The hum of machinery, the constant movement of materials, and the sheer scale of ambition define a construction site. Amidst this dynamic environment, hidden dangers often lurk in seemingly innocuous places: the depths of a trench, the interior of a large pipe, or the confined space of a utility vault. These enclosed areas, by their very nature, pose significant risks to workers, ranging from engulfment and hazardous atmospheres to limited entry and egress. Ensuring the safety of every worker in such environments isn’t just a regulatory requirement; it’s a fundamental ethical imperative.
Developing a robust, site-specific safety plan for these hazardous environments is crucial, and that’s where a well-crafted confined space program becomes indispensable. It’s more than just a document; it’s a living blueprint for protecting lives. For construction companies aiming to uphold the highest safety standards while navigating complex project demands, understanding and implementing an effective system for managing these risks is paramount. This article explores the vital components of such a program and how a comprehensive Construction Confined Space Program Template can serve as your foundation.
Why a Confined Space Program is Non-Negotiable in Construction
Construction sites are unique for their constantly evolving landscapes and varied hazards. Confined spaces, particularly those categorized as permit-required, present a magnified set of dangers that demand rigorous attention. These can include oxygen-deficient or enriched atmospheres, flammable or toxic gases, and the potential for materials to engulf a worker. Without a clear set of protocols, the risk of serious injury or fatality skyrockets.
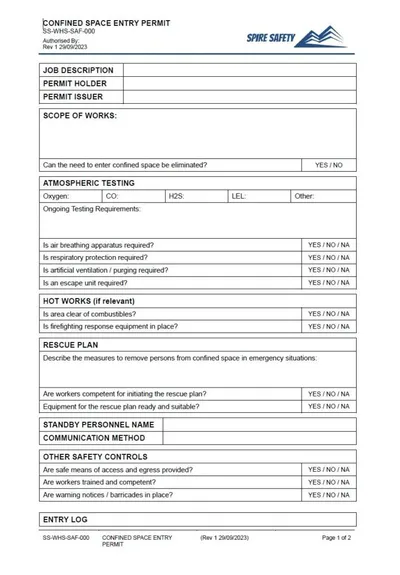
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards, specifically 29 CFR 1926 Subpart AA for confined spaces in construction, mandate that employers identify and evaluate confined spaces, develop a written entry program, and implement specific procedures to ensure worker safety. This isn’t merely about avoiding penalties; it’s about fostering a culture where every worker returns home safely at the end of the day. A dedicated confined space program provides the framework to achieve this, establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and emergency procedures.
Understanding Permit-Required Confined Spaces
Not all enclosed areas on a construction site are classified as “permit-required confined spaces,” but understanding the distinction is vital. A confined space is one that: (1) is large enough and configured so an employee can bodily enter and perform assigned work; (2) has limited or restricted means for entry or exit; and (3) is not designed for continuous employee occupancy. Think of manholes, vaults, tanks, pits, or even certain trenches.
A permit-required confined space adds another layer of hazard. It contains or has the potential to contain one or more of the following: a hazardous atmosphere; material that could engulf an entrant; an internal configuration that could trap or asphyxiate an entrant by inwardly converging walls or a floor that slopes downward and tapers to a smaller cross-section; or any other recognized serious safety or health hazard. Identifying these spaces is the first critical step, and a comprehensive safety management system for confined spaces will guide this assessment.
Key Elements of an Effective Confined Space Entry Program
A robust construction safety program for confined spaces isn’t a simple checklist; it’s a detailed, multi-faceted approach to risk management. It should systematically address every aspect of confined space operations, from initial identification to post-entry review. Leveraging a well-structured Construction Confined Space Program Template can help ensure all critical components are included and organized logically.
Here are the essential elements that any comprehensive confined space entry program should include:
- **Hazard Identification and Evaluation:** Thoroughly assess all potential confined spaces on site. Identify specific hazards present (e.g., atmospheric, engulfment, mechanical, electrical) and determine if they are permit-required.
- **Written Program Development:** Establish a clear, written safety plan for hazardous environments. This document should outline policies, procedures, and responsibilities for all confined space entry operations.
- **Entry Permit System:** Implement a standardized **permit-to-enter system**. This requires a written permit to be completed and authorized before entry into any permit-required confined space. It details the space, the work to be performed, hazards, control measures, rescue procedures, and authorized personnel.
- **Roles and Responsibilities:** Clearly define the duties of all personnel involved, including:
- **Authorized Entrants:** Those permitted to enter the confined space.
- **Attendants:** Individuals stationed outside the confined space to monitor entrants and initiate rescue if necessary.
- **Entry Supervisors:** Responsible for authorizing entry, overseeing operations, and terminating the permit.
- **Rescue Personnel:** Trained and equipped individuals or services capable of performing non-entry or entry rescues.
- **Atmospheric Monitoring:** Specify procedures for **testing the atmosphere** before entry and continuously during entry. This includes checking for oxygen levels, flammable gases, and toxic substances.
- **Hazard Control Measures:** Detail methods to eliminate or control identified hazards, such as **ventilation**, lockout/tagout (LOTO) for energy sources, inerting, purging, or isolating the space.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):** Mandate the appropriate PPE for all entrants and attendants, including respirators, fall protection, communication devices, and protective clothing.
- **Emergency Response and Rescue Procedures:** Develop **detailed plans for rescue** and emergency services. This includes both non-entry rescue methods (e.g., retrieval systems) and entry rescue protocols, ensuring rescue personnel are available, trained, and equipped.
- **Communication Procedures:** Establish clear **communication protocols** between entrants, attendants, and entry supervisors, using radios, hand signals, or other reliable methods.
- **Training Requirements:** Outline comprehensive **training programs** for all personnel involved in confined space operations, covering hazard recognition, safe entry procedures, use of equipment, and emergency response.
- **Contractor Control:** Specify procedures for informing **contractors** about permit-required confined spaces and ensuring their compliance with the program.
- **Program Review and Revision:** Establish a schedule for **periodic review** and updating of the confined space program, especially after incidents or changes in operations.
Leveraging a Program Template for Efficiency and Compliance
Developing a comprehensive confined space program from scratch can be a daunting and time-consuming task. This is where a robust Construction Confined Space Program Template proves invaluable. It provides a structured starting point, ensuring that no critical element is overlooked and that your safety protocols align with regulatory requirements. Instead of reinventing the wheel, you can leverage expertly crafted content and frameworks.
A quality template offers pre-written sections covering everything from hazard assessment forms and entry permit examples to roles and responsibilities and emergency action plans. This significantly reduces the administrative burden on your safety managers, allowing them to focus more on implementation and training rather than documentation creation. It also helps in maintaining consistency across various projects and teams, ensuring a uniform approach to worker safety for enclosed spaces, regardless of the site.
Customizing Your Program for Site-Specific Needs
While a template provides an excellent foundation, it’s crucial to remember that it is a *template*. No two construction sites are exactly alike, and therefore, no two confined space programs can be identical. The true value of a safety program for hazardous environments comes from its ability to be adapted and tailored to the unique conditions, hazards, and personnel of each specific project.
Begin by conducting a thorough site-specific hazard assessment for every potential confined space. This involves identifying the dimensions of the space, its internal configuration, any potential atmospheric hazards (e.g., gases, vapors), the presence of liquids or solid materials that could engulf a worker, and potential energy sources that need lockout/tagout. Incorporate specific site maps, equipment lists, and emergency contact information directly into your permit-required confined space procedures. The template serves as a guide, prompting you to fill in the blanks with project-specific details, transforming a generic document into an actionable, tailored safety manual.
Training and Continuous Improvement
Even the most meticulously crafted confined space program is only as effective as the people who implement it. Comprehensive training is a cornerstone of any successful construction site confined space protocols. All employees who may encounter, enter, or oversee work in confined spaces must receive adequate training, and this training must be refreshed periodically and whenever there are changes in operations or the program itself.
Training should cover hazard recognition, the proper use of atmospheric monitoring equipment, understanding entry permits, the function and proper use of PPE, and emergency response procedures. Beyond initial training, continuous improvement is vital. Regular drills for rescue scenarios, post-incident reviews, and scheduled program audits help to identify weaknesses, refine procedures, and ensure the safety plan remains dynamic and effective. Encouraging open communication and feedback from workers on the ground can provide invaluable insights for enhancing safety protocols and overall OSHA confined space compliance.
Protecting workers in confined spaces is a complex yet absolutely essential aspect of construction safety. By understanding the unique hazards and proactively implementing a robust safety program, companies not only meet regulatory requirements but also cultivate a culture where safety is prioritized above all else. A well-designed Construction Confined Space Program Template acts as an indispensable tool in this endeavor, providing a solid framework that can be customized to fit any project’s specific needs.
Investing in a thorough confined space program is an investment in your most valuable asset: your people. It demonstrates a commitment to their well-being, minimizes risks, and ultimately contributes to a more efficient and successful project. Don’t leave safety to chance; equip your team with the knowledge, procedures, and resources necessary to navigate these challenging environments safely and confidently every single day.