Embarking on the development of a new web application can feel like navigating uncharted waters. The initial spark of an idea, brimming with potential, often needs a solid roadmap to evolve into a tangible, successful product. Without a clear, universally understood blueprint, projects can quickly veer off course, leading to missed deadlines, budget overruns, and features that don’t quite hit the mark. This is precisely where a well-structured Business Requirement Document (BRD) becomes not just useful, but absolutely indispensable.
A robust Business Requirement Document serves as the cornerstone of any successful web application project. It acts as the critical bridge between stakeholder visions and developer execution, translating high-level business goals into actionable, detailed specifications. By meticulously outlining every aspect of what the web application needs to achieve, who it serves, and how it will function, it ensures that all parties involved are on the same page from concept to launch and beyond.
Why a BRD is Indispensable for Web Application Development
In the fast-paced world of digital product development, clarity is paramount. A comprehensive Business Requirements Document for a web application is the single source of truth that guides the entire project lifecycle. It minimizes assumptions, reduces miscommunications, and provides a framework for decision-making at every stage.
This crucial document sets the stage for accurate scoping, allowing project managers to estimate timelines and resources more effectively. For developers, it provides the detailed instructions needed to build the right features, while quality assurance teams rely on it to define their test cases. Ultimately, it protects the project from scope creep and ensures that the final product genuinely addresses the original business need and delivers value to its users. Without a detailed requirements document for web projects, teams risk building something that looks good but fails to solve the user’s core problem or meet strategic business objectives.
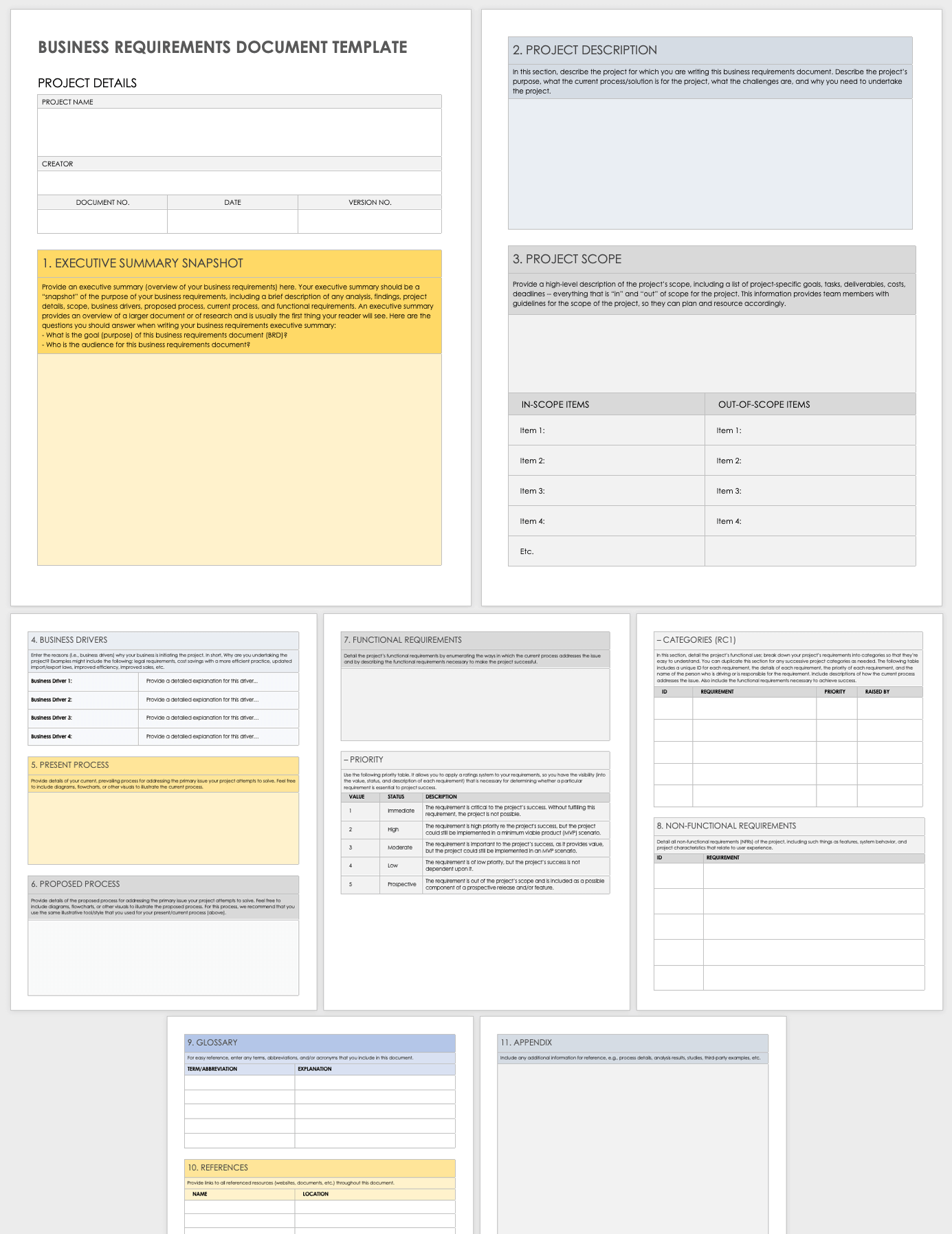
Key Elements of an Effective Web Application BRD
A truly effective web application BRD template is more than just a checklist; it’s a living document that captures the essence of your project. While the specific sections may vary based on project complexity, several core elements are universally critical for defining your digital product requirements outline. These sections ensure a holistic view, from overarching goals to minute operational details.
A robust template will guide you through articulating the "what" and "why" before delving into the "how." It fosters a structured approach, preventing critical details from being overlooked. By breaking down the web app requirement specification into logical segments, it becomes easier to manage and review.
Here are the essential components typically found within a well-structured Business Requirement Document Template For Web Application:
- **Executive Summary:** A high-level overview of the entire document, summarizing the project’s purpose, goals, and key deliverables. This section quickly informs stakeholders of the project’s essence.
- **Project Background and Objectives:** Details the problem the web application aims to solve, the current state, and the clear, measurable goals (SMART objectives) it intends to achieve. It answers the fundamental question of “why are we building this?”
- **Scope (In-Scope & Out-of-Scope):** Clearly defines what functionalities and features are included in the current project phase and, just as importantly, what is explicitly excluded. This is critical for managing expectations and preventing scope creep.
- **Stakeholders:** Identifies all individuals or groups who have an interest in the project’s outcome, including end-users, business owners, technical teams, and external partners. Understanding their roles and needs is vital.
- **User Personas and User Stories:** Describes the typical users of the web application, their goals, motivations, and pain points. User stories then articulate specific features from a user’s perspective (e.g., “As a customer, I want to be able to reset my password so I can regain access to my account”).
- **Functional Requirements:** Specifies *what* the system must do. These are the actions the web application will perform, covering everything from user authentication and data processing to reporting capabilities and search functions.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** Describes *how* the system should perform. This includes aspects like performance (speed, responsiveness), security (data protection, access control), usability (ease of use, accessibility), scalability (handling increased load), and reliability (uptime, error recovery).
- **Data Requirements:** Defines the types of data the web application will collect, store, process, and display, including data models, sources, and data integrity rules.
- **Technical Requirements/System Architecture (High-Level):** While not a full technical specification, this section might outline high-level architectural considerations, technology stack preferences, or integration points with existing systems.
- **Reporting and Analytics Requirements:** Specifies any dashboards, reports, or data analytics capabilities the web application needs to provide to stakeholders for monitoring performance and making informed decisions.
- **Security and Compliance Requirements:** Details security measures, authentication methods, authorization rules, and any regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) the web application must adhere to.
- **Success Metrics and KPIs:** Defines how the success of the web application will be measured post-launch, linking back to the initial project objectives.
- **Assumptions, Constraints, and Dependencies:** Lists any factors assumed to be true, limitations or restrictions on the project, and elements that the project relies on from external sources.
Crafting Your Web Application Requirements Document: Best Practices
Beyond simply filling out sections, the true power of leveraging a web application BRD template lies in how you approach its creation and maintenance. It’s a collaborative effort that requires clarity, precision, and continuous engagement. Adopting best practices ensures your BRD for web development becomes a valuable asset rather than a cumbersome formality.
Firstly, start early and iterate often. The initial draft should begin as soon as the project concept is solid, but don’t expect it to be perfect immediately. Treat it as a living document that will evolve through feedback and discovery. Engaging key stakeholders from the outset is crucial for gathering comprehensive input and achieving buy-in. Facilitate workshops, conduct interviews, and actively listen to ensure all perspectives are captured in this blueprint for web application development.
Secondly, be precise and avoid ambiguity. Every requirement should be clear, concise, and testable. Use active voice and specific terms, avoiding vague language that can lead to misinterpretations. For instance, instead of "The system should be fast," specify "The system shall load the homepage within 3 seconds for 95% of users." This level of detail in your detailed requirements document for online platforms empowers developers and QA teams alike.
Thirdly, prioritize requirements. Not all requirements carry the same weight. Work with stakeholders to categorize features based on their business value, urgency, and feasibility. Techniques like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) can be incredibly useful here. This prioritization helps teams focus on the most critical elements first, especially when resources or timelines are constrained. Regularly review and update the document, especially as the project progresses and new information comes to light.
Leveraging the Template for Project Success
The impact of a well-executed project requirements template for web apps extends far beyond the initial planning phase. It acts as a continuous reference point, fostering alignment and reducing risks throughout the entire development lifecycle. By adopting a structured approach to defining scope for web applications, you create an environment where transparency and accountability thrive.
For development teams, this comprehensive web solution guide translates abstract ideas into concrete tasks, streamlining the coding process and minimizing rework. Quality assurance teams use it to design robust test plans, ensuring every feature meets the specified criteria. Furthermore, it serves as an invaluable tool for managing changes. When new requirements emerge or existing ones need modification, the BRD provides a baseline against which proposed changes can be evaluated for their impact on scope, budget, and timeline. This structured approach to web app design becomes a protective shield against costly deviations.
Ultimately, a strong application requirements template empowers you to deliver web applications that are not only technically sound but also strategically aligned with business objectives. It helps in creating clear web application specifications that ensure the final product truly meets user needs and delivers measurable value. This dedication to detailed planning with a framework for web project requirements is what differentiates successful projects from those that struggle to find their footing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between a BRD and an SRS (Software Requirements Specification)?
A BRD (Business Requirement Document) focuses on the “what” and “why” from a business perspective, outlining the problem, business goals, and the high-level needs of stakeholders and users. An SRS (Software Requirements Specification) delves into the “how,” providing detailed technical specifications for the software, including functional and non-functional requirements, data models, and architectural considerations from a technical viewpoint. The BRD typically precedes and informs the SRS.
Who is responsible for creating a Business Requirements Document for a web application?
While a Business Analyst (BA) often takes the lead in facilitating, writing, and managing the BRD, its creation is a collaborative effort. It requires significant input from business stakeholders, product owners, subject matter experts, and sometimes even technical leads, to ensure all aspects of the project are accurately captured and agreed upon.
How often should a web application BRD be updated?
A BRD should be considered a living document and updated whenever there are changes to the project scope, requirements, or business objectives. This could be during new discovery phases, following stakeholder feedback, or when market conditions shift. Regular reviews and updates ensure that it remains an accurate and relevant guide for the development team.
Can a BRD be used for agile development methodologies?
Absolutely. While agile methodologies emphasize flexibility and iterative development, a BRD still plays a crucial role. It can serve as a high-level vision document that sets the initial product backlog and defines epics. Instead of a rigid, all-encompassing document, it becomes a guide for creating user stories and features for individual sprints, evolving as the project progresses. It provides the initial comprehensive web solution guide necessary for kickstarting agile cycles.
What are the risks of not having a detailed Business Requirement Document for a web application?
Skipping or inadequately defining a BRD can lead to numerous risks, including misaligned expectations between stakeholders and developers, frequent scope changes (scope creep), significant rework, budget overruns, and delayed project delivery. Ultimately, it increases the likelihood of delivering a web application that does not meet business objectives or user needs, resulting in wasted resources and lost opportunities.
Building a web application is a significant investment of time, resources, and vision. To ensure that this investment yields the desired returns, a systematic and thorough approach to defining requirements is non-negotiable. The proper utilization of a robust Business Requirement Document Template For Web Application transforms a mere concept into a clear, executable plan, minimizing ambiguities and maximizing the chances of project success.
Embrace the power of clear communication and structured planning from the outset. By diligently outlining every detail, from the overarching business goals to the nuanced functional requirements, you lay a solid foundation for your web application. This commitment to precision not only streamlines development but also secures stakeholder alignment, fosters innovation, and ultimately delivers a product that truly resonates with its users and achieves its strategic objectives.


