In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, launching a successful software application hinges on much more than brilliant ideas and skilled developers. It requires a crystal-clear understanding of what needs to be built, why it’s needed, and how it will function. Without this shared vision, projects can quickly derail, leading to missed deadlines, budget overruns, and applications that simply don’t meet user expectations. This is precisely where a well-crafted Application Development Requirements Template becomes an indispensable tool.
Far from being a rigid, bureaucratic hurdle, such a template serves as the foundational blueprint for any development project. It acts as a universal translator, bridging the gap between business objectives, user needs, and technical specifications. Whether you’re a product manager defining a new feature, a developer building complex logic, or a stakeholder reviewing progress, this template ensures everyone involved is speaking the same language and working towards a unified goal, setting the stage for a smooth and successful delivery.
The Imperative of Clarity: Why a Requirements Blueprint Matters
The digital world is rife with stories of projects that started with great promise but stumbled due to vague or misunderstood requirements. Imagine embarking on building a house without a detailed architectural plan – it’s almost guaranteed to result in a structure that doesn’t meet the owner’s vision, is over budget, and requires significant rework. The same principle applies to software. A robust `software requirements template` mitigates these risks by forcing clarity and consensus early in the development lifecycle. It’s the difference between guessing what users want and explicitly documenting it.
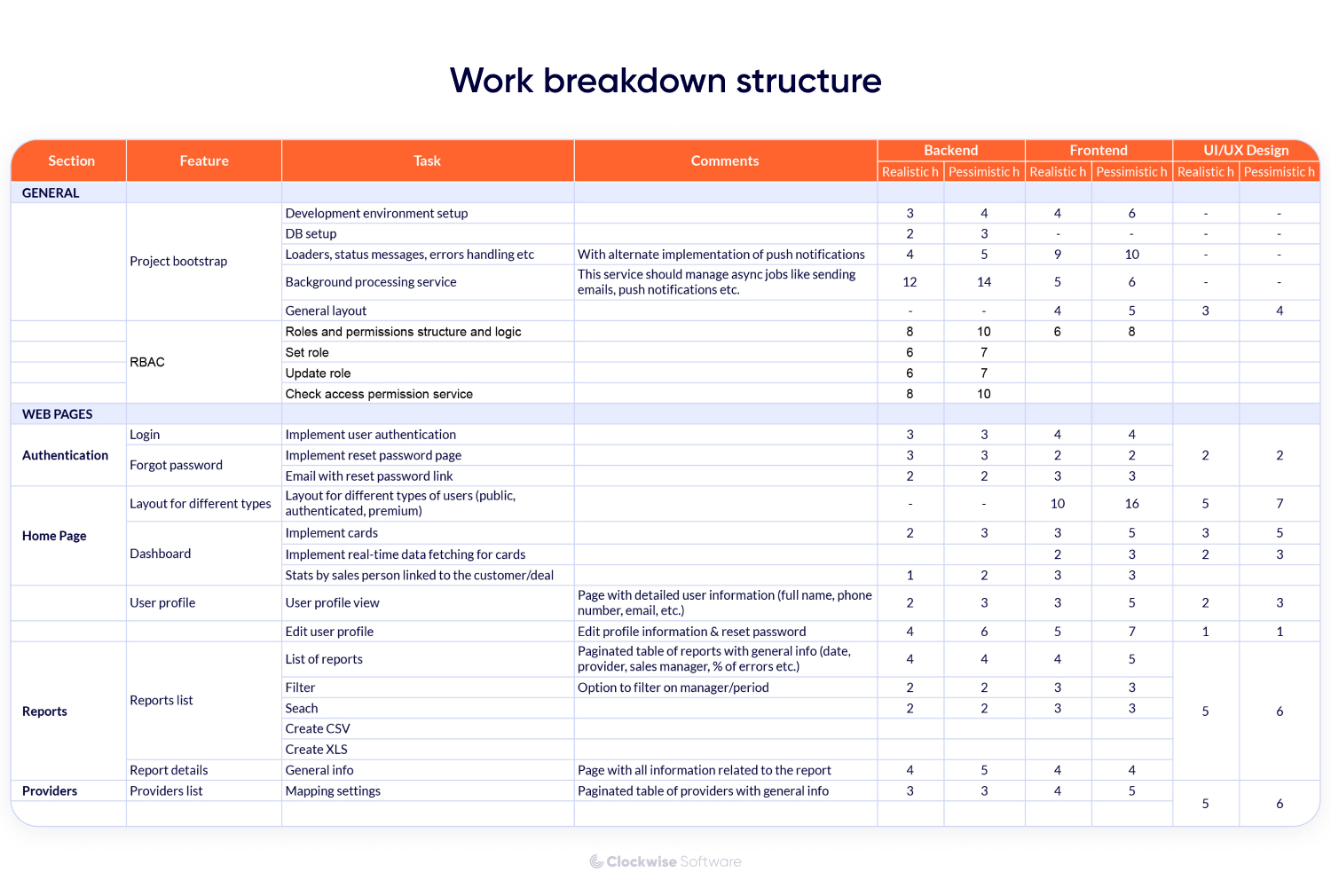
This foundational document acts as the single source of truth, eliminating assumptions and misinterpretations that often plague complex projects. It ensures that every line of code written, every design decision made, and every test case executed aligns with the agreed-upon project scope and objectives. By formalizing the documentation of application development requirements, organizations can significantly reduce project churn, enhance team collaboration, and ultimately deliver a product that truly satisfies its intended users.
Unlocking Efficiency: Key Benefits of a Structured Requirements Document
Implementing a standardized `project requirements document` brings a multitude of advantages that cascade throughout the entire development lifecycle, benefiting every team member and stakeholder.
**Improved Communication:** A well-defined document provides a common language and understanding for all parties involved, from business analysts to UI/UX designers, developers, and quality assurance testers. This clarity minimizes misunderstandings and ensures everyone is aligned on project goals and deliverables.
**Reduced Risk and Rework:** By identifying and documenting requirements upfront, potential issues, ambiguities, and scope creep are addressed early. This proactive approach significantly reduces the likelihood of costly changes, redesigns, and re-coding later in the development cycle.
**Accurate Estimations and Budgeting:** Clear `dev project requirements` enable project managers and development leads to provide more precise estimates for time, resources, and budget. This leads to more realistic planning and better financial control throughout the project’s duration.
**Better Quality and User Satisfaction:** When requirements are explicitly defined, the development team has a clear target to hit. This results in an application that not only functions as intended but also meets the specific needs and expectations of the end-users, leading to higher product quality and user satisfaction.
**Streamlined Testing and Validation:** Quality assurance teams can use the `development needs documentation` as a direct basis for creating comprehensive test plans and cases. This ensures that every feature and functionality is thoroughly tested against the defined criteria, making the validation process more efficient and effective.
**Enhanced Project Transparency:** A formalized requirements document offers stakeholders a clear overview of the project’s scope, progress, and objectives. This transparency fosters trust and allows for informed decision-making at every stage of the development process.
Core Components of a Comprehensive Requirements Template
While the specifics might vary based on project size and methodology, an effective `system requirements outline` generally includes several key sections to ensure all critical information is captured.
- **Project Overview:** A high-level summary of the application, its purpose, vision, and the problem it aims to solve. This section sets the stage and provides context for the entire document, often including the business goals and measurable objectives.
- **Stakeholder Analysis:** Identifies all key individuals or groups affected by the project, their roles, responsibilities, and how their needs will be addressed. Understanding stakeholder perspectives is crucial for capturing holistic requirements.
- **Functional Requirements:** These describe what the system *must do*. They detail the specific behaviors, features, and functions that users will interact with. This often includes:
- **User Stories:** Short, simple descriptions of a feature told from the perspective of the end-user (e.g., “As a customer, I want to be able to track my order so I know when it will arrive”).
- **Use Cases:** Detailed scenarios describing how a user interacts with the system to achieve a specific goal, outlining steps and alternative flows.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** These define how the system *performs* or its quality attributes, rather than specific behaviors. Examples include:
- **Performance:** Speed, response time, scalability, throughput.
- **Security:** Authentication, authorization, data encryption, vulnerability management.
- **Usability:** Ease of use, learnability, accessibility.
- **Reliability:** Uptime, error handling, recoverability.
- **Maintainability:** Ease of modifying and supporting the system.
- **User Interface (UI) / User Experience (UX) Requirements:** Specifies the visual design, layout, navigation, and overall user interaction. This can involve wireframes, mockups, prototypes, and design system guidelines to illustrate the intended user journey.
- **Data Requirements:** Details the data to be stored, managed, and processed by the application. This covers data models, data sources, data privacy, and integration needs with existing databases or external services.
- **Technical Requirements:** Outlines the underlying technological choices, architecture, hardware/software infrastructure, programming languages, APIs, and third-party integrations necessary for the application’s development and deployment.
- **Assumptions and Constraints:** Documents any factors assumed to be true for the project to proceed (e.g., availability of an external API) and any limitations or restrictions (e.g., specific budget limits, regulatory compliance requirements).
- **Testing and Acceptance Criteria:** Defines how the success of each requirement will be measured. Clear acceptance criteria ensure that developers know when a feature is complete and working correctly, and testers know what to validate against.
Best Practices for Utilizing Your Development Requirements Document
Simply having an `Application Development Requirements Template` isn’t enough; its effective utilization is key to project success. To truly leverage its power, adopt a proactive and collaborative approach. Begin gathering requirements early in the project lifecycle, involving key stakeholders from the outset to capture diverse perspectives and foster ownership.
Ensure that all requirements are clear, concise, unambiguous, and testable. Avoid vague language that can lead to misinterpretation. Prioritize requirements using methods like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) or simple high/medium/low rankings to guide development efforts and manage scope effectively. Implement robust version control to track changes, ensuring that all team members are always working with the latest iteration of the product requirements specification. Regular reviews and iterations with stakeholders are crucial to keep the document current and aligned with evolving project needs.
Make the document easily accessible to the entire development team and relevant stakeholders, fostering transparency and reducing communication silos. Finally, focus on transforming complex requirements into actionable user stories and use cases, which are often more digestible and provide better context for development tasks.
Customizing for Success: Adapting Your Software Specification Document
No two development projects are identical, and therefore, a “one-size-fits-all” mentality rarely works for a requirements template. The true power of a comprehensive `software specification document` lies in its adaptability. For a small, internal utility application, you might streamline sections, focusing heavily on functional requirements and a concise technical overview. Conversely, a large-scale enterprise application with stringent regulatory demands will necessitate much greater detail in areas like security, scalability, and data privacy.
Consider the development methodology you’re employing. In an Agile environment, the template might be less prescriptive, focusing on high-level epics and user stories that are continuously refined in sprints, rather than an exhaustive upfront waterfall-style document. The template should be treated as a living document, evolving alongside the project itself. Embrace flexibility; don’t be afraid to add or remove sections, or adjust the level of detail, to match the unique characteristics of your development project requirements. Leveraging specialized tools for requirements gathering tool can also help manage complexity and promote collaboration as your documentation grows.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a requirements document?
The primary purpose is to clearly define the scope, functionalities, and constraints of a software project. It ensures a shared understanding among all parties involved and serves as the authoritative guide throughout the entire development process, minimizing ambiguity and maximizing success.
Who should contribute to creating the project requirements document?
Creating this crucial document is a collaborative effort. Key contributors typically include product owners, business analysts, subject matter experts, developers, testers, and end-user representatives. Involving a diverse group ensures that various perspectives are captured and aligned.
How often should the system requirements outline be updated?
The `system requirements outline` should be treated as a living document. In Agile methodologies, it’s continuously refined and updated with each sprint. In more traditional Waterfall approaches, updates typically occur at specific project milestones or whenever significant changes in scope or functionality are introduced. Regular reviews are essential to keep it current.
Can a single template work for both small and large projects?
While a basic `software requirements template` can be a starting point, it’s often more effective to customize it. Larger projects typically require more detailed sections and greater granularity, whereas smaller projects might benefit from a more streamlined and concise version, focusing only on the most critical elements to avoid unnecessary overhead.
What’s the difference between functional and non-functional requirements?
**Functional requirements** describe what the system *does* (e.g., “The user shall be able to log in”). They outline specific features and behaviors. **Non-functional requirements** describe how the system *performs* or its quality attributes (e.g., “The system shall load pages within 2 seconds”). They focus on aspects like performance, security, usability, and scalability.
Embracing a robust development project requirements process, guided by a well-structured template, transforms an abstract idea into a tangible, high-quality application. It’s more than just paperwork; it’s a strategic investment in clarity, collaboration, and ultimate project success. By setting clear expectations, defining the boundaries, and providing a shared reference point, you empower your teams to build with confidence and precision.
So, don’t just start coding; start planning with purpose. By investing time upfront in defining and documenting your requirements, you lay a solid foundation for delivering applications that not only meet technical specifications but also delight users and achieve core business objectives. Make the Application Development Requirements Template a cornerstone of your development toolkit, and watch your projects thrive.