In the complex landscape of modern business and technology, the journey from an initial idea to a successful product or service is fraught with potential missteps. One of the most common pitfalls, and arguably the most damaging, is a misunderstanding or miscommunication of what a project is actually supposed to achieve. This is where the meticulous process of defining business requirements becomes not just important, but absolutely critical.
Imagine building a house without a blueprint, or baking a cake without a recipe; the outcome would likely be chaotic, expensive, and far from the original vision. Similarly, embarking on a project without a clear, documented understanding of its goals, functionalities, and constraints is a recipe for disaster. A well-structured approach to documenting these needs ensures everyone—stakeholders, developers, project managers, and end-users—is on the same page, aligning expectations and paving the way for predictable, successful delivery.
Why Effective Requirement Gathering Matters
The foundation of any successful project lies in a clear, unambiguous understanding of its objectives. Without this clarity, projects often suffer from scope creep, budget overruns, and missed deadlines. Misinterpretations of needs can lead to features that no one wants, or, worse, to a product that fails to solve the core problem it was designed to address. This wastage of resources, time, and effort is entirely avoidable with a disciplined approach to defining what is truly needed.
Effective requirement gathering helps in identifying potential risks early, allowing teams to strategize and mitigate them before they escalate. It fosters better communication across departments, breaking down silos and promoting a unified vision. Ultimately, a thorough process of detailing business needs safeguards against assumptions and ensures that the final deliverable genuinely meets the strategic goals of the organization and the operational needs of its users.
The Core Purpose of a Requirements Document
At its heart, a business requirements template serves as a comprehensive roadmap for a project. It’s a formalized structure that guides the process of eliciting, analyzing, documenting, and validating the needs of stakeholders. Rather than starting from scratch with every new initiative, a standardized template provides a consistent framework, ensuring that no critical detail is overlooked and that all essential information is captured systematically.
This structured approach streamlines the initial phases of a project, accelerating the documentation process while maintaining high quality. It acts as a single source of truth, a reference point that can be revisited at any stage of the project lifecycle to confirm alignment with original objectives. By utilizing such a framework, organizations can significantly enhance their project success rates, delivering solutions that are precisely tailored to their business challenges.
Key Components of a Robust Requirements Document
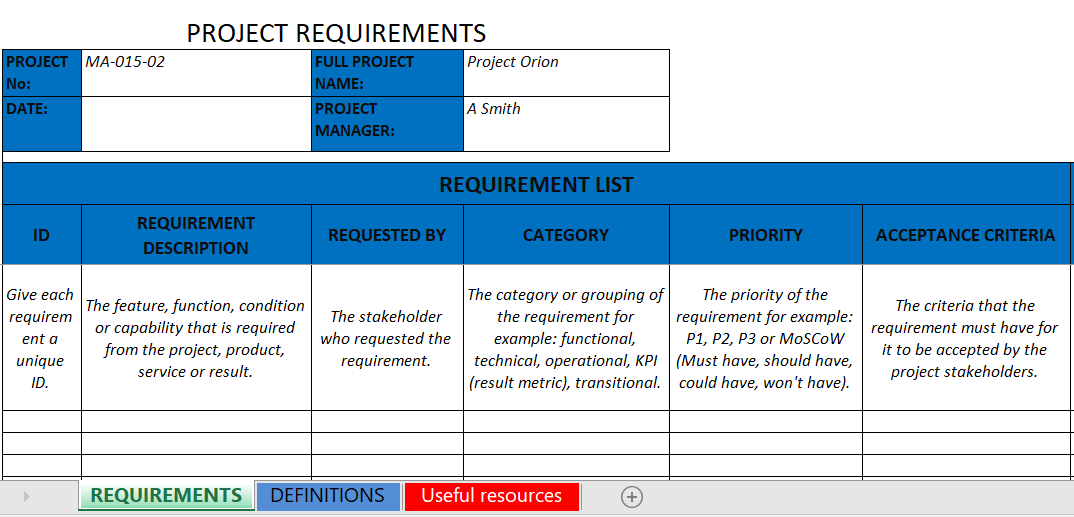
A comprehensive document designed to capture business requirements goes beyond a simple list of features. It’s a living document that evolves with the project but maintains a core structure that addresses all critical facets. While specific elements may vary based on project type, here are common sections found in an effective requirements gathering template:
- **Executive Summary:** A concise overview of the project, its goals, and the problems it aims to solve.
- **Project Scope:** Clearly defines what is **in scope** and **out of scope** for the project, setting boundaries.
- **Business Objectives:** The strategic goals the project is intended to support, linking it to organizational value.
- **Stakeholder Identification:** Lists all key individuals or groups affected by the project, along with their roles and interests.
- **Current State Analysis:** Describes the existing processes or systems that the project intends to modify or replace.
- **Future State / To-Be Processes:** Details the desired future state, outlining how processes or systems will function after implementation.
- **Functional Requirements:** Specifies what the system or product **must do**, often broken down into user stories or use cases.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** Describes how the system should perform, including aspects like **performance**, **security**, **usability**, **scalability**, and **reliability**.
- **Data Requirements:** Defines the data elements, their sources, transformations, and storage.
- **Assumptions and Constraints:** Documents any factors assumed to be true for the project to proceed and any limitations that must be adhered to.
- **Risks and Dependencies:** Identifies potential issues that could impact the project and any interdependencies with other projects or systems.
- **Glossary of Terms:** Provides definitions for technical terms or acronyms used within the document to ensure clarity.
How to Leverage Your Template for Success
Simply having a template isn’t enough; its true value comes from how it’s used within the project lifecycle. A well-implemented requirements documentation template becomes an integral part of project planning and execution.
First, use it as a **discovery tool**. During initial stakeholder interviews and workshops, the structured fields of the template guide conversations, prompting questions that might otherwise be missed. This proactive approach helps in uncovering hidden needs and unspoken expectations.
Second, it serves as a communication catalyst. Once initial details are captured, the structured document provides a common language for all parties. It facilitates reviews, ensuring that everyone involved can understand, validate, and sign off on the defined needs. This collaborative review process minimizes ambiguities and builds shared understanding, crucial for development and testing phases.
Finally, consider it a control mechanism. As the project progresses, the detailed requirements specification document acts as a benchmark against which all deliverables are measured. It helps in managing scope changes, providing a basis to evaluate the impact of new requests against the agreed-upon initial scope. This discipline prevents uncontrolled expansion of the project, keeping it on track and within budget.
Best Practices for Requirements Elicitation
Eliciting accurate and complete requirements is an art as much as a science. Here are some best practices to maximize the effectiveness of your requirements gathering efforts:
1. **Engage the Right Stakeholders:** Identify and involve all relevant individuals who will be affected by or contribute to the project. This includes end-users, subject matter experts, management, and even external partners.
2. **Choose Appropriate Techniques:** Don’t rely on a single method. Utilize a variety of techniques such as interviews, workshops, surveys, prototyping, observation, and document analysis to gather diverse perspectives and validate information.
3. **Ask “Why?”:** Always delve deeper than surface-level requests. Understanding the underlying business problem or opportunity helps in defining solutions that deliver true value, rather than just implementing requested features.
4. **Prioritize Requirements:** Not all needs are equally important. Work with stakeholders to prioritize requirements based on business value, effort, and urgency. Techniques like MoSCoW (Must, Should, Could, Won’t) can be very helpful here.
5. **Visualize and Model:** Use diagrams, wireframes, flowcharts, and other visual aids to communicate complex requirements. A picture often conveys more clearly than pages of text and helps identify gaps or inconsistencies.
6. **Validate and Verify:** Regularly review documented requirements with stakeholders. Ensure they are complete, consistent, unambiguous, and testable. Early validation reduces rework later in the project.
7. **Manage Expectations:** Clearly communicate what can and cannot be achieved within project constraints. Be transparent about trade-offs and ensure stakeholders understand the implications of their choices.
Customizing Your Approach
While a standard business requirements template provides an excellent starting point, it’s crucial to remember that it’s a flexible tool, not a rigid straitjacket. Every project is unique, with its own set of complexities, stakeholders, and organizational contexts. Therefore, the template should be adapted to fit the specific needs of each initiative.
Consider the project’s scale: a small, internal process improvement might require a less detailed document than a large-scale enterprise system implementation. The project’s methodology also matters; Agile projects, for instance, might prioritize user stories and epics over extensive upfront documentation, using the template as a guide for what information needs to be captured iteratively. Customization might involve adding industry-specific sections, streamlining less relevant areas, or integrating with other project management tools. The goal is always to create a requirements definition process that is effective and efficient for the project at hand, ensuring thoroughness without unnecessary bureaucracy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary benefit of using a standardized requirements template?
The primary benefit is consistency and completeness. A standardized requirements template ensures that all essential information is captured systematically across projects, reducing the risk of overlooked details, improving communication, and streamlining the documentation process. It acts as a guide, preventing teams from having to reinvent the wheel for every new initiative.
Can a business requirements template be used for Agile projects?
Absolutely. While Agile methodologies emphasize iterative development and less upfront documentation, a requirements gathering template can still be highly valuable. It can be adapted to focus on high-level epics and features initially, with detailed user stories and acceptance criteria being captured in subsequent iterations. It provides a structured backbone for what information needs to be understood before development, ensuring alignment with overall business goals.
Who typically uses or benefits from a detailed requirements document?
A wide range of stakeholders benefits from a detailed requirements document. This includes business analysts who create it, project managers who use it for planning and tracking, developers who build the solution based on it, quality assurance testers who use it to create test cases, and business stakeholders who rely on it to ensure the final product meets their needs. It serves as a common reference point for everyone involved.
How often should the requirements document be updated?
The requirements document should be treated as a living document, updated whenever there are changes to the agreed-upon scope, functionalities, or non-functional aspects of the project. This means updates can occur throughout the project lifecycle, especially during phases of discovery, feedback, or scope adjustments. It’s crucial to maintain version control and communicate changes effectively to all stakeholders to ensure everyone is working from the latest information.
What’s the difference between business requirements and technical requirements?
Business requirements define *what* the business needs to achieve or *why* a solution is being built, focusing on the problems to be solved or opportunities to be seized from a strategic perspective. Technical requirements, also known as system requirements, define *how* the solution will be built, detailing the specific functionalities, data structures, architectural components, and technical specifications necessary to meet the business requirements. They are complementary, with business requirements driving the technical ones.
The journey from a nascent idea to a tangible, value-delivering solution is paved with careful planning and clear communication. A well-designed and diligently applied Capturing Business Requirements Template serves as an indispensable tool in this journey, transforming abstract needs into concrete, actionable plans. It’s more than just a document; it’s a commitment to clarity, a guardrail against ambiguity, and a catalyst for successful project outcomes.
By embracing a structured approach to defining business needs, organizations empower their teams to build precisely what is required, on time and within budget. This foresight not only saves resources but also fosters a culture of precision and accountability, ensuring that every project contributes meaningfully to strategic objectives. Invest in a robust framework for documenting requirements, and watch your projects move from uncertainty to predictable success.


