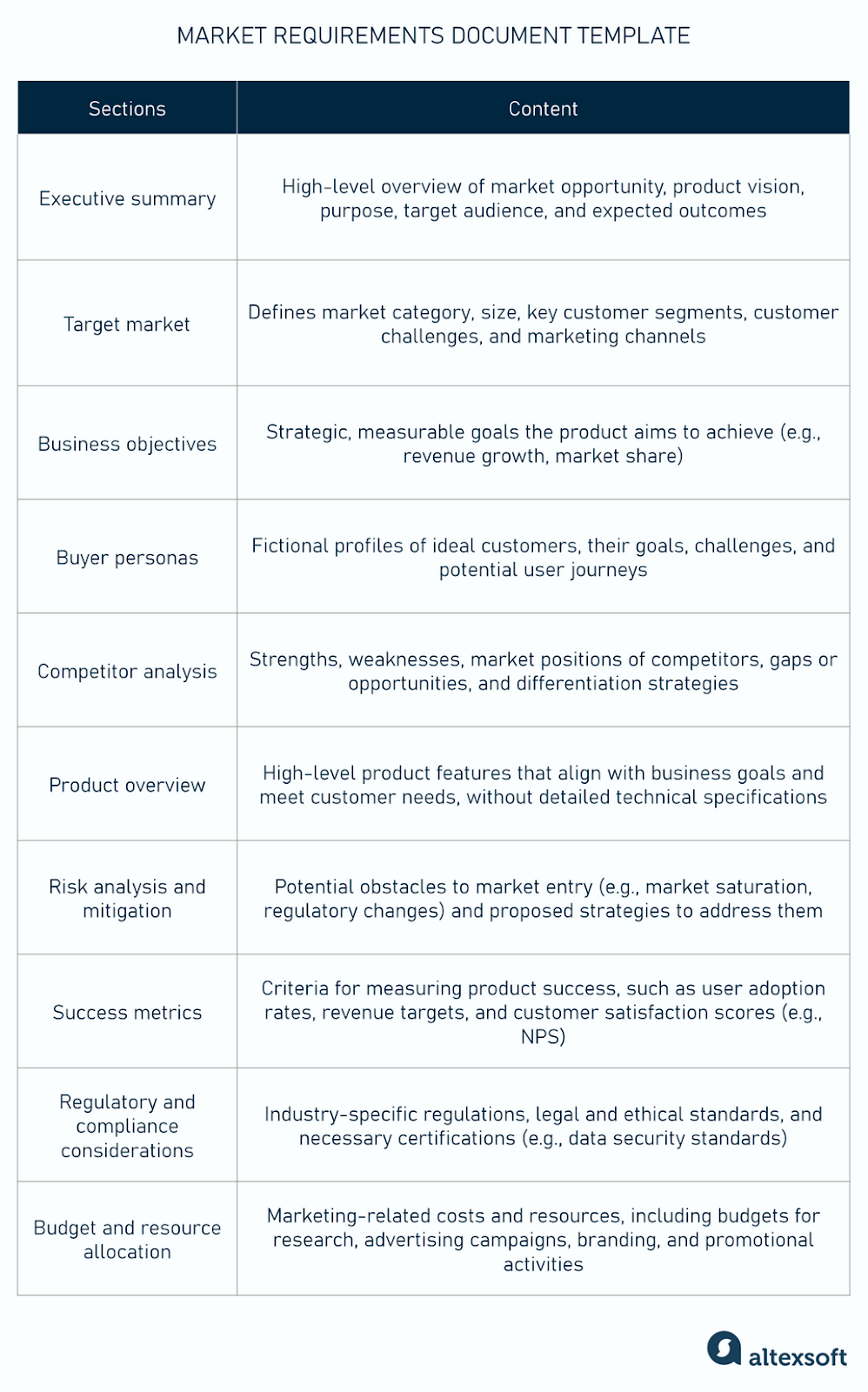
A robust product market requirements document typically includes several critical sections, each contributing to a holistic understanding of the market and the proposed solution. While the specific components may vary slightly depending on the industry and product complexity, these elements form the backbone of a comprehensive MRD.
- **Executive Summary:** A concise, high-level overview of the entire document, highlighting the key market problem, proposed solution, and expected business impact. It allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the essence of the document.
- **Market Overview:** An analysis of the current market landscape, including market size, trends, growth opportunities, and a competitive analysis. This section provides context for the product’s place in the ecosystem.
- **Target Audience:** Detailed personas of the ideal customers, including their demographics, psychographics, behaviors, pain points, and unmet needs that the product aims to address.
- **Product Vision & Goals:** A clear articulation of what the product aims to achieve for both the customer and the business. This section outlines the long-term strategic direction and the measurable objectives for the product’s success.
- **Market Problems:** A thorough description of the specific problems, challenges, or desires experienced by the target market that the product is designed to solve or fulfill. This is articulated from the customer’s perspective.
- **Product Requirements (High-Level):** A list of essential functional and non-functional requirements necessary to solve the identified market problems. These are still focused on *what* the product must do, not *how* it will do it.
- **Use Cases:** Scenarios or stories illustrating how users will interact with the product to achieve their goals, providing a practical context for the high-level requirements.
- **Success Metrics:** Clearly defined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure the product’s success in the market, such as adoption rates, customer satisfaction, or revenue targets.
- **Pricing Strategy (brief):** High-level considerations regarding how the product will be priced to capture value from the market and achieve business goals.
- **Go-to-Market Strategy (brief):** Initial thoughts on how the product will be introduced to the market, including channels, promotional activities, and positioning.
- **Assumptions & Constraints:** Any critical assumptions made during the market analysis, as well as any known limitations or restrictions that might impact the product’s development or market success.
Leveraging a Market Requirements Document Template for Success
The thought of creating a comprehensive product strategy roadmap from scratch can be daunting. This is precisely where a market requirement document template proves invaluable. It provides a pre-structured framework, eliminating the need to start with a blank page and ensuring that no critical section is overlooked. A good template acts as a guide, prompting you to consider all necessary aspects of market definition.
By utilizing a structured template for market requirements, organizations can establish consistency across different product lines and projects. This standardization simplifies the process for product managers, makes it easier for stakeholders to navigate and understand documents, and ultimately accelerates the initial phase of product planning. A robust MRD template isn’t just a document; it’s a strategic asset that streamlines communication and alignment, allowing teams to focus their energy on validating market needs rather than formatting documents. Embracing a Market Requirement Document Template streamlines the process, ensuring that the market needs are captured comprehensively and consistently.
Tips for Customizing and Maximizing Your MRD
While a market requirements template provides a solid foundation, its true power comes from customization and thoughtful application. It’s not a rigid form to merely fill out, but a flexible tool to adapt to your specific product, market, and organizational context.
- Know Your Audience: Tailor the depth and technicality of the document to the primary stakeholders who will be reading it. While engineering needs detailed requirements, sales might benefit more from a focus on customer value propositions.
- Collaborate Widely: The best MRDs are not created in a vacuum. Involve representatives from sales, marketing, engineering, customer support, and leadership early in the process. Their diverse perspectives are crucial for a well-rounded and validated market requirements specification.
- Iterate and Refine: Consider the MRD a living document, not a static artifact. Market conditions change, customer feedback emerges, and strategic priorities evolve. Be prepared to revisit and update the document periodically to ensure its continued relevance.
- Focus on Problems, Not Solutions: Resist the urge to dictate technical solutions within the MRD. Your primary role is to articulate the market problem and the desired outcomes. Allow engineering teams the flexibility to devise the most effective "how."
- Keep it Concise but Comprehensive: Strive for clarity and brevity without sacrificing essential detail. Eliminate jargon where possible and ensure that every section adds value. A shorter, clearer document is more likely to be read and understood.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic review sessions with key stakeholders. These meetings can help maintain alignment, gather new insights, and address any evolving assumptions or constraints.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with a stellar requirements document framework, missteps can occur that undermine its effectiveness. Being aware of these common pitfalls can help you navigate the process more smoothly and ensure your MRD truly serves its purpose.
- Solutionizing Too Early: One of the most common errors is for the MRD to prescribe technical solutions rather than focusing purely on market problems and needs. This stifles innovation and removes critical decision-making from the development team.
- Lack of Stakeholder Buy-in: If key stakeholders, particularly engineering and leadership, aren’t involved and don’t "buy into" the MRD, its guidance will likely be ignored, leading to misalignment and wasted effort.
- Ignoring Market Feedback: Developing a market definition document without continuous engagement with actual or potential customers is a recipe for failure. The document must be grounded in real-world market insights.
- Treating it as a Static Document: An MRD that is written once and then filed away quickly becomes obsolete. The market is dynamic, and your document needs to reflect ongoing changes and learning.
- Overly Technical Language: While engineers will be a key audience, avoid language that is so technical that it alienates marketing, sales, or executive stakeholders. The document should be accessible to a broad audience.
- Insufficient Detail: While conciseness is good, insufficient detail can leave too much open to interpretation, leading to ambiguity, disagreements, and ultimately, a product that doesn’t meet expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between an MRD and a PRD?
An MRD (Market Requirements Document) focuses on the *what* and *why* from the market’s perspective – defining market problems, needs, and opportunities. A PRD (Product Requirements Document) expands on the MRD, delving into the *how* from a product team’s perspective, detailing specific features, functionalities, and technical specifications for the product to meet those market needs. The MRD sets the strategic context, while the PRD translates that strategy into actionable development tasks.
Who typically creates a market requirements document?
Often, a product manager or product marketing manager is primarily responsible for authoring the market definition document. However, its creation is a collaborative effort, involving extensive input from various departments such as sales, marketing, engineering, customer support, and executive leadership to ensure a holistic understanding of the market and product strategy. This collaboration is crucial for buy-in and comprehensive insights.
How often should an MRD be updated?
A product planning document like this is not static. It should be a living document, reviewed and updated regularly, especially when market conditions change, new competitor products emerge, significant customer feedback provides new insights, or the product vision itself evolves. Quarterly reviews are a good baseline for most industries, but more frequent updates may be necessary in rapidly changing sectors or during intensive discovery phases.
Can an MRD be used for services, not just products?
Absolutely. While commonly associated with physical or software products, the principles of defining market needs and outlining market problems apply equally to services. A service outline document based on market requirements helps ensure that the service offering is relevant, valuable, and directly addresses genuine customer challenges, fostering a market-driven approach to service development.
Is an MRD mandatory for every new product?
While not strictly “mandatory” in a regulatory sense for all industries, creating an MRD or an equivalent market-driven product development document is highly recommended for any significant new product or service initiative. It provides critical clarity, reduces risk, and increases the likelihood of market success. The level of detail might vary for smaller features or iterative updates, but the core thinking behind market requirements remains essential.
The journey from a nascent idea to a successful product in the market is fraught with challenges, yet it is also ripe with opportunity. The differentiating factor often lies in the clarity and discipline with which market needs are understood and articulated. A well-crafted market requirements document serves as that guiding light, ensuring every step taken is purposeful and aligned with what customers truly seek.
By embracing the structure and insights offered by a robust Market Requirement Document Template, organizations can move beyond guesswork and into a realm of strategic, data-driven product development. It empowers teams to build not just products, but solutions that solve real-world problems, resonate deeply with target audiences, and ultimately drive sustainable business growth. Make this foundational document your strategic asset, and witness the transformation in your product outcomes.


