In the complex landscape of modern project management, the journey from a nascent idea to a fully realized solution is often fraught with miscommunication, scope creep, and unexpected hurdles. Far too many projects falter not because of technical limitations or resource scarcity, but due to a fundamental misunderstanding of what truly needs to be built. This chasm between initial vision and final product can lead to costly rework, delayed launches, and ultimately, a solution that fails to meet its intended purpose.
Bridging this gap requires a disciplined approach, a clear methodology, and a shared understanding among all stakeholders. This is precisely where a robust framework for capturing business needs becomes indispensable. It serves as the bedrock upon which successful projects are built, ensuring that every participant, from the executive sponsor to the development team, speaks the same language and works towards a common, well-defined objective.
Why Effective Requirements Gathering Matters
The success of any project hinges significantly on the clarity and completeness of its initial requirements. Without a comprehensive understanding of what a business needs to achieve, and how a new system or process will support those objectives, projects are prone to veering off course. Poorly defined requirements are a leading cause of project failure, contributing to budget overruns, missed deadlines, and solutions that don’t quite hit the mark.
Imagine building a house without a blueprint, or embarking on a journey without a map. The outcomes would be unpredictable, costly, and likely frustrating. In the same vein, launching a project without thoroughly documented expectations is an invitation to chaos. Effective requirements elicitation minimizes risks, reduces the need for expensive changes late in the development cycle, and ensures that the final product delivers tangible value. It lays the groundwork for accurate estimations, realistic timelines, and a development process that is both efficient and aligned with strategic goals.
The Power of a Structured Approach
While the act of understanding and documenting business needs might seem intuitive, doing it effectively requires more than just informal conversations. A structured approach, often facilitated by a comprehensive requirements gathering template, transforms an abstract idea into a tangible, actionable plan. It provides a consistent framework for capturing information, ensuring no critical detail is overlooked and that all perspectives are considered.
This systematic methodology brings clarity, consistency, and traceability to the entire project lifecycle. It acts as a single source of truth, establishing a common reference point for everyone involved. By formalizing the documentation process, it streamlines communication, eliminates ambiguity, and fosters a shared understanding of project scope and objectives. This structured document becomes the blueprint for solution design, development, testing, and deployment, guiding every step and decision along the way.
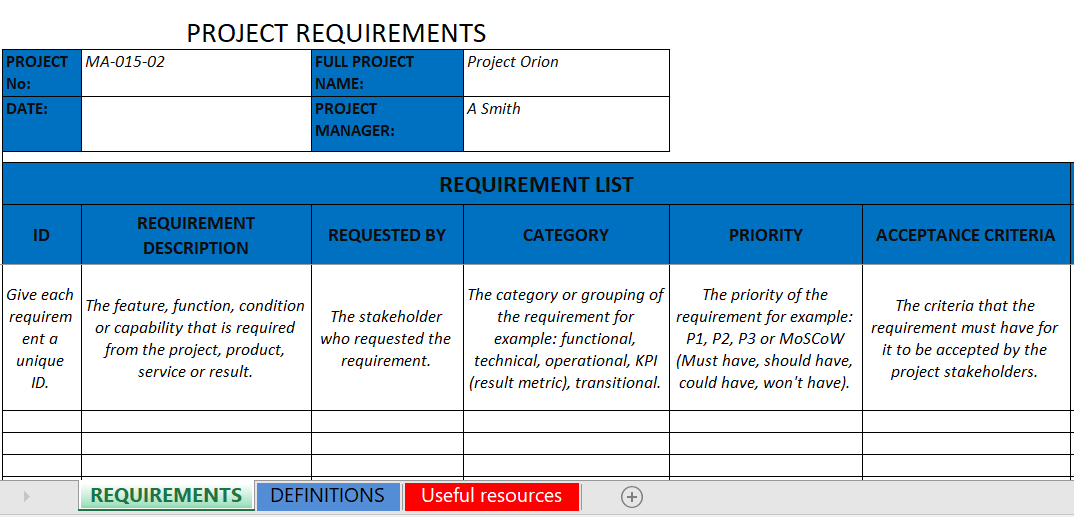
Key Elements of a Robust Requirements Template
A truly effective business requirements gathering template is more than just a blank document; it’s a comprehensive guide designed to prompt critical thinking and ensure thorough coverage of all essential project facets. While the specific sections may vary based on project complexity and industry, core components universally contribute to a powerful requirements specification document.
Here are the vital sections you should expect in a well-designed template:
- Project Overview and Vision: Clearly define the project’s purpose, its overarching goals, and how it aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives. This section sets the stage and provides context for all subsequent details.
- Scope Definition: Precisely delineate what is and is not included within the project’s boundaries. A clear scope statement prevents scope creep and manages expectations effectively.
- Stakeholder Analysis: Identify all individuals or groups who will be affected by the project or whose input is critical. Understanding their roles, responsibilities, and influence is crucial for successful engagement.
- Business Requirements: Describe the high-level needs of the organization that the project aims to address. These are typically statements about “what the business needs to achieve” to solve a problem or capitalize on an opportunity.
- Functional Requirements: Detail the specific behaviors, functions, or features that the system or solution must perform. These describe “what the system will do” from a user’s perspective, often broken down into user stories or use cases.
- Non-Functional Requirements: Specify the quality attributes or constraints on the system’s operation. This includes aspects like **performance** (speed, response time), **security** (access control, data protection), **usability** (ease of use, intuitability), **scalability**, **reliability**, and **maintainability**.
- Data Requirements: Outline the data elements that need to be captured, stored, processed, and reported. This covers data sources, formats, retention policies, and data migration needs.
- Assumptions and Constraints: Document any factors believed to be true for planning purposes (assumptions) and any limitations or restrictions that could impact the project (constraints), such as budget, technology, or regulatory requirements.
- Success Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define how the project’s success will be measured. Establishing clear KPIs ensures that the delivered solution can be objectively evaluated against its intended impact.
- Approval and Sign-off: A critical section where key stakeholders formally acknowledge and approve the documented requirements. This signifies a shared understanding and commitment, reducing disputes later on.
Implementing Your Requirements Document
The creation of a comprehensive requirements document is an iterative process, not a one-time event. It begins with active engagement with stakeholders, employing various elicitation techniques such as interviews, workshops, surveys, and observation. The goal is to gather a holistic view of needs and expectations from all angles.
Once initial information is gathered, it’s meticulously documented within the structured framework. This draft then undergoes a rigorous review process, where stakeholders validate the accuracy and completeness of the captured information. Feedback is incorporated, discrepancies are resolved, and the document evolves until it accurately reflects the agreed-upon vision. It’s crucial to remember that this project requirements template is a living document, subject to review and updates as the project progresses and understanding matures. Establishing a robust change management process ensures that any modifications are properly evaluated, approved, and communicated.
Tips for Successful Requirements Elicitation
Beyond simply filling out sections of a template, the art of successful requirements gathering lies in effective communication and strategic execution. Here are some actionable tips to maximize your efforts:
- Engage Stakeholders Early and Often: Don’t wait until the requirements are "final" to involve key players. Continuous engagement fosters buy-in and ensures diverse perspectives are captured.
- Utilize Diverse Elicitation Techniques: Relying solely on interviews might miss crucial details. Incorporate brainstorming sessions, prototyping, use case analysis, and even ethnographic observation to uncover unspoken needs.
- Prioritize Requirements Collaboratively: Not all requirements hold equal weight. Work with stakeholders to prioritize them based on business value, urgency, and feasibility. Techniques like MoSCoW (Must, Should, Could, Won’t have) can be incredibly helpful.
- Validate and Verify: Regularly check your understanding of requirements with stakeholders. Ask clarifying questions, create mock-ups, and review documented needs to ensure they are accurate, unambiguous, and testable.
- Focus on the "Why" Before the "What": Understand the underlying business problem or opportunity a requirement addresses. This deeper insight helps in designing more effective solutions, rather than just implementing surface-level requests.
- Manage Expectations: Be transparent about what can and cannot be achieved within project constraints. Clearly communicate assumptions and potential limitations early on.
- Keep it Concise and Clear: Avoid jargon, unnecessary technical details, and overly complex language. Requirements should be easy for all stakeholders to understand, regardless of their technical background.
- Embrace Iteration: Requirements evolve. Be prepared to revisit, refine, and update your documentation as new information emerges or as business needs shift. Implement a formal change control process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main purpose of a requirements document?
The main purpose of a requirements document is to provide a single, comprehensive, and clear source of truth about what a project or solution needs to achieve. It defines the scope, functionalities, and quality attributes required, ensuring alignment among all stakeholders and guiding the development process.
Who is typically responsible for creating and maintaining the requirements template?
Typically, a Business Analyst (BA) or Project Manager (PM) is responsible for creating and maintaining the requirements template. However, it’s a collaborative effort, with significant input and validation from product owners, subject matter experts, and other key business stakeholders.
How often should project requirements be reviewed and updated?
Project requirements should be reviewed and updated regularly throughout the project lifecycle, especially during key project phases or when significant changes to business needs or external factors occur. For agile projects, this might happen at the start of each sprint or iteration. A formal change management process should dictate how and when updates are made.
Can a requirements specification document be used in Agile environments?
Absolutely. While Agile often favors user stories and backlogs, a higher-level requirements specification document can still serve as a foundational “vision” document. It provides essential context and an overarching framework that individual user stories and sprint planning can refer back to, ensuring alignment with strategic business goals.
What’s the difference between business requirements and functional requirements?
Business requirements describe the high-level goals and objectives a business wants to achieve (e.g., “The company needs to reduce customer churn by 15%”). Functional requirements, on the other hand, detail specific features or functions a system or solution must possess to meet those business needs (e.g., “The system must allow users to track customer support interactions over the last 12 months”). Business requirements define “why,” while functional requirements define “what” the solution will do.
The path to successful project delivery is paved with clarity, collaboration, and a meticulous understanding of needs. A well-crafted requirements elicitation framework is not merely a bureaucratic hurdle; it is a strategic asset that empowers teams, minimizes risk, and ensures that the end product truly serves its intended purpose. It transforms vague ideas into concrete plans, providing a shared vision that drives efficiency and innovation.
By investing time and effort into defining robust business expectations, organizations can significantly improve their project success rates, deliver solutions that exceed expectations, and realize tangible returns on their investments. Embrace the power of a structured approach to requirements, and lay a solid foundation for your next great project endeavor. The clarity it brings will be your most valuable tool.