In today’s intricate digital landscape, where cyber threats evolve with alarming speed and regulatory compliance is paramount, organizations face immense pressure to secure their IT infrastructures. Meeting stringent security benchmarks, especially those mandated by governmental bodies, often requires a meticulous and systematic approach. This is precisely where the Disa Stig Group Policy Template emerges as an indispensable tool, offering a structured pathway to achieve and maintain robust security configurations.
For IT professionals, security administrators, and any organization operating with or for the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD), understanding and implementing Security Technical Implementation Guides (STIGs) is not merely a best practice—it’s an obligation. These guides, developed by the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA), specify configuration standards for various technologies to eliminate security vulnerabilities. A well-crafted Disa Stig Group Policy Template streamlines this complex process, transforming a daunting task into a manageable, repeatable, and highly effective security strategy.
Why Disa Stig Group Policy Template is Essential in Today’s Digital Landscape
The continuous barrage of cyberattacks and the ever-expanding threat surface underscore the critical need for proactive security measures. Organizations cannot afford to rely on ad-hoc security configurations; a standardized and rigorously enforced approach is vital. This is why the Disa Stig Group Policy Template has become an essential asset, acting as a foundational layer for cybersecurity defense.
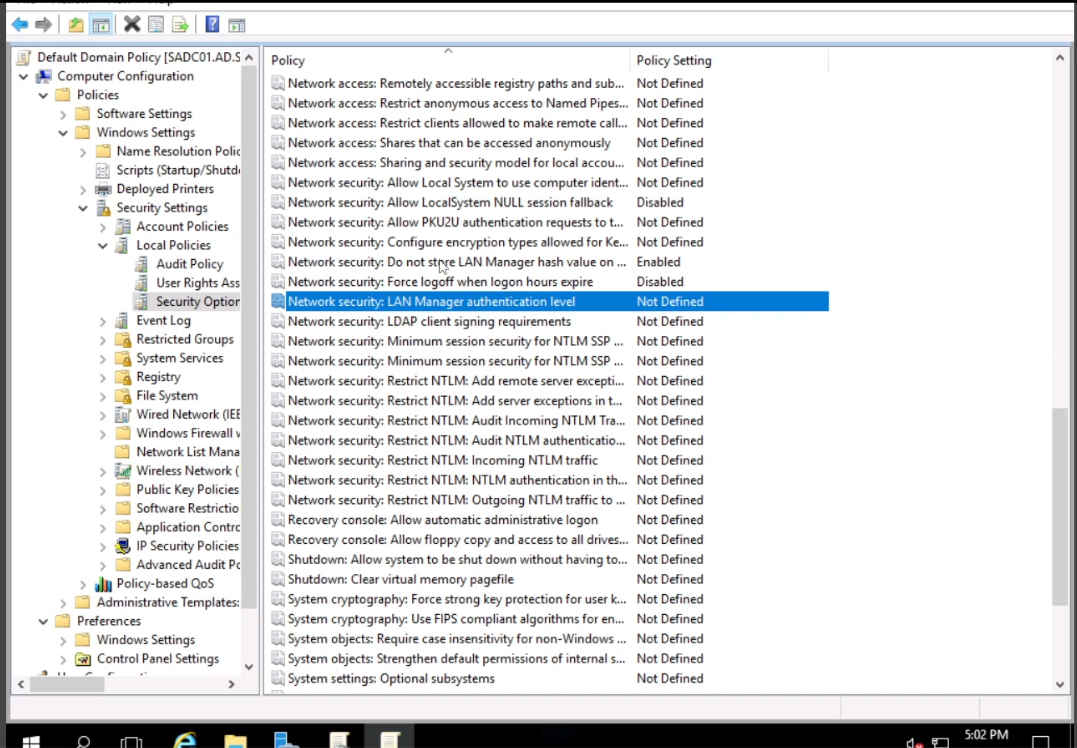
DISA STIGs provide a detailed roadmap for hardening systems against known vulnerabilities. However, manually implementing these thousands of security controls across a vast enterprise can be an overwhelming and error-prone endeavor. A robust Disa Stig Group Policy Template automates much of this process, ensuring that security policies are consistently applied, reducing the likelihood of configuration drift, and significantly bolstering an organization’s overall cybersecurity posture. It helps meet not only DoD compliance obligations but also informs best practices for other regulatory frameworks like NIST, HIPAA, and CMMC.
Key Benefits of Leveraging the Disa Stig Group Policy Template
The adoption of a comprehensive Disa Stig Group Policy Template brings with it a multitude of advantages that extend beyond mere compliance. These benefits translate directly into enhanced security, operational efficiency, and a stronger defensive stance against sophisticated threats. Embracing this templated approach is a strategic investment in an organization’s digital resilience.
Firstly, it ensures streamlined compliance. Organizations can more easily demonstrate adherence to the stringent DISA STIG requirements during audits, simplifying what is often a complex and time-consuming process. This reduces audit fatigue and minimizes the risk of non-compliance penalties. Secondly, it leads to an enhanced security posture. By systematically applying hardened configurations, the Disa Stig Group Policy Template proactively closes common attack vectors and strengthens defenses against exploits, protecting sensitive data and critical systems.
Furthermore, operational efficiency sees a significant boost. Automating the deployment of security settings across an Active Directory environment dramatically reduces manual effort and human error, freeing up valuable IT resources for more strategic initiatives. This consistency and standardization ensure that every system, regardless of its location or administrator, adheres to the same high level of security. Finally, the long-term cost savings are substantial, stemming from avoided data breaches, simplified audit processes, and optimized IT staff productivity.
Customizing the Disa Stig Group Policy Template for Unique Organizational Needs
While DISA STIGs provide a robust baseline, a "one-size-fits-all" approach rarely suffices for diverse organizational environments. The true power of a Disa Stig Group Policy Template lies in its adaptability and the ability to customize it to meet specific operational requirements without compromising security objectives. Tailoring the template intelligently is crucial for seamless integration and optimal performance.
Organizations must assess their unique technological footprint, including various operating systems, specialized applications, and network segmentation. A tailored Disa Stig Group Policy Template might differentiate between security policies for a highly sensitive data center versus those for a less critical office workstation, or between cloud-based assets and on-premise infrastructure. This involves carefully analyzing the impact of each STIG control, identifying false positives, and making informed decisions about exceptions or modifications, always with thorough documentation and risk acceptance.
The process of customization is iterative. It requires initial planning, testing in a controlled environment, phased rollout, and continuous refinement based on feedback and evolving threat intelligence. Engaging stakeholders from different departments, including security, operations, and application owners, ensures that the customized Disa Stig Group Policy Template balances stringent security with essential operational functionality, fostering a stronger security culture across the enterprise.
Important Elements and Fields Within the Disa Stig Group Policy Template
A comprehensive Disa Stig Group Policy Template is a granular framework, encompassing a wide array of security settings designed to harden various aspects of an IT system. Understanding the critical elements and fields within such a template is paramount for effective deployment and management. These components collectively form a formidable defense against potential vulnerabilities.
Here are some of the important elements and fields typically included:
- Password Policy Settings: Defining parameters such as minimum password length, complexity requirements (e.g., uppercase, lowercase, numbers, special characters), password history enforcement, and maximum password age.
- Account Lockout Policies: Configuring thresholds for failed logon attempts before an account is locked out, and specifying the lockout duration.
- Audit Policy Configuration: Detailing what events should be logged (e.g., successful/failed logons, object access, policy changes, system events) to ensure thorough traceability for incident response and compliance.
- User Rights Assignment: Carefully defining which users or groups have specific privileges, adhering to the principle of least privilege. This includes rights like "Act as part of the operating system" or "Shut down the system."
- Security Options: Configuring various system behaviors such as interactive logon messages, network access restrictions, and administrative sharing settings.
- Event Log Settings: Specifying the maximum size of security, system, and application event logs, and defining retention policies to ensure logs are not overwritten prematurely.
- Restricted Groups: Enforcing membership for critical local groups (e.g., Administrators, Backup Operators) to prevent unauthorized users from gaining elevated privileges.
- System Services Configuration: Disabling or configuring the startup type of non-essential services to reduce the attack surface.
- Windows Firewall Rules: Establishing inbound and outbound rules to control network traffic, blocking unauthorized access and preventing malicious egress.
- Software Restriction Policies or AppLocker: Limiting the execution of unauthorized applications to prevent malware and enhance system integrity.
- Removable Storage Device Control: Managing the use of USB drives and other removable media to prevent data exfiltration and malware introduction.
- Registry Settings: Applying specific registry modifications to address particular STIG requirements or vulnerabilities not covered by other Group Policy sections.
- Administrative Templates: Configuring settings for various operating system components, applications, and features, often mapping directly to STIG requirements.
Tips for Designing, Implementing, and Ensuring Usability of Your Disa Stig Group Policy Template
Successfully implementing a Disa Stig Group Policy Template requires more than just technical configuration; it demands thoughtful design, careful rollout, and ongoing management. Usability, documentation, and continuous improvement are critical to transforming a set of rules into a truly effective and sustainable security solution.
Firstly, start with a solid baseline and test rigorously. Never deploy a comprehensive Disa Stig Group Policy Template directly into a production environment without extensive testing in a non-production or pilot group. This helps identify conflicts, performance impacts, and unexpected behaviors. Thorough documentation of your testing methodology and results is vital for demonstrating due diligence.
Secondly, document everything comprehensively. Create clear, concise documentation for each policy within the Disa Stig Group Policy Template, detailing its purpose, the specific STIG ID it addresses, its expected impact, and any exceptions or rationale for deviations. This digital documentation should be version-controlled, searchable, and easily accessible, complementing any printable compliance reports required. Effective labeling and commenting within the GPOs themselves are also crucial for manageability.
Thirdly, consider a phased rollout approach. Instead of a "big bang" deployment, introduce the Disa Stig Group Policy Template to smaller, less critical groups first. This allows for fine-tuning and reduces the risk of widespread operational disruptions. Regular review and update cycles are also indispensable, as STIGs themselves are periodically updated, and your organization’s environment evolves.
Finally, provide adequate training for administrators and end-users. Administrators need to understand the implications of the policies and how to troubleshoot issues. End-users might need awareness training if certain policies (e.g., password complexity, removable media restrictions) impact their daily workflow. Utilizing GPO management tools for reporting, monitoring, and auditing ensures continuous compliance and swift identification of non-conforming systems.
The strategic implementation of a robust Disa Stig Group Policy Template is not merely a technical task; it’s a fundamental commitment to cybersecurity excellence. By providing a structured, repeatable, and auditable framework for system hardening, it empowers organizations to meet stringent regulatory obligations while simultaneously elevating their defense against an increasingly complex threat landscape. This proactive approach minimizes vulnerabilities, reduces the likelihood of costly breaches, and ultimately safeguards critical information assets.
As digital threats continue to evolve, the necessity of maintaining a hardened and compliant IT environment will only intensify. Investing in and continually refining your Disa Stig Group Policy Template serves as a cornerstone of your overall risk management strategy. It’s a practical, actionable solution that delivers tangible benefits, ensuring operational continuity, preserving data integrity, and fostering greater trust in your organization’s security posture. Embrace this powerful tool to transform your security challenges into opportunities for resilience and growth.


