In today’s data-rich business landscape, the ability to extract meaningful insights from vast oceans of information is paramount. Business Intelligence (BI) tools are designed to do just that, transforming raw data into actionable knowledge. However, the journey from data to decision isn’t always smooth; it often hits roadblocks when the vision for a report isn’t clearly articulated, leading to frustration, delays, and reports that simply miss the mark.
This is where a well-crafted Bi Report Requirements Template becomes an indispensable asset. It serves as the blueprint, the shared understanding, and the guiding document that bridges the gap between what business stakeholders need to know and what BI developers or analysts are tasked to build. By standardizing the process of gathering and documenting reporting needs, organizations can ensure that every report, dashboard, or analytical view delivers precisely the value intended.
Navigating the Data Deluge: Why Clear Requirements Matter
The absence of clear, concise, and comprehensive requirements is a leading cause of project failure in the world of business intelligence. Without a defined structure, requests can be vague, open to interpretation, and prone to “scope creep,” where the initial vision expands uncontrollably. This often results in reports that are either irrelevant to the strategic objectives, technically infeasible, or require extensive rework, wasting valuable time and resources.
A structured approach, like utilizing a robust BI reporting template, helps to preempt these issues. It forces all parties involved—from the executive asking for a strategic overview to the data analyst building the query—to align on what success looks like. This clarity minimizes miscommunication, accelerates development cycles, and ultimately delivers more impactful business intelligence solutions that truly empower decision-makers.
The Core Benefits of Adopting a Standardized BI Reporting Template
Implementing a standardized framework for documenting data reporting needs brings a multitude of advantages that extend across the entire organization. It’s more than just a document; it’s a strategic tool that enhances collaboration and efficiency.
- Improved Communication: A common language and structure ensure everyone understands the scope and objectives of a report. It minimizes ambiguity, translating business needs into technical specifications effectively.
- Enhanced Efficiency: With clear guidelines, developers spend less time deciphering vague requests and more time building accurate, relevant reports. This reduces rework and accelerates delivery timelines.
- Consistency Across Reports: A template helps enforce best practices and a consistent reporting style, making it easier for users to navigate and understand different reports and dashboards.
- Better Resource Allocation: By clearly defining what’s needed, organizations can better estimate the effort required, allocate appropriate resources, and manage expectations for project completion.
- Reduced Risk of Scope Creep: The structured nature of a report specification document helps to contain requirements within defined boundaries, preventing projects from expanding beyond their initial intent without proper approval.
- Easier Maintenance and Updates: Well-documented requirements make it simpler to understand the logic behind existing reports, facilitating easier updates, troubleshooting, and modifications as business needs evolve.
Key Elements of an Effective Business Intelligence Report Requirements Document
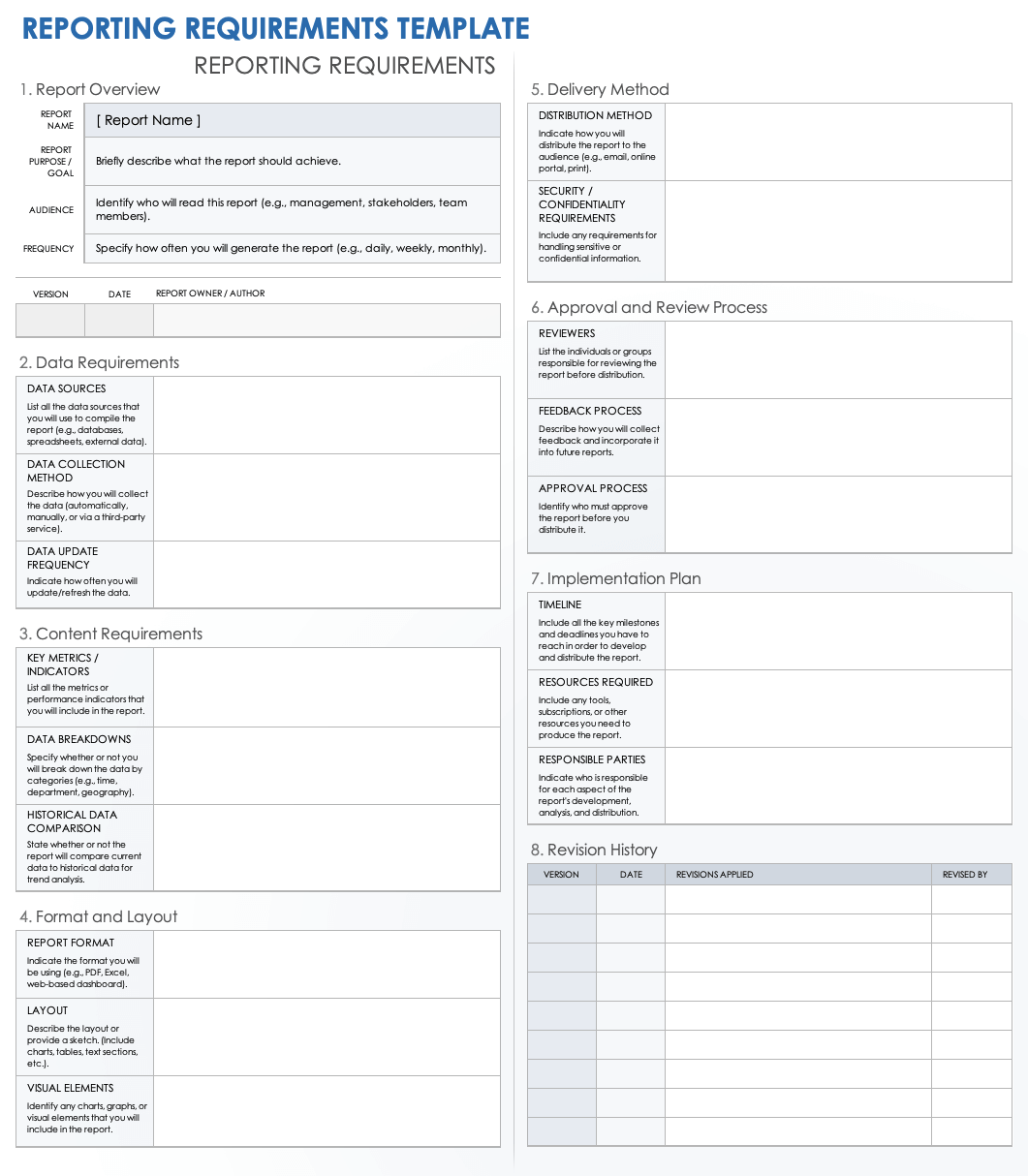
While every organization’s specific needs may vary, a comprehensive template for BI reports should include several core sections. These elements ensure that all critical aspects of a report are considered and documented, leaving little room for assumptions.
- **Report Name and Purpose:** A clear, concise title and a paragraph explaining the strategic objective or question the report aims to answer. What specific business decision will it support?
- **Target Audience:** Who will be using this report? Understanding the audience (e.g., executives, marketing teams, operations managers) helps tailor the level of detail, complexity, and visualization style.
- **Key Metrics and KPIs:** A precise list of the specific measures (e.g., sales revenue, customer churn rate, website traffic) and key performance indicators the report needs to display. Define how each is calculated.
- **Data Sources:** Identify where the data for the report will originate (e.g., CRM, ERP, transactional database, external APIs). This helps in understanding data availability and integration efforts.
- **Filters and Parameters:** Detail any criteria users should be able to apply to the data (e.g., date range, product category, region, sales representative). Specify if these are single-select, multi-select, or required.
- **Visualizations and Layout:** Describe the preferred chart types (e.g., bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, tables), dashboard layout, and any specific branding or formatting requirements. Provide mockups or sketches if possible.
- **Frequency and Delivery Method:** How often should the report be generated (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly, on-demand)? How will it be delivered (e.g., emailed, published to a portal, embedded in an application)?
- **Data Refresh Rate:** How current does the data need to be? (e.g., real-time, daily batch, hourly refresh). This has significant implications for system architecture and performance.
- **Security and Access:** Who should have access to this report, and at what level of detail? Specify any data masking or row-level security requirements.
- **Performance Expectations:** Define acceptable load times for the report or dashboard. Slow reports lead to user frustration and underutilization.
- **Validation Criteria:** How will the business users confirm that the report is accurate and meets their needs? This could involve comparing against existing reports or known data points.
- **Business Rules and Logic:** Document any complex calculations, aggregations, or conditional formatting that needs to be applied. For instance, “profit margin is calculated as (revenue – cost) / revenue.”
- **Dependencies:** Are there other reports, data feeds, or systems that this report relies on or impacts?
Crafting Your Ideal Report Specification Document: Best Practices and Tips
Simply having a template isn’t enough; knowing how to use it effectively is key to successful BI project delivery. These best practices will guide you in maximizing the value of your business intelligence report requirements.
Engage stakeholders early and often. The most effective reporting requirement guides are developed through collaborative efforts. Involve the end-users, subject matter experts, and data owners from the very beginning. Their insights are invaluable for ensuring the report meets real-world needs. Conduct workshops, interviews, and feedback sessions to gather comprehensive input.
Start with the "why" before diving into the "what." Before listing metrics or visualizations, always ensure there’s a clear understanding of the business problem or decision the report is intended to support. This strategic alignment prevents the creation of "vanity metrics" or reports that provide data without actionable insights.
Prioritize your requirements. Not all requirements are equally critical. Work with stakeholders to identify "must-haves," "should-haves," and "nice-to-haves." This prioritization helps manage scope, especially in iterative development cycles, ensuring the most important elements are delivered first.
Define success metrics for the report itself. How will you know if the report is successful? Is it increased user adoption, faster decision-making, or a measurable improvement in a business process? Establishing these benchmarks helps demonstrate the return on investment of your BI efforts.
Keep the documentation concise but comprehensive. While it’s important to capture all necessary details, avoid excessive jargon or overly complex language. The reporting needs outline should be understandable to both business and technical audiences. Use diagrams or mock-ups to clarify complex visual requirements.
Review and validate requirements thoroughly. Before any development work begins, have all key stakeholders sign off on the report specification document. This formal agreement confirms that everyone is aligned and minimizes the chance of misunderstandings downstream. Regular reviews throughout the development process are also crucial.
Implementing and Customizing Your BI Report Requirements Template
A generic Bi Report Requirements Template is a fantastic starting point, but its true power is unlocked when it’s tailored to your organization’s unique context. Consider your industry, your specific data governance policies, and your typical BI development lifecycle. Some companies might need more detailed sections on regulatory compliance, while others might focus heavily on user experience and interactivity.
Once customized, the template needs to be integrated into your existing project management and BI development workflows. This might involve creating a central repository for all report requirements documents, establishing a clear process for submitting and approving new report requests, and training relevant personnel on how to effectively complete the template. Version control is also critical; ensure that changes to requirements are tracked and communicated to all involved parties, preventing confusion and ensuring everyone works from the most current specifications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a BI report requirements template?
A BI report requirements template is a structured document that guides stakeholders through the process of articulating their needs for a business intelligence report or dashboard. It ensures all critical aspects, such as purpose, audience, metrics, data sources, and delivery methods, are captured clearly and comprehensively.
Who typically uses these report specification documents?
These documents are used by a wide range of individuals within an organization. Business users and stakeholders leverage them to convey their information needs, while BI developers, data analysts, and project managers use them to understand, plan, and execute the creation of the reports.
How often should report requirements be reviewed?
Report requirements should ideally be reviewed at key milestones during the report development lifecycle, such as after initial drafting, before development begins, and during user acceptance testing. Additionally, existing report requirements should be revisited periodically, perhaps annually or whenever significant business changes occur, to ensure their continued relevance.
Can a single template serve all types of BI reports?
While a core template for BI reports can be highly effective, it’s often beneficial to have minor variations for different types of reports. For example, a template for an executive dashboard might emphasize high-level KPIs and interactive visualizations, whereas a template for an operational report might focus more on detailed transactional data and specific filtering capabilities. Customization ensures optimal fit.
What’s the biggest challenge in gathering reporting needs?
The biggest challenge is often the translation gap between business language and technical specifications. Stakeholders may know what they want to achieve, but articulating the precise data points, calculations, and visual representations can be difficult. A well-designed data requirement outline helps bridge this gap by prompting specific, actionable details.
Embracing a structured approach to defining your business intelligence reporting specifications isn’t just about efficiency; it’s about strategic alignment and maximizing the return on your data investments. By providing a clear framework for communication and documentation, a robust template empowers teams to move beyond ambiguous requests to deliver insightful, impactful reports that truly drive the business forward.
Start with a template, customize it to fit your unique ecosystem, and embed it into your processes. The clarity and consistency it brings will transform your BI initiatives, turning data into a powerful engine for growth and innovation. Equip your teams with the right tools, and watch your organization make smarter, faster, and more confident decisions.


