In the intricate world of project management and software development, clarity is not just a virtue—it’s a necessity. Too often, projects embark on a journey fraught with misunderstandings, miscommunications, and missed expectations, ultimately leading to budget overruns, delayed timelines, and solutions that fail to meet their intended purpose. The root cause frequently lies in inadequately defined business requirements—the foundational blueprints that dictate what a project must achieve to deliver value. Without a robust and comprehensive understanding of these needs, even the most talented teams can find themselves building the wrong thing, beautifully.
This is where a structured approach becomes invaluable, transforming ambiguity into actionable insights. Imagine having a systematic way to ensure every critical detail, every stakeholder’s need, and every essential function is considered and documented before development even begins. This article explores the profound impact of adopting such a framework, specifically focusing on how a well-crafted Business Requirements Checklist Template can serve as your navigational star, guiding projects from conception to successful delivery, fostering alignment, and significantly mitigating risks. It’s not just about ticking boxes; it’s about building a shared vision and setting the stage for unwavering project success.
Why Clear Business Requirements Are Non-Negotiable
The journey from a nascent idea to a fully realized product or service is paved with countless decisions. Each decision, if not grounded in clear objectives, can send a project veering off course. Poorly defined requirements are a leading cause of project failure, creating a ripple effect that impacts everything from technical design to user adoption. When stakeholders lack a unified understanding of what needs to be built, developers interpret needs differently, and testers struggle to validate outcomes, the entire project ecosystem suffers.
Robust business requirements act as the Rosetta Stone for your project team, translating high-level business goals into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. They serve as a single source of truth, establishing a baseline against which all future work, changes, and progress are measured. Investing time upfront in defining these requirements meticulously is not an overhead; it’s a strategic investment that pays dividends in reduced rework, enhanced collaboration, and ultimately, a solution that truly solves the business problem it was designed for.
The Unseen Value of a Structured Requirements Document
While the importance of requirements is widely acknowledged, their effective documentation often falls short. Ad-hoc notes, scattered emails, or verbal agreements simply aren’t enough to sustain a complex project. A structured requirements document, often guided by a comprehensive framework, ensures that all critical aspects are covered systematically. This structured approach fosters consistency across projects and teams, making it easier to onboard new members, conduct reviews, and maintain historical records.
Such a framework compels project teams to think through every angle, anticipating potential challenges and gaps before they become costly issues. It provides a formal basis for stakeholder agreement, ensuring that everyone from end-users to executive sponsors has signed off on the proposed solution. This shared understanding minimizes scope creep and provides a clear definition of project completion. The discipline imposed by a structured requirements document elevates the quality of the project definition, leading to more predictable outcomes and greater confidence in delivery.
Key Elements of an Effective Requirements Checklist
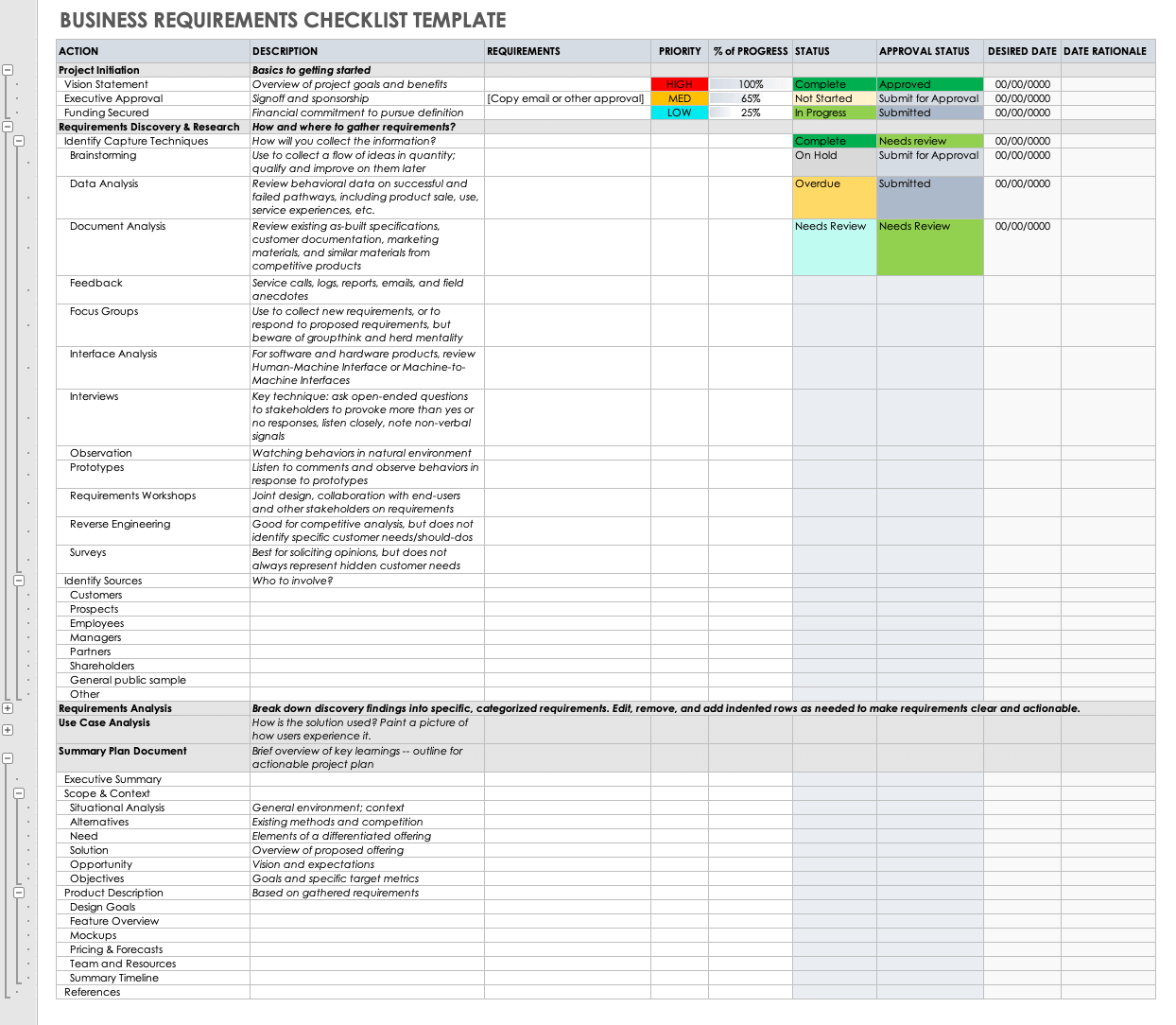
A comprehensive requirements checklist is far more than a simple to-do list; it’s a strategic tool designed to prompt thorough consideration of every dimension of a project. It ensures that no critical stone is left unturned during the requirements gathering phase. Here are some indispensable sections and items typically found within such a framework, guiding the development of robust project specifications:
- **Project Vision and Scope Definition:** Clearly articulating the project’s purpose, its overarching goals, and the boundaries of what will (and will not) be included.
- **Stakeholder Identification and Analysis:** Listing all individuals or groups impacted by the project, understanding their roles, interests, and influence. This ensures all voices are heard.
- **Business Objectives and Goals:** Defining the specific, measurable outcomes the project aims to achieve, directly linking to organizational strategy.
- **Current State Analysis:** Documenting existing processes, systems, and challenges that the new solution intends to address.
- **Future State Vision:** Describing the desired future state, outlining how the new solution will operate and the benefits it will deliver.
- **Functional Requirements:** Detailing what the system *must do*, including specific features, user interactions, and system behaviors. These are typically captured as **user stories** or use cases.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** Specifying the quality attributes of the system, such as its **performance**, security, usability, scalability, and maintainability.
- **Data Requirements:** Identifying all data elements involved, their sources, relationships, formats, and any specific **data migration** needs.
- **Integration Requirements:** Outlining how the new system will interact with existing systems, including APIs, data exchange protocols, and interface specifications.
- **User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) Requirements:** Describing the visual design, layout, navigation, and overall user interaction paradigm.
- **Regulatory and Compliance Requirements:** Identifying any legal, industry, or internal standards that the solution must adhere to.
- **Assumptions and Constraints:** Documenting conditions believed to be true (assumptions) and limitations (constraints) that could impact the project.
- **Dependencies:** Listing internal or external factors that the project relies on, such as other projects, third-party vendors, or specific technologies.
- **Success Metrics and Acceptance Criteria:** Defining how the project’s success will be measured and the specific conditions that must be met for the solution to be accepted by stakeholders.
- **Glossary of Terms:** Providing clear definitions for technical jargon or project-specific terminology to ensure a common language.
Practical Application: Leveraging Your Requirements Template
A **Business Requirements Checklist Template** isn’t just a static document; it’s a dynamic tool that evolves with your project. Its true value is realized through active application across various project phases. Initially, it serves as a guide for systematic elicitation, ensuring business analysts and project managers ask the right questions and gather comprehensive input from all stakeholders. During this phase, it helps identify conflicting requirements and areas needing further clarification.
Once initial requirements are documented, the template aids in structuring review sessions, allowing stakeholders to easily validate completeness and accuracy. Throughout development, it acts as a reference point for designers and developers, clarifying ambiguities and ensuring features are built according to specification. For quality assurance teams, it provides a basis for creating test cases and validating that the delivered solution meets all defined criteria. Furthermore, in an agile context, the template can be adapted to structure epics and user stories, providing a holistic view while allowing for iterative delivery.
Customizing Your Approach for Different Projects
While a standard requirements template offers a solid foundation, recognizing that one size doesn’t fit all is crucial. The level of detail and formality required for project requirements can vary significantly based on the project’s size, complexity, industry, and the chosen development methodology. A small internal tool might only need a concise set of functional requirements and acceptance criteria, whereas a large-scale, mission-critical system will demand exhaustive documentation across all categories.
For agile projects, the structure of a requirements template can be adapted to support user stories, epics, and features, with the checklist serving as a guide to ensure all necessary information is captured within these agile artifacts. Waterfall or traditional projects, conversely, might necessitate more extensive, detailed specifications upfront. The key is to use the template as a flexible framework, selecting relevant sections, adjusting the granularity of detail, and incorporating project-specific nuances to create a requirements document that is both comprehensive and appropriate for your context.
Best Practices for Requirements Gathering and Management
Effective requirements management goes beyond simply filling out a form; it encompasses a continuous cycle of elicitation, analysis, documentation, validation, and change management. To truly harness the power of a comprehensive requirements document, consider these best practices:
**Engage Stakeholders Early and Often:** Foster continuous communication with all project stakeholders. Early engagement ensures buy-in and reduces the likelihood of late-stage requirement changes. Conduct workshops, interviews, and user observation to gather diverse perspectives.
**Prioritize Requirements:** Not all requirements are equally important. Work with stakeholders to prioritize them based on business value, technical feasibility, and dependencies. Techniques like MoSCoW (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won’t have) can be effective.
**Use Visual Aids:** Supplement textual requirements with diagrams, mock-ups, flowcharts, and wireframes. Visual representations can often convey complex information more effectively than text alone, enhancing clarity and reducing misinterpretation.
**Ensure Traceability:** Establish clear links between business objectives, high-level requirements, functional specifications, design elements, and test cases. A traceability matrix helps ensure that every requirement is addressed and tested, providing a clear audit trail.
**Manage Changes Systematically:** Requirements are rarely static. Implement a robust change management process to evaluate, approve, and track any modifications. Communicate changes clearly to all affected parties to maintain alignment.
**Validate and Verify:** Regularly review requirements with stakeholders to ensure they are accurate, complete, unambiguous, and feasible. Verification ensures the requirements are well-formed; validation confirms they meet the actual business need.
**Maintain a Living Document:** A requirements document should be treated as a living artifact, updated as the project progresses and requirements evolve. Ensure version control is in place to track changes over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a business requirements checklist only for large projects?
Absolutely not. While highly beneficial for complex endeavors, a requirements checklist provides value for projects of all sizes. For smaller projects, it helps ensure that even fundamental aspects aren’t overlooked. The template can be scaled down or customized to fit the scope and complexity, still offering a structured approach to prevent miscommunication and rework.
How often should requirements be reviewed?
The frequency of requirements review depends heavily on the project methodology and stability of the requirements. In agile environments, requirements (often in the form of user stories) are reviewed and refined continuously, typically at the beginning of each sprint. For traditional projects, formal reviews might occur at key milestones, but informal check-ins should be frequent to address any emerging issues or clarifications.
What’s the difference between business and functional requirements?
Business requirements describe the high-level goals and objectives the business aims to achieve, focusing on *why* the project is being undertaken and the value it will deliver. Functional requirements, on the other hand, specify *what* the system must do to meet those business needs, detailing specific features, functions, and behaviors of the solution from the user’s perspective. Business requirements drive functional requirements.
Can I use an agile methodology with a requirements template?
Yes, indeed. While agile emphasizes iterative development and adapting to change, a requirements template can still be incredibly useful. It can guide the definition of epics and features, ensuring that the overarching business goals and non-functional requirements are thoroughly considered. The checklist can help ensure completeness at the epic level, while user stories further detail functional aspects in an iterative manner.
Who is responsible for completing the requirements checklist?
Typically, a Business Analyst (BA) or Project Manager (PM) leads the effort to complete the requirements checklist. However, it’s a collaborative process that involves significant input from various stakeholders, including business owners, subject matter experts, end-users, and technical leads. The BA/PM facilitates the gathering, documentation, and validation of these requirements, acting as the bridge between business needs and technical solutions.
Embracing a systematic approach to defining project needs is no longer a luxury but a fundamental necessity for project success in today’s dynamic business environment. A well-utilized Business Requirements Checklist Template empowers teams to navigate complexity with confidence, transforming vague ideas into tangible, well-understood objectives. It ensures that every stakeholder is aligned, every technical consideration is addressed, and every deliverable contributes directly to the project’s intended value.
By integrating such a powerful tool into your project lifecycle, you’re not just documenting requirements; you’re building a shared vision, fostering collaboration, and significantly de-risking your investments. The commitment to clear, comprehensive requirements upfront pays dividends throughout the entire project, leading to solutions that truly meet needs, delight users, and drive meaningful business outcomes. Make the commitment today to elevate your project definition, and watch your success rates soar.


