In the intricate dance of modern business, where processes are the choreography and technology the music, achieving harmony often hinges on one critical element: clarity. Without a precise understanding of *what* needs to be built or improved, projects can quickly devolve into a cacophony of miscommunication, rework, and missed deadlines. This is where a structured approach becomes not just beneficial, but essential.
Imagine embarking on a complex journey without a map, or constructing a building without blueprints. The outcome would be unpredictable, at best. Similarly, any endeavor to develop a new system, optimize a business process, or implement a technological solution requires a robust framework for defining its very foundation. That framework is precisely what a well-crafted Workflow Requirements Gathering Template offers – a guiding star in the often-turbulent seas of project development.
The Cornerstone of Successful Projects
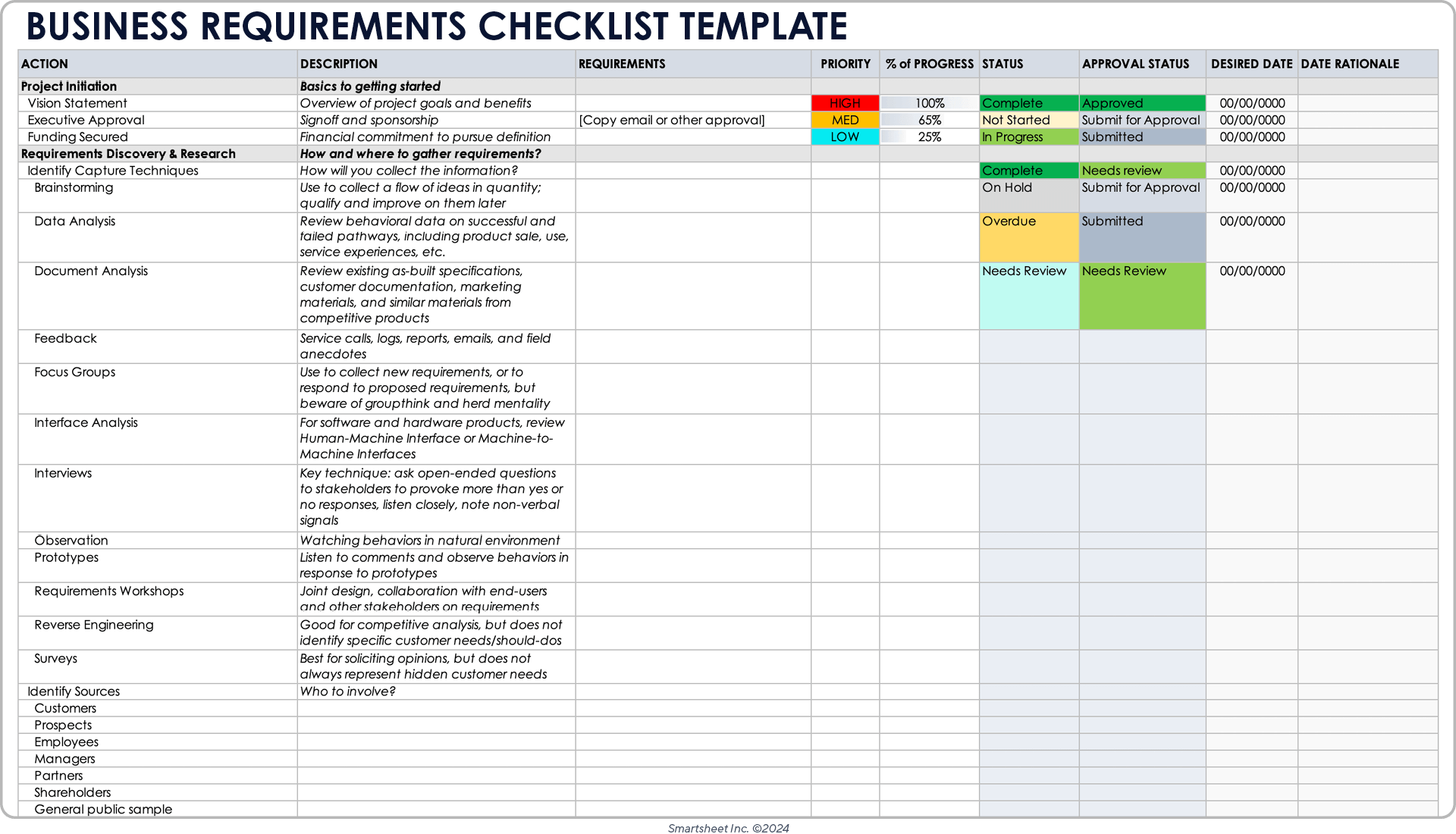
At its core, a Workflow Requirements Gathering Template serves as a structured questionnaire and documentation tool designed to systematically capture all the necessary details about a process or system. It moves beyond vague requests and delves into the specifics, helping stakeholders articulate their needs, expectations, and desired outcomes with precision. By providing a consistent format, it ensures that no critical piece of information is overlooked, forming a comprehensive blueprint that guides development, testing, and deployment. This meticulous approach is vital for mitigating risks, preventing scope creep, and ensuring that the final solution truly aligns with business objectives.
Key Benefits of a Standardized Approach
Implementing a consistent requirements collection framework across your projects yields a multitude of advantages, transforming the way your teams operate and deliver value. It’s not just about ticking boxes; it’s about fostering a culture of clarity and precision.
- **Enhanced Clarity and Understanding:** A well-defined requirements gathering template forces all parties to articulate needs explicitly, leaving less room for assumptions and misinterpretations. This ensures everyone is on the same page from the outset.
- **Reduced Rework and Costs:** By identifying and clarifying requirements upfront, teams can avoid costly changes and redevelopments down the line. Catching issues early saves significant time and resources.
- **Improved Communication and Collaboration:** The template acts as a common language, facilitating clearer dialogue between business users, technical teams, and other stakeholders, fostering a more collaborative environment.
- **Faster Project Delivery:** With clear requirements, development teams can work more efficiently, minimizing delays caused by ambiguities or changing specifications. This accelerates the entire project lifecycle.
- **Better Alignment with Business Goals:** By focusing on the “why” behind each requirement, the template helps ensure that every feature or process improvement directly supports overarching strategic objectives.
- **Higher User Adoption:** Solutions built on thoroughly gathered workflow requirements are more likely to meet user needs and expectations, leading to greater satisfaction and enthusiastic adoption.
Essential Components of an Effective Template
While the specifics may vary depending on the project and industry, a robust Workflow Requirements Gathering Template typically encompasses several core sections designed to capture a holistic view of the process or system. These elements work in concert to build a complete picture, from high-level objectives down to granular data points.
It typically begins with a Project Overview section, detailing the project name, ID, date, author, and version history. This ensures proper documentation control and provides immediate context. Following this, Stakeholder Identification is crucial. Listing all key individuals and groups involved, along with their roles and responsibilities, helps in understanding different perspectives and ensures all relevant voices are heard.
A critical segment is the Current State Analysis. This involves documenting the "as-is" process – how things operate right now. Understanding existing bottlenecks, manual steps, pain points, and current systems provides a baseline for improvement. This often includes process maps, data flows, and an assessment of current technology. Building on this, the Desired State / Future Process section outlines the "to-be" process, detailing how the workflow should function after the changes are implemented. This articulates the vision, improved efficiencies, and expected outcomes.
Further down, the template delves into Functional Requirements, which describe what the system or process must do. These are the actions, features, and capabilities that directly support the business objectives. Examples include "The system must allow users to submit expense reports" or "The process must automatically route invoices for approval." Equally important are Non-Functional Requirements, which specify how the system should perform. This covers aspects like performance (speed, responsiveness), security (access control, data protection), usability (user-friendliness), reliability, and scalability.
Use Cases and User Stories often form another vital part, illustrating how different users will interact with the system or process to achieve specific goals. These narrative-driven descriptions help visualize the workflow from the end-user’s perspective. Data Requirements specify what data needs to be captured, stored, processed, and reported, including data types, formats, and relationships. Assumptions and Constraints are also critical to document, as they define boundaries and potential risks. Assumptions are factors believed to be true without proof, while constraints are limitations or restrictions that must be considered. Finally, Acceptance Criteria outline the conditions that must be met for a requirement to be considered complete and satisfactory, providing clear benchmarks for success.
Leveraging Your Requirements Gathering Template for Optimal Results
Simply having a requirements gathering template isn’t enough; its true power lies in how effectively it’s utilized. Strategic application turns a static document into a dynamic tool for project success.
Start by preparing thoroughly before any stakeholder engagement. Understand the project’s scope, objectives, and known challenges. Tailor your template to the specific project needs, adding or removing sections as appropriate. Generic templates are a good starting point, but customization makes them truly effective. During interviews and workshops, use the template as a guide to facilitate discussions, not just a form to fill. Ask open-ended questions, listen actively, and probe for details to uncover underlying needs rather than just stated wants.
Document all findings meticulously, ensuring accuracy and completeness. Use clear, unambiguous language. Avoid jargon where possible, or define it if necessary, to ensure all stakeholders can understand the specifications. Validate the documented requirements with all relevant stakeholders, especially the business owners. This iterative review process helps catch misunderstandings early and secures buy-off. Finally, ensure the documented requirements are formally approved and signed off, establishing a baseline that helps manage changes throughout the project lifecycle. This sign-off is a crucial step for preventing scope creep and ensuring alignment.
Best Practices for Eliciting Workflow Needs
The act of eliciting workflow needs is as much an art as it is a science. Employing certain best practices can significantly improve the quality and completeness of the information you gather.
- **Engage the Right Stakeholders:** Identify and involve all individuals who are impacted by or have an influence on the workflow, from end-users to senior management. Their diverse perspectives are invaluable.
- **Use Multiple Techniques:** Don’t rely solely on interviews. Incorporate workshops, surveys, observation, prototyping, and user story mapping to gather a comprehensive view.
- **Visualize the Workflow:** Use flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, or process maps to visually represent current and future processes. Visual aids often reveal gaps or inefficiencies that text alone might miss.
- **Prioritize Requirements:** Work with stakeholders to prioritize requirements based on business value, effort, and urgency. Not all requirements are created equal, and prioritization guides development efforts.
- **Manage Scope Creep Proactively:** Clearly define the project boundaries early on and establish a formal change management process for any new requirements that emerge.
- **Focus on the “Why”:** For every requirement, ask *why* it’s needed. Understanding the underlying business problem or objective helps validate its necessity and identify better solutions.
- **Iterate and Refine:** Requirements gathering is rarely a one-time event. Plan for iterative cycles of elicitation, documentation, and validation, especially in agile environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is a workflow requirements template?
A workflow requirements template is a structured document or tool designed to systematically capture, organize, and document all the necessary information about a business process or system that needs to be developed or improved. It acts as a guide to ensure no critical detail is missed during the requirements gathering phase of a project.
Who should use this type of template?
Project managers, business analysts, system architects, solution designers, and even key business stakeholders can all benefit from using a well-structured requirements collection framework. It provides a common ground for understanding and communicating project needs across different roles and departments.
How does it prevent scope creep?
By providing a clear, comprehensive, and agreed-upon baseline of requirements upfront, the template significantly reduces the likelihood of new features or changes being added without proper review and approval. It formalizes what is in scope, making it easier to identify and manage out-of-scope requests.
Can it be adapted for agile projects?
Absolutely. While agile methodologies emphasize iterative development, a process requirements template can still be highly valuable. It can be used to capture initial high-level epics and features, which are then broken down into user stories in subsequent sprints. The template ensures a foundational understanding of the overall workflow even as details emerge incrementally.
What’s the difference between functional and non-functional requirements?
Functional requirements describe *what* a system or process must *do* (e.g., “The system must allow users to log in”). Non-functional requirements describe *how* the system or process must *perform* (e.g., “The system must load login pages within 2 seconds” or “The system must be secure against unauthorized access”). Both are critical for a complete solution.
In the complex landscape of project development, precision and foresight are invaluable currencies. The investment in a robust Workflow Requirements Gathering Template pays dividends by transforming ambiguity into clarity, reducing costly rework, and fostering a shared understanding across teams. It’s more than just a document; it’s a strategic asset that underpins the success of any initiative aiming to build, improve, or innovate.
By embracing a standardized, thorough approach to documenting process specifications, organizations can navigate their projects with greater confidence and control. The path to achieving project goals efficiently and effectively begins with a well-defined understanding of the destination. So, empower your teams with the right tools, cultivate a culture of meticulous planning, and watch as your projects move from conception to successful delivery with unparalleled clarity.


