In today’s data-rich business landscape, the ability to transform raw information into actionable insights is no longer a luxury—it’s a fundamental necessity. Organizations are awash in data, from sales transactions to customer interactions, operational metrics to financial performance. Yet, the sheer volume can be overwhelming, making it difficult to discern what truly matters and how to present it effectively to decision-makers. This is where a strategic approach to defining what information is needed, by whom, and in what format becomes critically important.
The journey from data deluge to informed decision-making hinges on clear, concise, and well-structured reporting. Without a defined roadmap, the process of developing business intelligence (BI) reports can quickly devolve into a chaotic cycle of rework, missed expectations, and underutilized resources. This critical roadmap is precisely what a robust Business Intelligence Reporting Requirements Template provides, serving as the essential bridge between the vast ocean of data and the specific, insightful reports that drive strategic growth and operational efficiency. It’s a foundational tool that empowers teams to articulate their data needs with precision, ensuring that the BI solutions developed truly serve the organization’s overarching goals.
Why a Robust BI Reporting Requirements Document Matters
Developing effective business intelligence reports is an art and a science, but its foundation lies in clear communication. A well-defined reporting requirements document acts as the single source of truth, aligning business users, data analysts, and BI developers on a common vision. This clarity prevents misunderstandings that often lead to costly redevelopments and delays, ensuring that the final output perfectly matches stakeholder expectations.
The benefits extend far beyond mere alignment. By systematically capturing reporting needs, organizations can streamline the development process, reducing the time from concept to delivery. It fosters a proactive approach to data analysis, allowing teams to anticipate questions and build reports that provide answers before they’re explicitly asked. Ultimately, a strong framework for defining reporting specifications leads to more accurate, relevant, and impactful reports, transforming data from a mere collection of facts into a powerful engine for strategic decision-making and continuous improvement across the enterprise.
The Core Components of an Effective Reporting Requirements Framework
Crafting a comprehensive document for your reporting requirements is key to ensuring your BI initiatives succeed. It’s not just about listing desired charts; it’s about deeply understanding the business context and the decisions each report will support. A holistic approach ensures that every aspect, from data source to delivery mechanism, is considered. This structured approach helps prevent scope creep and ensures the final product is both useful and sustainable.
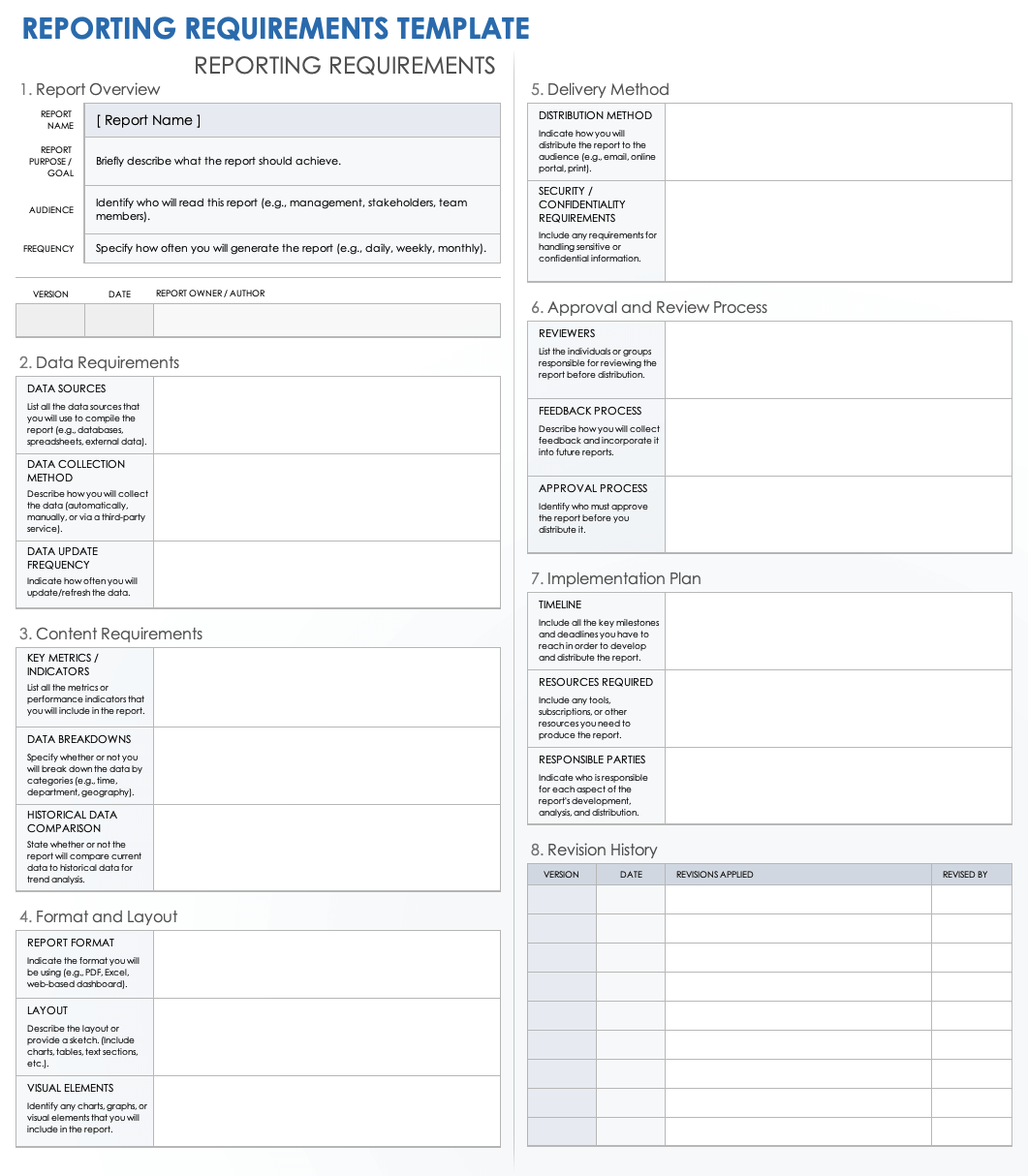
An effective framework for defining business intelligence reports should systematically cover several critical areas. These components ensure that no crucial detail is overlooked, facilitating a smooth development process and maximizing the utility of the resulting dashboards and reports for all stakeholders.
- **Report Identification:** A unique name, brief description of its purpose, and the primary **business owner**.
- **Target Audience & Use Cases:** Who will use this report? What **decisions** will they make based on it? What business questions will it answer?
- **Key Metrics and KPIs:** A clear list of the specific metrics, key performance indicators (KPIs), and dimensions to be included. This specifies **what data points** are essential.
- **Data Sources:** Identification of all necessary data sources (e.g., CRM, ERP, financial systems, external APIs). This helps the BI team understand where to **extract information**.
- **Calculations & Business Logic:** Detailed definitions for how metrics are calculated, including formulas, aggregation rules, and any specific business rules or **transformations**.
- **Visualizations & Layout:** Preferred chart types (bar, line, pie), table formats, dashboard layouts, and any specific branding or **design guidelines**. Mock-ups or wireframes are highly recommended here.
- **Filters, Parameters, and Drill-downs:** Specification of desired interactivity, such as filters for date ranges, geographical regions, product categories, or the ability to **drill into details**.
- **Frequency & Delivery:** How often the report needs to be refreshed (real-time, daily, weekly, monthly) and the preferred delivery method (email, BI portal, embedded in an application).
- **Security & Access:** Who has access to the report, what data they can see, and any necessary **row-level security** considerations.
- **Performance Expectations:** Desired report load times and data refresh rates.
- **Acceptance Criteria:** Clear conditions that must be met for the report to be considered complete and accurate, ensuring **quality assurance**.
Crafting Your Reporting Requirements: A Step-by-Step Approach
Developing a comprehensive set of reporting needs is an iterative process that requires collaboration and attention to detail. It begins long before any data modeling or report development takes place, focusing instead on understanding the fundamental business challenges and opportunities. By following a structured approach, organizations can ensure that their analytical reporting framework yields the most valuable insights. This methodical journey from initial concept to detailed specification minimizes assumptions and maximizes the relevance of the final BI output.
The goal is to build a robust foundation for your BI solutions.
- **Initiate Stakeholder Engagement:** Begin by identifying all key stakeholders who will use or benefit from the reports. Conduct interviews, workshops, and surveys to gather their perspectives. Understand their roles, their current challenges, and the types of questions they regularly ask.
- **Define Business Objectives:** Before diving into specific data points, clearly articulate the overarching business goals that the reports are intended to support. Are you trying to increase sales, reduce operational costs, improve customer satisfaction, or optimize marketing spend? This high-level understanding ensures that all subsequent requirements are strategically aligned.
- **Identify Key Business Questions:** Translate the business objectives into specific, measurable questions that the reports must answer. For example, instead of “increase sales,” ask “Which product lines are underperforming in the Western region this quarter compared to last year?”
- **Inventory Existing Data & Systems:** Assess what data is currently available and where it resides. Understand the quality, accessibility, and lineage of your data. This step helps identify potential gaps or limitations that might impact reporting capabilities and highlights the need for data integration efforts.
- **Prioritize Reporting Needs:** Not all desired reports will have equal importance or feasibility. Work with stakeholders to prioritize requirements based on business impact, urgency, and technical complexity. This ensures that the most critical reports are developed first, delivering immediate value.
- **Document Detailed Specifications:** Using a structured format, document each requirement comprehensively. Include all the core components mentioned previously, such as metrics, calculations, visualization preferences, frequency, and security. Be as specific as possible to avoid ambiguity.
- **Validate and Iterate:** Share the documented requirements with all stakeholders for review and feedback. This iterative process allows for adjustments and clarifications before development begins, ensuring that the detailed reporting specifications accurately reflect user needs. Mock-ups and prototypes can be extremely valuable at this stage.
Best Practices for Successful Reporting Requirements Definition
Success in BI reporting goes beyond simply listing data points; it involves a deep understanding of how those data points drive strategic decisions. To truly leverage the power of a Business Intelligence Reporting Requirements Template, several best practices should be embraced throughout the requirements gathering process. These practices help to mitigate common challenges, ensure the development of relevant and impactful reports, and foster a data-driven culture within the organization. By adopting these approaches, teams can transition from merely reporting data to delivering genuine, actionable insights that move the needle.
- Focus on Business Outcomes, Not Just Data: Always tie a report back to a specific business problem it solves or a decision it enables. Don’t just ask "What data do you want to see?" but "What decision are you trying to make, and what information do you need to make it?"
- Keep it Concise, Yet Comprehensive: Strive for clarity and completeness without unnecessary jargon or excessive detail. The document should be easy to read and understand for both business and technical audiences.
- Utilize Visual Mock-ups Early: Static or interactive mock-ups (wireframes) of desired reports or dashboards can be incredibly powerful. They help stakeholders visualize the final product, clarify expectations, and identify issues far earlier than traditional text-based requirements.
- Involve Data Governance and Data Stewards: Ensure that data quality, definitions, and security standards are considered from the outset. Involving data governance helps establish trust in the reports and ensures compliance.
- Think Scalability and Future Needs: While focusing on immediate needs, consider how reports might evolve. Can the underlying data model support future analyses? Will the current design accommodate growth or changes in business strategy?
- Document Assumptions and Constraints: Clearly state any assumptions made during requirements gathering (e.g., data availability, system integrations) and any known constraints (e.g., budget, technology limitations).
- Establish Clear Acceptance Criteria: Define what constitutes a "successful" report. This includes data accuracy, performance, usability, and adherence to design specifications, providing a clear benchmark for quality assurance.
Leveraging Your Requirements for Greater Business Impact
Once meticulously defined, your reporting needs become a powerful asset, extending their value far beyond the initial development phase. These well-articulated specifications serve as a living document, guiding not only the creation of individual reports but also shaping the broader BI strategy. They foster greater data literacy within the organization, as users understand the purpose and utility of each metric and visualization. This deeper comprehension empowers employees at all levels to interpret data more effectively and apply insights directly to their daily work.
The impact of precise reporting requirements definition resonates throughout the business. It ensures that BI investments are targeted and efficient, leading to solutions that truly address critical organizational needs. By providing a clear framework for analytical reporting, these requirements enable continuous improvement, allowing teams to adapt and evolve their data strategies as business priorities shift. Ultimately, an expertly crafted framework for defining data reporting needs transforms raw information into a strategic differentiator, driving informed decisions, fostering innovation, and securing a competitive edge in a constantly evolving market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a BI reporting requirement and a business requirement?
A business requirement describes *what* the business needs to achieve (e.g., “We need to understand customer churn to improve retention”). A BI reporting requirement details *how* data will be presented to meet that business need (e.g., “A dashboard showing churn rate by customer segment, with drill-down to individual customer data, refreshed daily”). The BI requirement specifies the data, format, and delivery to fulfill the broader business objective.
Who should be involved in defining these requirements?
Key stakeholders typically include business users who will consume the reports, data analysts who understand the data, BI developers who will build the reports, IT representatives for technical infrastructure, and project managers to oversee the process. Involving a diverse group ensures all perspectives are captured and the final solution meets a wide range of needs.
How often should these requirements be reviewed or updated?
Reporting requirements are not static; they should be reviewed periodically, ideally annually or bi-annually, or whenever there are significant changes in business strategy, operations, or data availability. Agile development approaches might even call for more frequent, iterative reviews. Regular updates ensure reports remain relevant and valuable.
Can I use a generic template, or should I customize it?
While a generic Business Intelligence Reporting Requirements Template can provide an excellent starting point and structure, it is crucial to customize it to fit your organization’s specific needs, industry, terminology, and existing BI tools. A tailored template will better reflect your unique business processes and data environment, leading to more precise and effective requirements.
What are common pitfalls to avoid when gathering reporting needs?
Common pitfalls include vague requirements (e.g., “make it useful”), lack of clear business objectives, insufficient stakeholder engagement, not validating data availability or quality upfront, allowing scope creep without proper management, and failing to define clear acceptance criteria. Avoiding these ensures a smoother, more successful BI project.
The diligent work of defining your reporting requirements through a structured framework is far from a mere administrative task; it is a strategic investment. This critical groundwork ensures that every business intelligence report, dashboard, and analytical solution developed is precisely tailored to empower your teams, clarify your market position, and illuminate the path to achieving your strategic objectives. It transforms the abstract concept of "data-driven" into a tangible, operational reality.
By embracing a methodical approach to identifying your data reporting needs, you equip your organization with the clarity and precision required to navigate the complexities of modern business. It’s about building a robust foundation that supports not just current decisions, but future growth and innovation. Don’t underestimate the power of a well-articulated set of reporting requirements to unlock profound insights and truly elevate your business intelligence capabilities. Start defining your needs today to transform your data into your most valuable asset.


