In the fast-paced world of digital product development, launching a successful mobile or web application often feels like navigating a complex maze. Without a clear map, projects can quickly derail, budgets can balloon, and the final product might bear little resemblance to the initial vision. This common pitfall highlights a fundamental truth: clarity and precise communication are the bedrock of any successful app venture.
Imagine embarking on a major construction project without blueprints. The outcome would be chaotic, inefficient, and likely unsatisfactory. Developing an app is no different. It requires a detailed plan, a single source of truth that all stakeholders can reference and understand. This is where a well-crafted requirements document becomes not just useful, but absolutely essential. It bridges the gap between idea and execution, ensuring everyone is aligned on what needs to be built, why, and for whom.
Why a Requirements Document is Non-Negotiable
The journey from concept to launch for any app is fraught with potential miscommunications and shifting priorities. A comprehensive set of requirements serves as the foundational agreement between all parties involved, from the client and project manager to the design and development teams. It acts as a compass, guiding decisions and preventing costly reworks later in the development cycle.
Without a solid requirements document, projects often suffer from scope creep, where new features are added haphazardly, expanding the project’s timeline and budget unnecessarily. It also helps in identifying potential technical challenges early on, allowing for strategic planning rather than reactive problem-solving. Ultimately, a detailed specification reduces ambiguity, fosters better collaboration, and significantly increases the chances of delivering a product that meets user needs and business objectives.
Key Benefits of a Well-Defined Requirements Document
Implementing a structured approach to defining app requirements yields a multitude of advantages that streamline the entire development process. From initial planning to final deployment, its impact is profound and far-reaching, ensuring a more efficient and successful outcome.
Here are some of the critical benefits:
- **Clearer Communication:** It establishes a common language and understanding among all stakeholders, minimizing misunderstandings and ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- **Reduced Risk:** By outlining potential challenges and requirements upfront, it helps identify and mitigate risks related to technical feasibility, budget, and timelines.
- **Scope Management:** A detailed app requirements document acts as a boundary, preventing uncontrolled feature additions (scope creep) and keeping the project focused.
- **Efficient Development:** Developers have a precise guide to follow, reducing guesswork and allowing them to write cleaner, more effective code.
- **Accurate Estimates:** With a clear outline of features and functionalities, project managers can provide more accurate estimations for budget and timeline.
- **Improved Quality Assurance:** QA teams can design more effective test cases based on defined functional and non-functional requirements, leading to a higher quality product.
- **Better Decision-Making:** It serves as a reference point for making informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle, especially when trade-offs are necessary.
- **Stakeholder Alignment:** Ensures that the final product aligns with the initial vision and business goals of the client and other key stakeholders.
Essential Components of an Effective Requirements Document
While there’s no one-size-fits-all formula, a robust requirements document typically includes several core sections that systematically break down the app’s purpose, features, and technical specifications. This structured approach ensures no critical aspect is overlooked.
A good App Requirements Document Template will typically include:
Executive Summary
This section provides a high-level overview of the app. It briefly describes the product, its purpose, the problem it solves, and its target audience. Think of it as an elevator pitch for the entire project, quickly informing anyone who reads it about the core idea.
Business Goals and Objectives
Here, you’ll clearly define what the app aims to achieve from a business perspective. This might include increasing customer engagement, generating revenue, improving operational efficiency, or expanding market reach. Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives are crucial here.
Target Audience and User Personas
Understanding who will use the app is paramount. This section details the demographic and psychographic characteristics of the primary users. Creating user personas—fictional representations of your ideal users—helps in empathy-driven design and development, ensuring the app truly serves its users’ needs.
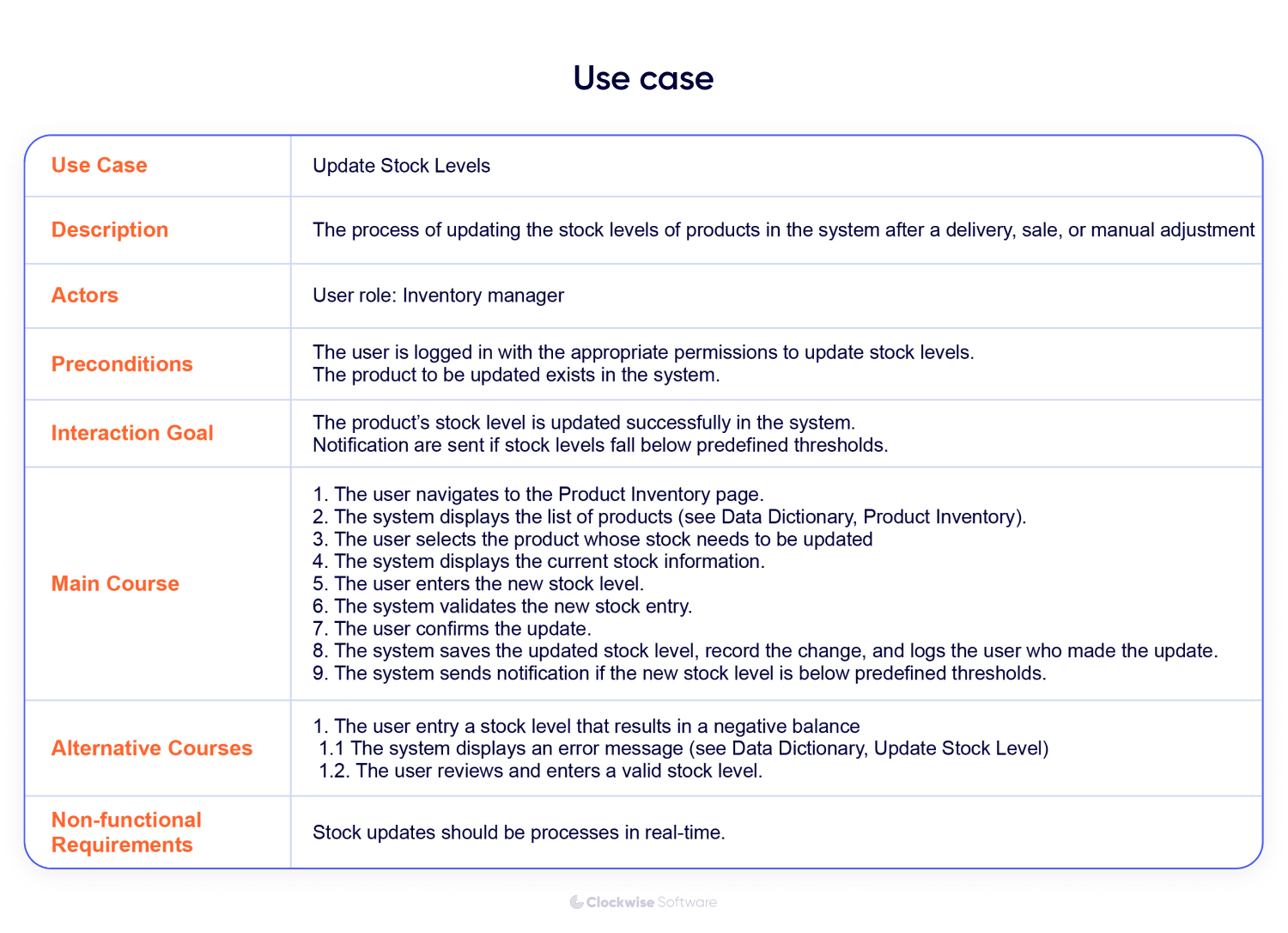
User Stories or Use Cases
These describe how a user will interact with the app to achieve a specific goal. User stories are typically written from the perspective of the end-user (e.g., “As a user, I want to be able to log in securely, so I can access my personalized dashboard”). Use cases provide a more detailed sequence of interactions between the user and the system.
Functional Requirements
These are the core features and functions that the app *must* perform. They describe what the system does, such as “The app shall allow users to create an account,” “The app shall display a list of available products,” or “The app shall process secure payments.” Each requirement should be clear, unambiguous, and testable.
Non-Functional Requirements
Beyond *what* the app does, non-functional requirements describe *how well* the app performs its functions. This includes aspects like:
- **Performance:** How fast the app loads, response times, handling concurrent users.
- **Security:** Data encryption, authentication methods, protection against vulnerabilities.
- **Usability:** Ease of use, intuitiveness, accessibility for users with disabilities.
- **Reliability:** Uptime, error handling, data recovery.
- **Scalability:** Ability to handle increasing loads of users or data.
- **Maintainability:** Ease of updating and fixing bugs in the future.
User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) Specifications
This section outlines the visual design and overall user flow. It includes wireframes, mockups, design guidelines (colors, fonts, branding), and descriptions of navigation paths. It ensures a consistent and intuitive experience across the app.
Technical Requirements and Architecture
Details about the underlying technology, programming languages, platforms (iOS, Android, web), third-party integrations (APIs), databases, and server infrastructure are defined here. This provides the development team with a clear technical roadmap.
Future Scope and Roadmap
No app is ever truly “finished.” This section outlines features planned for future phases, indicating potential enhancements or new functionalities that are not part of the initial launch but are considered for the app’s long-term evolution.
Practical Tips for Crafting Your Document
Creating an effective specification for your digital product is an iterative process that benefits from collaboration and clarity. Here are some actionable tips to ensure your document is a living, valuable asset:
- Start Early and Involve Key Stakeholders: Begin documenting requirements as soon as the app concept takes shape. Include not just business owners and project managers, but also representatives from design, development, and QA teams from the outset. Their early input can prevent costly revisions down the line.
- Keep it Clear and Concise: Avoid jargon where possible. Write in simple, unambiguous language. Each requirement should be specific enough to be understood by technical and non-technical readers alike, and testable.
- Prioritize Requirements: Not all features are created equal. Use methods like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) or a numerical prioritization system to rank features. This helps in managing scope and making informed decisions when resources are limited.
- Use Visual Aids: Wireframes, flowcharts, user journey maps, and mockups can communicate complex ideas much more effectively than text alone. Integrate these visuals directly into your mobile app requirements document.
- Version Control is Crucial: As requirements evolve, it’s essential to track changes. Implement a robust version control system to ensure everyone is working from the latest document and to maintain an audit trail of modifications.
- Review and Validate Regularly: The requirements are not set in stone; they should be reviewed and validated throughout the development lifecycle. Schedule regular meetings with all stakeholders to discuss progress, clarify ambiguities, and incorporate feedback.
- Focus on the "Why": For each feature or requirement, try to articulate the underlying business need or user problem it solves. Understanding the "why" provides context and helps teams make better design and implementation choices.
Who Benefits from a Comprehensive Requirements Document?
A robust outline of what an app should do serves as the central point of reference for everyone involved in its creation and lifecycle. The benefits cascade across various roles and departments, underscoring its indispensable nature.
- Clients/Product Owners: Gain a clear understanding of what they are getting and can ensure the final product aligns with their vision and business goals. They can track progress against defined deliverables.
- Project Managers: Use the document to plan timelines, allocate resources, manage scope, and monitor project health. It empowers them to make informed decisions and communicate effectively with all parties.
- Designers (UI/UX): Leverage the functional and non-functional requirements, user stories, and target audience descriptions to create intuitive, user-friendly, and visually appealing interfaces.
- Developers: Receive a precise blueprint for coding, reducing ambiguity and minimizing rework. They can focus on building what’s needed without constant clarification.
- Quality Assurance (QA) Testers: Refer to the requirements to develop comprehensive test plans, scenarios, and cases, ensuring that the app functions as intended and meets all specified criteria.
- Marketing and Sales Teams: Can use the documented features and benefits to craft compelling marketing messages and sales pitches, even before the app is fully launched.
- Future Maintenance Teams: Have a complete reference point for understanding the app’s architecture, features, and underlying logic, making future updates, bug fixes, and enhancements much smoother.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between functional and non-functional requirements?
Functional requirements define *what* the system does (e.g., “The app shall allow users to log in”), specifying its behavior and features. Non-functional requirements describe *how well* the system performs its functions (e.g., “The app shall load within 3 seconds”), focusing on quality attributes like performance, security, and usability.
How often should an app’s requirements document be updated?
The requirements document should be a living document, updated whenever there are significant changes to the project scope, features, or technical specifications. Regular reviews (e.g., weekly or bi-weekly during active development) with all stakeholders are crucial to ensure it remains current and accurate, reflecting the latest agreements and decisions.
Is a detailed requirements document necessary for small apps or MVPs?
Absolutely. Even for Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) or smaller applications, a concise but clear set of requirements is vital. It helps define the core features needed for the MVP, prevents scope creep, and provides a clear direction for development. While it might be less exhaustive than for a large-scale project, its fundamental purpose of alignment and clarity remains indispensable.
Who is responsible for creating and maintaining the requirements document?
Typically, the Product Owner or Business Analyst, often in collaboration with the Project Manager, takes the lead in creating the initial requirements document. However, its maintenance and validation are a shared responsibility. All key stakeholders—including clients, designers, and developers—must actively participate in reviews, provide feedback, and confirm that the document accurately reflects the evolving project needs.
Creating an app is a significant investment of time, resources, and vision. To protect that investment and maximize the chances of success, a well-structured and meticulously crafted requirements document is your most powerful tool. It transforms abstract ideas into concrete specifications, setting a clear path for everyone involved.
By embracing the discipline of thorough requirements gathering and documentation, you lay a solid foundation for your digital product. This proactive approach not only streamlines development but also ensures that the final app genuinely meets user needs and achieves its intended business objectives, setting you apart in a competitive digital landscape.