In the complex landscape of product development and project management, clarity and control are paramount. Imagine a world where every single requirement, from the highest-level business objective to the smallest technical detail, is meticulously linked, tracked, and validated throughout its entire lifecycle. This isn’t a utopian dream; it’s the operational efficiency delivered by a robust Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM).
For anyone navigating the intricate web of software development, system integration, or even large-scale organizational change, understanding and implementing an RTM template isn’t just a best practice—it’s a critical safeguard. It mitigates the risk of scope creep, missed requirements, and costly rework. It provides a crystal-clear lineage, ensuring that what was asked for is what is ultimately delivered, tested, and approved. It’s the silent guardian of project integrity, invaluable for business analysts, project managers, quality assurance teams, and developers alike.
What Exactly is Requirement Traceability?
At its core, requirement traceability is the ability to describe and follow the life of a requirement, in both a forward and backward direction. This includes tracking its origins, development, testing, and deployment, and its eventual retirement. It means knowing exactly which business need led to a particular functional specification, which design element implements that specification, which test cases validate it, and which features in the final product fulfill it.
This intricate web of connections transforms abstract requirements into tangible, verifiable components. It’s more than just a list; it’s a living document that illustrates the relationships between different project artifacts. A comprehensive requirement traceability matrix, therefore, becomes the central hub for understanding these dependencies and ensuring nothing falls through the cracks. It connects the dots from initial concept to final delivery, providing an unbroken chain of accountability.
Why a Traceability Matrix is Indispensable
Implementing a robust RTM offers a myriad of benefits that enhance project success, reduce risks, and improve overall product quality. Its value extends far beyond mere documentation, acting as a strategic tool for various stakeholders. Understanding these advantages underscores why investing time in an effective Rtm Requirement Traceability Matrix Template is a wise decision for any project.
One of the primary benefits is risk reduction. By linking requirements to test cases, design elements, and business objectives, the matrix helps identify gaps where requirements are not being met or where too many resources are allocated to a low-priority item. This proactive identification significantly lowers the chances of costly rework and project delays.
A well-maintained traceability matrix also dramatically improves product quality. It ensures comprehensive test coverage, as every requirement can be directly linked to one or more test cases. This linkage helps guarantee that all specified functionalities are thoroughly validated before product release, minimizing defects and enhancing user satisfaction.
Furthermore, a traceability matrix fosters enhanced communication and collaboration across teams. When stakeholders—from product owners to developers and QA testers—can easily see the relationships between different project elements, it reduces misunderstandings and facilitates a shared understanding of the project’s goals and scope. This clarity is invaluable in fast-paced development environments.
For change management, the matrix is an invaluable asset. When a requirement changes, the RTM allows teams to quickly perform an impact analysis, identifying all affected design components, test cases, and dependent requirements. This capability prevents ripple effects from turning into unmanageable chaos, allowing for controlled and informed adjustments.
Finally, for projects subject to regulatory compliance or audits, a detailed traceability matrix provides irrefutable evidence that all specified requirements have been addressed and validated. This level of documentation is often crucial for demonstrating adherence to industry standards, legal mandates, and internal quality processes, protecting organizations from potential penalties.
Key Elements of an Effective Requirement Traceability Matrix
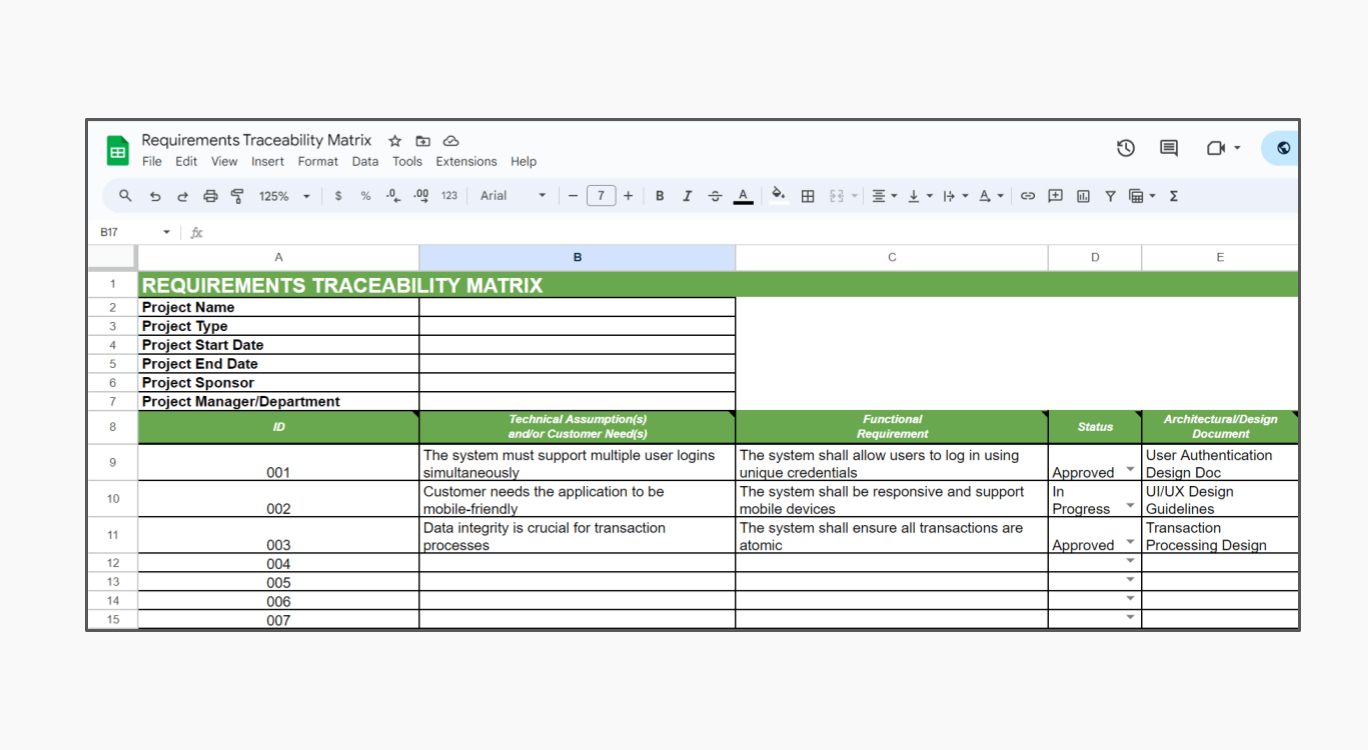
To be truly effective, a requirement traceability matrix must capture specific pieces of information and link them logically. While the exact columns and rows may vary based on project complexity and organizational needs, certain core elements are universally essential for any functional traceability template. These components form the backbone of the matrix, enabling comprehensive tracking and analysis.
Here are the fundamental elements you should consider including:
- **Requirement ID:** A **unique identifier** for each requirement. This ensures that every entry can be precisely referenced without ambiguity.
- **Requirement Description:** A **clear, concise summary** of the requirement. This helps stakeholders quickly understand the purpose and scope of each item.
- **Requirement Type:** Categorization (e.g., **functional, non-functional, business, technical**). This helps in organizing and prioritizing requirements.
- **Source:** The **origin of the requirement** (e.g., stakeholder, user story, regulatory body). Knowing the source provides context and helps validate its necessity.
- **Priority:** The **relative importance** of the requirement (e.g., critical, high, medium, low). This guides development and testing efforts.
- **Status:** The **current state** of the requirement (e.g., draft, approved, implemented, tested, deferred, rejected). This allows for real-time tracking of progress.
- **Design Specification ID(s):** Links to **design documents or components** that address this requirement. This establishes the connection between ‘what’ and ‘how’.
- **Test Case ID(s):** Links to **specific test cases** designed to validate this requirement. Essential for ensuring complete test coverage.
- **Use Case ID(s):** References to **use cases or user stories** that incorporate this requirement. Connects technical aspects to user interaction.
- **Related Requirements:** Identifiers of **dependent or conflicting requirements**. This highlights interdependencies and potential issues.
- **Verification Method:** How the requirement will **ultimately be validated** (e.g., inspection, demonstration, testing, analysis).
- **Change History:** A record of **modifications and revisions**, including dates and reasons. Crucial for audit trails and understanding evolution.
Crafting Your Own: Steps to Using a Traceability Matrix Template
Adopting an Rtm Requirement Traceability Matrix Template into your project workflow can seem daunting at first, but by following a structured approach, you can integrate it smoothly and effectively. The key is to start systematically and maintain consistency throughout the project lifecycle.
Step 1: Define Your Scope and Objectives. Before populating any matrix, clearly understand what you need to trace and why. Are you tracing from business needs to tests, or just within the development and testing phases? This initial clarity will dictate the columns and level of detail required in your traceability matrix.
Step 2: Identify and Document All Requirements. Gather all your project requirements from various sources—stakeholder interviews, user stories, use cases, regulations, etc. Ensure each requirement is clearly articulated, unambiguous, and assigned a unique identifier. This foundational step is critical, as a poorly defined requirement will lead to a flawed matrix.
Step 3: Choose or Customize Your Template. You can start with a generic RTM template, often found in project management toolkits, or create one from scratch. The crucial aspect is to customize it to fit your specific project needs. Add or remove columns based on the elements identified as important in Step 1. Tools can range from simple spreadsheets to dedicated Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) software.
Step 4: Populate the Matrix with Initial Data. Begin by listing all your identified requirements in the matrix, filling in their IDs, descriptions, types, sources, and priorities. This establishes the baseline for your traceability efforts. It’s often helpful to do this incrementally, as requirements are approved.
Step 5: Establish Linking Rules and Populate Linkages. As design documents are created, development begins, and test cases are written, update the matrix to reflect these connections. This is where the actual "traceability" happens. Define clear rules for linking (e.g., "every functional requirement must have at least one design element and one test case"). Regularly update the corresponding columns (e.g., Design Spec IDs, Test Case IDs).
Step 6: Maintain and Update Regularly. A traceability matrix is a living document, not a one-time setup. As requirements change, designs evolve, or tests are executed, the matrix must be updated promptly. Assign clear ownership for maintaining the matrix to ensure its accuracy and relevance throughout the project lifecycle. Regular reviews are essential to keep the information current.
Common Challenges and Best Practices
While a traceability matrix offers significant advantages, its implementation is not without potential hurdles. Organizations often face challenges such as the perceived overhead, resistance from team members, and the sheer complexity of managing numerous links. Addressing these proactively can make a substantial difference in the success of your traceability efforts.
One common challenge is the initial time and effort required to set up and maintain the matrix. It can feel like an additional bureaucratic step, especially in fast-paced environments. To counter this, emphasize the long-term benefits of reduced rework and improved quality, and integrate the RTM into existing workflows rather than treating it as a separate task.
Another hurdle is maintaining accuracy and completeness. If the matrix is not updated consistently, it quickly loses its value. Best practices include assigning clear ownership for specific sections of the matrix, conducting regular review meetings, and providing training on the importance and process of updating it. Automation, where possible, can also significantly reduce manual effort.
Resistance from team members can also arise if they don’t understand the "why" behind the RTM. Educate your teams on how a robust traceability matrix benefits them—by clarifying scope, identifying impacts of changes, and ensuring their work is aligned with requirements. Start with a simplified approach, gradually increasing complexity as the team becomes comfortable.
To maximize the effectiveness of your requirement traceability matrix, consider these best practices:
- **Start Small:** Don’t try to trace every single artifact from day one. Begin with critical requirements or specific phases, then expand.
- **Integrate with Tools:** Leverage existing project management or ALM tools that support traceability rather than relying solely on manual spreadsheets, especially for large projects.
- **Automate Where Possible:** Use features within your chosen tools to automatically generate links or status updates, reducing manual entry and errors.
- **Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities:** Ensure everyone knows who is responsible for updating which parts of the matrix.
- **Regular Reviews:** Schedule periodic reviews of the traceability matrix with all relevant stakeholders to ensure its accuracy and address any discrepancies.
- **Keep It Relevant:** Remove or archive requirements that are no longer valid to prevent clutter and ensure the matrix remains a useful, focused tool.
Beyond the Spreadsheet: Tools and Automation
While a basic spreadsheet can serve as a starting point for an Rtm Requirement Traceability Matrix Template, especially for smaller projects, larger and more complex initiatives often benefit immensely from specialized tools and automation. Dedicated Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) or Requirements Management (RM) solutions offer capabilities that far surpass the limitations of manual systems.
These advanced platforms provide integrated environments where requirements, design documents, test cases, and defects can be linked dynamically. Features like automatic link generation, real-time status updates, customizable dashboards, and robust reporting capabilities significantly streamline the traceability process. They can visualize dependencies, highlight gaps in coverage, and provide instant impact analyses, saving countless hours of manual effort.
Many popular project management and development tools also offer built-in traceability features or integrations. Whether you’re using Jira, Azure DevOps, Jama Connect, Helix ALM, or similar platforms, exploring their native traceability options can vastly improve efficiency. These tools often allow for bidirectional linking, meaning you can navigate from a requirement to its associated test cases and vice versa with ease, fostering a more connected and transparent development environment. Embracing such technologies transforms the traceability matrix from a static document into a dynamic, interactive system that truly empowers project teams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between an RTM and a requirements list?
A requirements list simply enumerates all the requirements for a project. An RTM, or Requirement Traceability Matrix, goes a step further by showing the relationships and linkages between these requirements and other project artifacts like design documents, test cases, and business objectives. It illustrates how each requirement is addressed throughout the project lifecycle.
When should I start building my traceability matrix?
You should start building your traceability matrix as early as possible in the project lifecycle, ideally during the requirements gathering and definition phase. As requirements are identified and approved, they should be added to the matrix. This ensures that traceability is an integral part of your process from the outset, rather than a reactive task.
Can an RTM be used for agile projects?
Absolutely. While agile methodologies emphasize flexibility, traceability remains crucial. In agile, the RTM often links user stories to epics, acceptance criteria, sprint tasks, and corresponding automated tests. It helps agile teams maintain focus, understand dependencies, and ensure that delivered features align with product goals, adapting to iterative development.
What are the main types of traceability?
There are typically three main types: **Backward traceability** links requirements back to their origins (e.g., business needs). **Forward traceability** links requirements forward to their implementation (e.g., design, code, tests). **Bidirectional traceability** combines both, allowing movement in either direction, which is the most comprehensive and desired form.
Is an RTM always a spreadsheet?
No, while spreadsheets are a common and accessible format for a basic RTM, it is not the only option. Dedicated Requirement Management (RM) tools, Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) systems, and integrated project management platforms offer more sophisticated and automated ways to create and manage a traceability matrix, providing dynamic linking and reporting capabilities.
The journey from a nascent idea to a fully functional product is paved with countless decisions, details, and dependencies. Without a clear map, projects can easily veer off course, leading to wasted resources, missed deadlines, and ultimately, an unsatisfied end-user. The Requirement Traceability Matrix, in its various forms, serves as that essential map, providing the clarity and control needed to navigate complex development landscapes with confidence.
Embracing a well-crafted traceability matrix isn’t just about ticking a box for documentation; it’s about embedding a culture of precision, accountability, and quality into every fiber of your project. Whether you begin with a simple Rtm Requirement Traceability Matrix Template or leverage an advanced ALM solution, the investment in traceability will pay dividends in reduced risk, enhanced communication, and the delivery of products that truly meet their intended purpose. Start integrating this powerful tool today and transform the way your teams deliver exceptional results.


