In the complex landscape of modern business, where projects often falter due to miscommunication and undefined expectations, clarity is not just a virtue—it’s a necessity. Every successful initiative, whether it’s a new software implementation, an organizational change, or an operational efficiency drive, hinges on a crystal-clear understanding of "what" needs to be achieved and "why." This foundational clarity is precisely what a robust business process requirements document aims to deliver, serving as the definitive blueprint for transformation.
Navigating the intricacies of stakeholder expectations, technical possibilities, and operational realities can feel like charting a course through uncharted waters. Without a standardized, comprehensive method to capture and articulate these vital details, projects risk scope creep, budget overruns, and ultimately, failure to meet their intended objectives. This is where a Business Process Requirements Document Template becomes an indispensable asset, providing the structure and guidance needed to ensure every critical detail is identified, documented, and agreed upon, paving the way for predictable and positive outcomes.
What Exactly Are Business Process Requirements?
At its heart, a business process requirements document outlines the specific conditions, capabilities, and characteristics that a new or modified business process must possess to satisfy a business need or solve a problem. These are not merely technical specifications; rather, they describe the functionality and behavior from the perspective of the business user and the overall organization. They answer questions like: What must the process do? What data does it need? Who interacts with it, and how?
Unlike technical requirements, which detail how a system will be built, business process requirements focus on the "what." They articulate the desired outcomes, the steps involved, the roles responsible, and the rules governing each activity. Capturing these details thoroughly ensures that any subsequent solution, whether it’s a new software system, a revised workflow, or an updated policy, truly serves the strategic goals of the business and improves operational efficiency. It’s about defining the problem and the desired future state before jumping into solution design.
Why a Structured Approach Matters
Many organizations still rely on ad-hoc methods for defining their process needs, leading to inconsistencies, gaps, and misunderstandings that ripple throughout project lifecycles. Informal notes, scattered emails, and verbal agreements are prone to misinterpretation and are difficult to track. Such an unstructured approach inevitably results in rework, delays, and frustrated teams grappling with shifting expectations.
A structured approach, facilitated by a dedicated process requirements document, transforms this chaos into order. It provides a consistent framework for eliciting, analyzing, documenting, and validating all necessary information. By using a standardized format, teams can ensure that no critical detail is overlooked, that all stakeholders are aligned, and that the final solution precisely addresses the identified business problems. This disciplined methodology fosters a shared understanding and reduces ambiguity, acting as a single source of truth for the entire project team.
Key Benefits of Using a Business Process Requirements Document Template
Adopting a robust requirements document offers numerous strategic and operational advantages. It’s more than just a piece of paper; it’s a strategic tool that drives project success and business transformation.
- Enhanced Clarity and Understanding: A well-defined document eliminates ambiguity, ensuring everyone involved, from stakeholders to developers, has a clear, shared understanding of the process and its objectives. It provides a common language.
- Improved Stakeholder Alignment: By systematically capturing all process needs, the document serves as a central reference point, facilitating consensus among diverse stakeholders and ensuring their expectations are managed and met. This alignment prevents future disagreements.
- Reduced Scope Creep: Detailed process documentation clearly defines the boundaries of the project. This makes it easier to identify and manage changes, preventing the project from expanding beyond its initial scope and budget.
- Higher Quality Solutions: With precise requirements, development and implementation teams can design and build solutions that perfectly match business needs, leading to more effective and user-friendly outcomes.
- Cost and Time Savings: Catching errors and misunderstandings early in the requirements phase is significantly cheaper and faster than correcting them during development or after deployment. This proactive approach saves substantial resources.
- Facilitates Testing and Validation: Clear requirements provide objective criteria against which to test the implemented solution. This makes it easier to verify that the new process or system performs as expected and meets all defined conditions.
- Better Risk Management: By identifying assumptions, constraints, and dependencies upfront, the process documentation helps anticipate potential risks and develop mitigation strategies, ensuring a smoother project execution.
- Supports Future Enhancements: A comprehensive document provides a historical record and a foundation for future improvements or modifications, allowing for easier evolution of business processes over time.
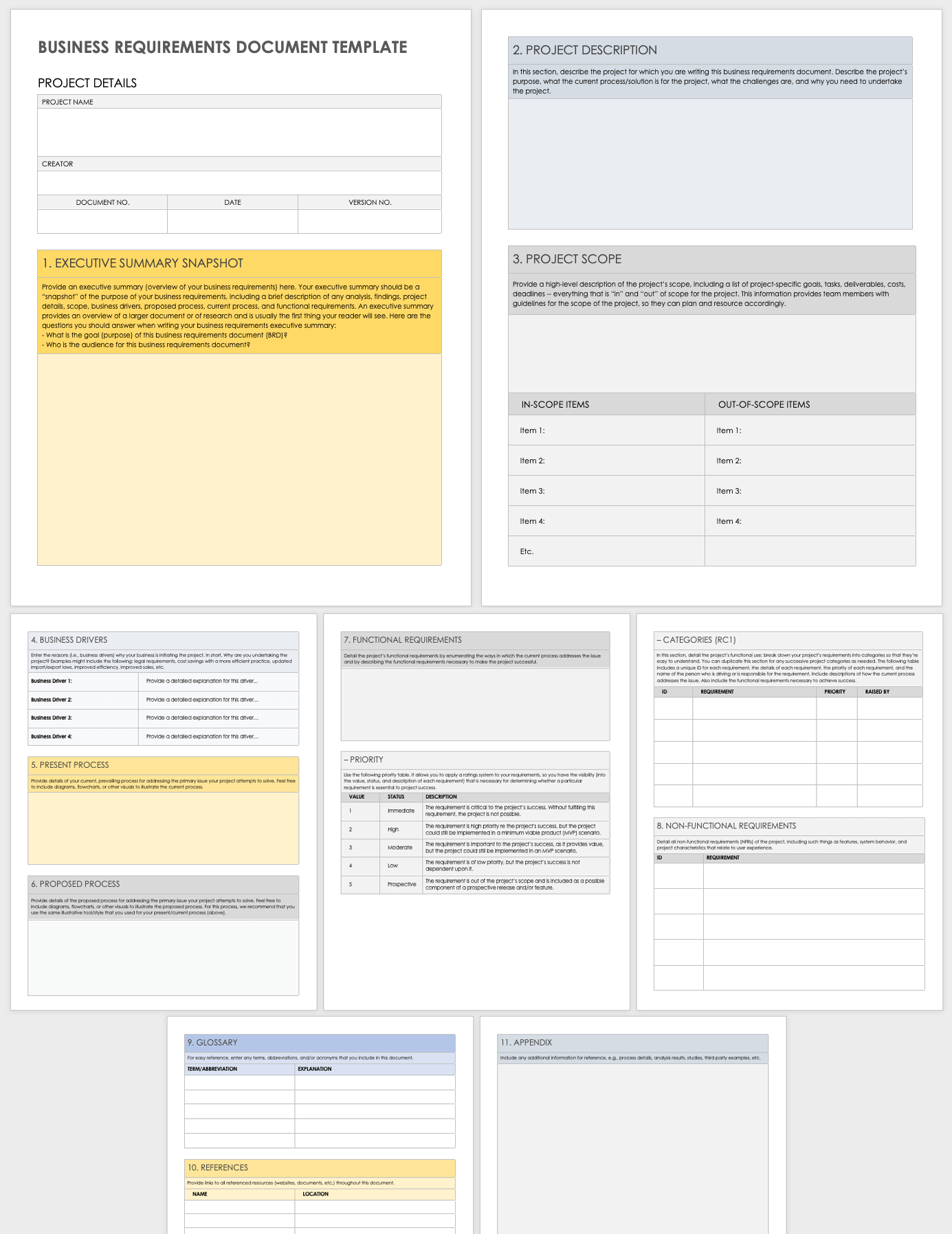
Core Components of an Effective Requirements Document
While every project is unique, a comprehensive process requirements document typically includes several key sections designed to capture all essential information. A well-designed Business Process Requirements Document Template will guide you through these critical areas.
- Executive Summary: A high-level overview of the project, its objectives, and the key business needs it addresses. This provides context quickly.
- Introduction: Details the purpose of the document, its scope (what’s in and what’s out), and who the target audience is.
- Business Context and Goals: Explains the organizational background, the current challenges, and the strategic objectives that the new or improved process aims to support.
- Current State Process Description (Optional but Recommended): Documents the "as-is" process, highlighting its inefficiencies, pain points, and current stakeholders. This provides a baseline for improvement.
- Future State Process Description: This is the heart of the document, detailing the "to-be" process. It includes:
- Process Overview: A high-level description of the new workflow.
- Detailed Process Steps: A step-by-step breakdown of activities, roles, and responsibilities. Visual aids like process flowcharts are incredibly useful here.
- Inputs and Outputs: What information or materials enter the process, and what are the expected results?
- Business Rules: The specific policies, regulations, or conditions that govern decisions and actions within the process.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Metrics to measure the success and effectiveness of the new process.
- Functional Requirements: What the process must do or what functions it must provide to the users. These are often described as user stories or use cases.
- Non-Functional Requirements: Criteria that describe how the process or system performs, such as performance (speed, responsiveness), usability, security, scalability, and reliability.
- Stakeholder Analysis: Identifies all individuals or groups affected by the process, their roles, and their level of involvement.
- Assumptions and Constraints: Explicitly states any assumptions made during requirement gathering and any limitations or restrictions that might impact the process or solution.
- Glossary: Defines key terms and acronyms to ensure consistent understanding across all stakeholders.
- Appendices: May include supporting documents like existing policy documents, diagrams, or external references.
Steps to Crafting Your Business Process Requirements
Leveraging a well-structured process documentation template is only half the battle; knowing how to populate it effectively is crucial. Follow these steps to develop a comprehensive and accurate document:
- Define the Scope and Objectives: Clearly articulate what process is being analyzed or designed and what the overarching business goals are. This sets the boundaries for your requirements gathering.
- Identify and Engage Stakeholders: Determine all individuals or groups who have a vested interest in the process. Actively involve them through interviews, workshops, and brainstorming sessions to elicit their needs and perspectives.
- Gather Requirements: Use a variety of techniques to collect information. This might include analyzing existing documentation, observing current operations, conducting surveys, and facilitating interactive sessions. Focus on understanding the "what" and "why" before "how."
- Analyze and Structure Requirements: Organize the collected information into logical categories. Use the sections of your chosen template as a guide. Prioritize requirements based on business value and feasibility.
- Document the Process Details: Fill out each section of the business process requirements document with clear, concise, and unambiguous language. Incorporate diagrams (like flowcharts or swimlane diagrams) to visually represent complex workflows.
- Review and Validate: Share the draft document with all key stakeholders for their feedback. This iterative process ensures accuracy, completeness, and agreement. Be prepared to clarify, refine, and update based on input.
- Obtain Sign-Off: Once all stakeholders are aligned and approve the content, secure formal sign-off. This formal agreement signifies commitment and reduces the likelihood of scope changes later in the project.
- Manage Changes: Establish a process for managing any subsequent changes to the requirements. Use version control to track modifications and ensure all stakeholders are working from the most current information.
Best Practices for Success
To maximize the effectiveness of your requirements gathering and documentation, consider these best practices:
- Start with the "Why": Always understand the underlying business problem or opportunity before defining the solution.
- Keep it Simple and Clear: Use plain language, avoid jargon, and ensure that your requirements are unambiguous and easy to understand for all audiences.
- Be Specific and Measurable: Vague requirements are useless. Ensure each requirement is precise and includes clear criteria for success, where possible.
- Visualize the Process: Utilize process maps, flowcharts, and other diagrams to illustrate workflows. Visual representations often convey complex information more effectively than text alone.
- Collaborate Continuously: Requirements gathering is not a one-time event. Foster ongoing collaboration with stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
- Prioritize Requirements: Not all requirements are equally important. Work with stakeholders to prioritize them based on business value, urgency, and feasibility.
- Iterate and Refine: Expect to revise your process requirements document multiple times. It’s a living document that evolves as understanding deepens.
- Ensure Traceability: Link requirements to business objectives, test cases, and solution components. This ensures that every part of the solution can be traced back to a specific need.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between business requirements and functional requirements?
Business requirements describe the high-level needs or goals of the organization, focusing on “what” the business needs to achieve to solve a problem or capitalize on an opportunity. Functional requirements, on the other hand, specify the specific features and functions that a system or solution must provide to meet those business requirements, detailing “how” the system will support the business need.
Who should be involved in creating a process requirements document?
Key participants typically include business analysts (who facilitate the process), subject matter experts (who understand the current process and desired future state), process owners, end-users, IT representatives (if a technical solution is involved), and project managers. Active involvement from all relevant stakeholders is critical for accuracy and buy-in.
How often should I update this documentation?
A business process specification should be treated as a living document. It should be updated whenever there are significant changes to the process itself, new business rules are introduced, or the scope of a project shifts. Regular reviews, perhaps annually or bi-annually, are also recommended to ensure it remains accurate and relevant.
Can this template be used for agile projects?
Absolutely. While agile methodologies emphasize flexibility and iterative development, a high-level understanding of process needs is still crucial. An agile team might use a streamlined version of a process requirements document to define the overall epic or initiative, then break down the detailed requirements into user stories and acceptance criteria for individual sprints.
Is a separate Business Process Requirements Document Template always necessary?
For significant projects involving complex processes, organizational change, or technology implementations, a dedicated requirements document is highly recommended. For smaller, less complex changes, its principles might be integrated into a broader project charter or scope document, but the core elements of defining process needs should still be addressed.
In an era defined by rapid change and fierce competition, the ability to clearly define and execute business processes is a critical differentiator. A well-constructed requirements document serves as the bedrock for effective project management, enabling organizations to translate abstract goals into tangible, measurable outcomes. It’s the unifying force that brings diverse teams and ideas together, ensuring everyone is working towards a common, well-understood vision.
Embracing a structured approach to defining your business processes, guided by a comprehensive framework, moves you beyond guesswork and into the realm of strategic clarity. It empowers your teams to build solutions that truly matter, streamline operations, and drive sustainable growth. Invest in the power of precise documentation, and you’ll not only deliver successful projects but also lay a strong foundation for continuous improvement and long-term organizational excellence.


