In the intricate world of project management and software development, clarity is not just a virtue; it’s a necessity. Projects, whether large or small, often flounder not from a lack of talent or effort, but from a fundamental misunderstanding of what needs to be built or achieved. This is precisely where a robust framework for defining project parameters becomes invaluable, serving as the bedrock upon which successful initiatives are constructed. Without a shared, unambiguous vision, teams can diverge, leading to costly rework, missed deadlines, and ultimately, project failure.
Enter the Business Requirements Specification Template – a vital tool designed to capture and formalize the core needs and expectations of a project. This isn’t just a bureaucratic hurdle; it’s a strategic asset that transforms vague ideas into actionable plans. It acts as a definitive guide, ensuring all stakeholders—from business leaders to technical developers—are aligned on objectives, scope, and deliverables. By articulating precisely what a system or solution must do to satisfy business objectives, it empowers teams to build the right thing, the first time.
Why a Robust Business Requirements Document is Indispensable
Every successful project begins with a clear understanding of its purpose and the problems it aims to solve. A comprehensive requirements specification is the primary mechanism for achieving this clarity. It acts as a single source of truth, minimizing assumptions and mitigating the risks associated with miscommunication. This foundational document ensures that development efforts are strategically aligned with business goals, preventing the wasteful expenditure of resources on features that don’t deliver real value.
Beyond mere clarity, a well-defined requirements document provides a framework for effective project governance. It facilitates accurate effort estimation, helps in defining test cases, and offers a benchmark against which project success can be measured. For project managers, it’s a compass; for developers, a blueprint; and for stakeholders, a contract outlining what they can expect. Investing time upfront in developing a thorough business requirements specification pays dividends throughout the project lifecycle, from initial planning through deployment and beyond.
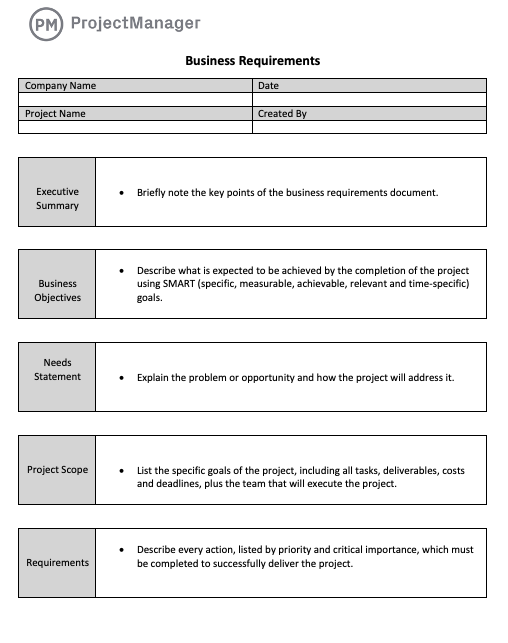
Key Components of an Effective Requirements Specification
A well-structured requirements document ensures that no critical detail is overlooked, providing a comprehensive view of the project’s scope and objectives. While specific sections may vary based on project complexity and industry, a strong Business Requirements Specification Template typically includes these core elements:
- Executive Summary: A high-level overview of the project, its goals, and the problems it addresses.
- Project Scope: Clearly defines the boundaries of the project, outlining what is included and, crucially, what is out of scope.
- Stakeholder Identification: Lists all individuals or groups who will be affected by the project, detailing their roles and responsibilities.
- Business Objectives: Articulates the specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals the project aims to achieve.
- Functional Requirements: Describes what the system or solution *must do*, often broken down into features, user stories, or use cases.
- Non-Functional Requirements: Specifies the quality attributes of the system, such as performance, security, usability, reliability, and scalability.
- Data Requirements: Details the data inputs, outputs, storage, and transformations required by the system.
- Reporting Requirements: Outlines any reports, dashboards, or data visualizations that the system needs to generate.
- Assumptions and Constraints: Documents any factors assumed to be true for the project to proceed, along with limitations or restrictions.
- Dependencies: Identifies external systems, projects, or resources that the project relies upon.
- Glossary: Defines key terms and acronyms used throughout the document to ensure a common understanding.
Crafting Your Requirements: A Step-by-Step Guide
Developing a comprehensive project requirements document is an iterative process that requires careful planning and collaboration. Adopting a structured approach ensures that all necessary information is captured and validated before development begins.
- Initiate and Discover: Begin by clearly defining the project’s vision and high-level goals. Conduct preliminary meetings with key stakeholders to understand the business problem, desired outcomes, and initial expectations. This phase sets the stage for more detailed requirements gathering.
- Engage Stakeholders: This is perhaps the most critical step. Facilitate workshops, interviews, and brainstorming sessions with all relevant stakeholders, including end-users, subject matter experts, and management. Tools like user stories, use cases, and process flow diagrams can help elicit detailed needs. Encourage open communication to uncover both stated and unstated requirements.
- Document and Detail: Translate the gathered information into clear, concise, and unambiguous statements. Populate each section of your requirements specification, ensuring that every requirement is traceable to a business objective. Avoid jargon where possible, or clearly define it in your glossary. Focus on what needs to be achieved, rather than how it will be implemented.
- Validate and Review: Once the draft is complete, present it to stakeholders for review and feedback. This is a crucial validation step to ensure that the documented requirements accurately reflect their needs and expectations. Obtain formal sign-off from all key stakeholders, signifying their agreement and commitment.
- Iterate and Refine: The requirements definition process isn’t a one-time event. As the project progresses, new information may emerge, or business priorities might shift. Be prepared to update and refine your requirements document, managing changes through a formal change control process. This ensures the specification remains a living, relevant guide throughout the project lifecycle.
Best Practices for Utilizing Your Specification
Simply creating a detailed specification is only half the battle; effectively using it throughout the project is what truly drives success. Treat your requirements specification not as a static artifact, but as a dynamic and central reference point for all project activities.
Firstly, ensure that all project team members, from developers to quality assurance engineers, have easy access to the document and understand its contents. Regular review sessions can help reinforce this understanding. Secondly, maintain strict version control to track all changes, ensuring everyone is working from the most current set of detailed requirements. Any modifications should be formally approved and communicated to avoid confusion.
Furthermore, integrate your requirements into other project activities. Link individual requirements to design specifications, test cases, and user acceptance criteria. This traceability ensures that every aspect of the solution is built to meet an identified business need and can be thoroughly validated. Prioritize requirements based on business value and urgency, guiding development efforts and facilitating informed decisions when trade-offs are necessary.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Requirements Definition
Even with the best intentions, the process of documenting business needs can be fraught with challenges. Recognizing and actively avoiding common pitfalls is essential for a successful outcome. One significant issue is vague or ambiguous language, which leads to misinterpretations and solutions that don’t meet expectations. Requirements should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
Another frequent problem is scope creep, where new requirements are added throughout the project without formal approval or adjustment to timelines and budgets. Establishing a robust change management process is crucial to control scope. Equally problematic is a lack of stakeholder involvement, leading to an incomplete or inaccurate understanding of the actual business needs. Proactive and continuous engagement with all relevant parties is non-negotiable.
Finally, resist the urge to jump directly into technical solutions without fully understanding the underlying business problem. A comprehensive project requirements document focuses on what needs to be achieved, allowing the how to be determined by the technical team. By focusing on clear communication, thorough engagement, and structured documentation, many of these challenges can be effectively navigated.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a business requirements document?
The primary purpose is to define what a new system or solution must do to satisfy specific business needs and objectives. It serves as a blueprint for development, ensuring all stakeholders have a shared understanding of the project’s scope and goals.
Who typically prepares a requirements specification?
Often, a Business Analyst (BA) or Project Manager (PM) is responsible for gathering, documenting, and managing requirements. However, it requires extensive collaboration with stakeholders, subject matter experts, and technical teams to ensure accuracy and completeness.
How does a BRS differ from a Functional Requirements Specification (FRS)?
A BRS (Business Requirements Specification) focuses on the *why* and *what* from a business perspective, outlining high-level business goals and the needs the system must address. An FRS (Functional Requirements Specification) delves into the *how*, detailing specific functions and features the system will perform to meet those business requirements, often with more technical precision.
Can a single template work for all project types?
While a core Business Requirements Specification Template provides a solid foundation, it should be flexible enough to be tailored. Different projects (e.g., software development, process improvement, infrastructure upgrades) may require specific sections or a different level of detail. The key is customization to fit the project’s unique context and complexity.
What are the benefits of using a standardized requirements template?
A standardized template ensures consistency across projects, reduces the effort required to start documenting, minimizes the risk of overlooking critical areas, and promotes a common language and structure for requirements definition within an organization. It streamlines communication and improves overall project efficiency.
Establishing a comprehensive requirements specification is not merely a bureaucratic task; it’s a strategic investment in project success. It serves as the definitive point of reference, guiding every decision from design and development through testing and deployment. By dedicating the necessary time and resources to clearly articulate your business needs, you lay a solid foundation for delivering solutions that genuinely meet expectations and provide tangible value.
Embracing a structured approach to defining project needs empowers teams to avoid costly missteps, fosters stronger collaboration, and ultimately enhances the likelihood of achieving project objectives. A meticulously crafted requirements document isn’t just a guide; it’s a commitment to excellence, ensuring that every effort contributes to a shared, successful outcome. Make it a cornerstone of your project methodology.


