In today’s fast-evolving business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and deliver superior customer experiences. Business Process Management (BPM) stands as a critical discipline for achieving these goals, providing a structured approach to analyzing, designing, implementing, monitoring, and refining an organization’s processes. However, the success of any BPM initiative hinges profoundly on one foundational element: thoroughly and accurately gathered requirements. Without a clear understanding of what a process needs to achieve, any effort to improve or automate it is destined for missteps and potential failure.
Navigating the complexities of diverse stakeholder needs, technical constraints, and business objectives can be daunting. This is where a robust and comprehensive framework becomes indispensable. A well-designed Bpm Requirements Gathering Template provides the structure and guidance necessary to systematically capture all pertinent information, ensuring nothing critical is overlooked. It acts as a compass, guiding business analysts, project managers, and process owners through the intricate journey of defining current states, envisioning future states, and articulating the exact specifications needed to bridge that gap. By standardizing this crucial phase, organizations can minimize errors, accelerate project timelines, and ultimately achieve more impactful process improvements.
Understanding the Core of Business Process Management
At its heart, Business Process Management is about continuously improving how work gets done. It involves more than just mapping out existing workflows; it’s a strategic discipline aimed at making an organization more agile, efficient, and responsive. Effective BPM initiatives are not born out of guesswork but from a deep, analytical understanding of current operations and a clear vision for desired outcomes. This understanding begins with a meticulous approach to defining the exact needs and expectations surrounding a process.
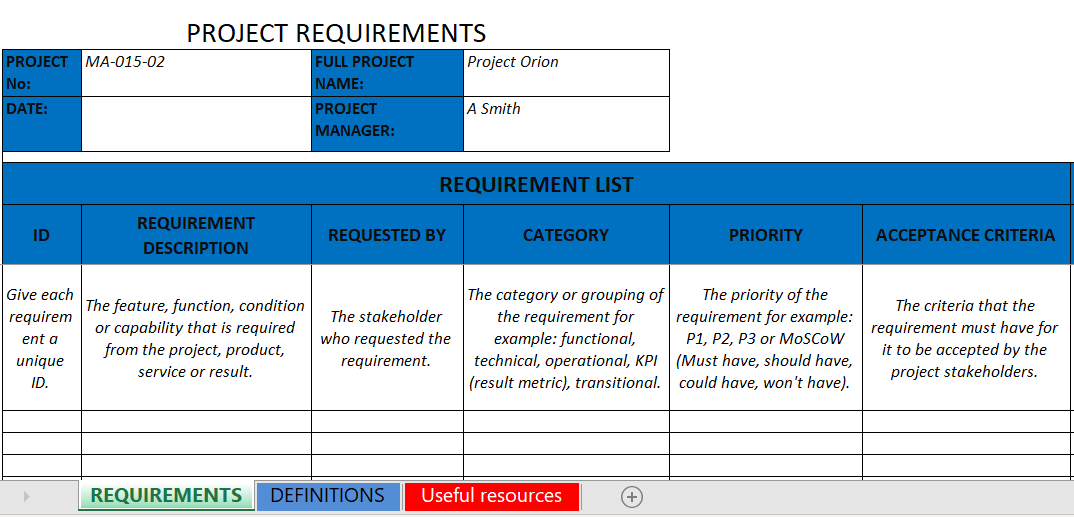
The initial phase of any BPM project, often referred to as the discovery or analysis phase, is paramount. During this period, teams must identify all relevant stakeholders, understand their perspectives, and document the current "as-is" process alongside the desired "to-be" state. This requires a systematic way to elicit, analyze, validate, and manage requirements throughout the project lifecycle. Without a standardized approach, vital information can be missed, leading to scope creep, rework, and project delays.
Why a Structured Approach to Process Requirements is Indispensable
Attempting to gather requirements without a structured framework is akin to building a house without blueprints. You might get something built, but it’s unlikely to be stable, functional, or meet the specific needs of its occupants. A dedicated template for BPM requirements gathering offers numerous benefits that streamline the process and enhance the quality of the outcomes. It provides consistency, reduces ambiguity, and fosters better communication among all parties involved.
A structured framework ensures that all critical aspects of a business process are considered, from trigger events and input data to process steps, decision points, and desired outputs. It helps in identifying potential bottlenecks, compliance requirements, and performance metrics right from the start. This proactive approach not only saves time and resources in later stages but also significantly increases the likelihood of delivering a solution that truly addresses the organization’s strategic objectives and operational challenges. It’s about building a solid foundation for sustainable process improvement.
Key Elements of an Effective Process Requirements Document
An effective requirements document goes beyond a simple list of features; it tells a complete story of the process, its purpose, its environment, and its desired future state. While specific content may vary based on the process’s complexity and industry, a comprehensive template for eliciting process specifications will typically include the following sections:
- **Executive Summary:** A high-level overview of the process and the scope of the improvement initiative.
- **Business Case/Justification:** Explaining the rationale for the process change, including problems identified and anticipated benefits.
- **Scope Definition:** Clearly delineating what is and isn’t included within the process improvement project. This helps prevent **scope creep**.
- **Stakeholder Identification:** Listing all individuals or groups impacted by the process, along with their roles and responsibilities.
- **Current State (“As-Is”) Analysis:** Detailed documentation of the existing process, including steps, roles, systems involved, and any identified pain points or inefficiencies. This often includes **process maps** and **flowcharts**.
- **Future State (“To-Be”) Definition:** A clear articulation of the desired improved process, detailing new steps, roles, system integrations, and expected outcomes.
- **Functional Requirements:** Specific actions or capabilities the new or improved process must perform. These describe **what the system does**.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** Criteria that define the quality of the process or system, such as performance, security, usability, and compliance. These describe **how well the system performs**.
- **Data Requirements:** What data is needed, where it comes from, how it’s transformed, and where it goes.
- **Integration Requirements:** How the process or system will interact with other existing systems or external services.
- **User Interface (UI) Requirements:** Specifications for any user-facing components, if applicable.
- **Reporting and Analytics Requirements:** What reports or metrics are needed to monitor process performance and compliance.
- **Business Rules:** Explicit statements that define or constrain aspects of the business, crucial for automation and decision-making within the process.
- **Assumptions:** Any factors considered to be true for the project planning, which if changed, could impact the requirements.
- **Constraints:** Limitations or restrictions that must be considered, such as budget, timeline, technology, or regulatory compliance.
- **Success Metrics:** Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure the success of the process improvement.
- **Sign-off:** A section for formal approval by key stakeholders, indicating their agreement with the documented requirements.
Steps to Successfully Implement Your Process Requirements Gathering Strategy
Adopting a structured template is only half the battle; successfully implementing your process requirements gathering strategy requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a practical guide to maximize the effectiveness of your efforts:
Begin by clearly defining the scope of the process improvement initiative. Understand what problem you’re trying to solve and what outcomes you aim to achieve. This initial clarity will guide all subsequent requirements elicitation activities. Identify all relevant stakeholders early on, including process owners, end-users, IT specialists, and regulatory compliance officers. Their diverse perspectives are crucial for a holistic understanding of the process.
Next, conduct thorough requirements elicitation using a variety of techniques. These might include workshops, interviews, surveys, observation, and document analysis. Leverage your Bpm Requirements Gathering Template during these sessions to ensure a consistent approach to capturing information. For instance, when interviewing stakeholders, systematically walk through each section of the template to gather specific details regarding their roles, current pain points, and desired functionalities.
Once requirements are gathered, it’s essential to analyze and document them with precision. Translate raw stakeholder input into clear, concise, and unambiguous statements within your process requirements documentation. Use visual aids like process flowcharts or Swimlane diagrams to illustrate complex workflows and ensure a shared understanding. Every requirement should be traceable back to a business need and align with the overall project objectives.
Validate the documented requirements with all key stakeholders. This step is critical for confirming that the requirements accurately reflect their needs and are achievable within the project’s constraints. Formal sign-off from stakeholders signifies their agreement and minimizes the risk of late-stage changes or misunderstandings. Finally, ensure a robust process for managing changes to requirements throughout the project lifecycle, as requirements are rarely static.
Leveraging Your BPM Requirements Gathering for Optimal Outcomes
The true value of a meticulous requirements gathering process extends far beyond the initial project phase. When done correctly, the detailed documentation provides an invaluable asset for the entire lifecycle of a process. It serves as a foundational reference for design, development, testing, and deployment. Developers will have a clear blueprint for building or configuring systems, and testers will use the requirements to create comprehensive test cases, ensuring the solution meets all specifications.
Furthermore, a well-defined set of process requirements supports effective training and change management. It provides the basis for creating user manuals and training materials, helping employees adapt to new processes with greater ease. In the long term, this detailed documentation becomes a living document for continuous process improvement. As business needs evolve or new technologies emerge, the original requirements can be revisited and updated, providing a clear starting point for future iterations and optimizations. This commitment to thoroughness in defining operational requirement blueprints lays the groundwork for sustained organizational excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a BPM requirements gathering template?
The primary purpose is to provide a standardized, comprehensive framework for systematically identifying, documenting, and validating all necessary information related to a business process improvement or automation initiative. It ensures consistency, reduces ambiguity, and enhances communication among all project stakeholders.
Who typically uses this type of requirements gathering tool?
This tool is primarily used by business analysts, project managers, process owners, and solution architects. It serves as a collaborative document that all stakeholders, including technical teams and end-users, can contribute to and reference throughout the project lifecycle.
How does a template improve the efficiency of a BPM project?
By offering a pre-defined structure, a template streamlines the elicitation process, ensuring no critical details are missed. It minimizes the time spent on formatting and organization, allowing teams to focus more on content. This structured approach helps in avoiding rework, reducing project delays, and accelerating time to value for process improvements.
Can a Bpm Requirements Gathering Template be customized?
Absolutely. While a template provides a strong starting point, it should always be adapted to fit the specific needs, complexity, and industry of your organization and the particular process under review. Customization allows you to add specific sections, terminology, or compliance details relevant to your context, making it a more effective tool.
What are the risks of not using a structured approach to gathering process needs?
Without a structured approach, organizations face risks such as incomplete or inaccurate requirements, leading to solutions that don’t meet business needs. This can result in costly rework, scope creep, project delays, stakeholder dissatisfaction, and ultimately, a failure to achieve the desired process improvements or automation benefits.
Embracing a robust methodology for defining process workflows is not merely a procedural step; it’s a strategic investment in the success and longevity of your business process initiatives. A well-constructed template acts as the cornerstone of this methodology, transforming what could be a chaotic information-gathering exercise into a precise and productive endeavor. It empowers teams to articulate complex needs with clarity, fostering alignment and understanding across all levels of an organization.
By consistently applying a structured framework for defining business process needs, organizations can significantly enhance their capability to deliver high-quality, impactful process solutions. This commitment to thoroughness in the initial stages lays a strong foundation for future growth, enabling greater agility, improved operational efficiency, and a more competitive edge in the marketplace. Leverage this strategic asset to transform your process improvement journey from challenging to exceptional, ensuring every initiative truly drives tangible value and achieves its full potential.


