Embarking on a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system implementation is often akin to building a new home for your business operations. Just as you wouldn’t start construction without detailed architectural blueprints, diving into a CRM project without a comprehensive requirements document can lead to costly delays, unmet expectations, and ultimately, a system that doesn’t quite fit your organization’s unique needs. This foundational planning stage is crucial for ensuring your investment yields the desired strategic returns.
The journey of selecting and implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system can be fraught with challenges, from defining complex workflows to integrating disparate data sources. Without a clear roadmap, teams risk diverging on priorities, stakeholders can become misaligned, and the entire project can veer off course. This is precisely where a robust Crm Requirements Document Template becomes an invaluable asset, providing a structured approach to defining, documenting, and validating every critical need before a single line of code is written or a vendor is chosen.
Why a CRM Requirements Document is Indispensable
A well-crafted CRM requirements document serves as the single source of truth for your entire CRM project. It clarifies your vision, outlines your specific operational needs, and sets clear expectations for all involved parties, from internal teams to potential software vendors. This comprehensive outline helps bridge the communication gap between business users, technical teams, and external consultants, ensuring everyone is working towards a common goal.
The benefits extend far beyond mere documentation; they directly impact the project’s success and efficiency. By investing time upfront in defining your requirements, you mitigate risks associated with scope creep, budget overruns, and feature mismatches. It empowers your team to make informed decisions throughout the selection and implementation phases, safeguarding your investment and accelerating time-to-value for your new CRM system. Ultimately, this foundational document lays the groundwork for a CRM solution that truly transforms how your business engages with its customers.
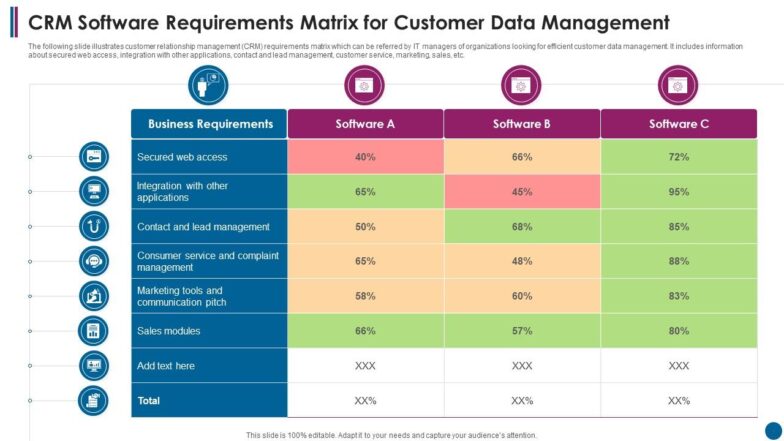
Core Components of an Effective CRM Requirements Outline
A comprehensive customer relationship management requirements framework should systematically address various facets of your business operations and technical infrastructure. It’s more than a checklist; it’s a strategic blueprint. While specific sections may vary based on industry and organizational size, several core components are universally critical for defining CRM needs.
Executive Summary & Business Objectives
This section provides a high-level overview of the project, its strategic goals, and the problems it aims to solve. Clearly articulate the overarching business objectives, such as improving customer retention, streamlining sales processes, enhancing customer service, or gaining deeper insights into customer behavior. These objectives will serve as guiding principles throughout the project.
Current State Analysis
Describe your existing processes, systems, and challenges related to customer management. This helps to identify pain points, inefficiencies, and gaps that the new CRM system needs to address. Document current technologies in use, data sources, and any existing workarounds or manual efforts.
Future State & Functional Requirements
This is the heart of your requirements document, detailing what the new CRM system *must do*. Functional requirements describe the specific features and capabilities the system needs to possess to meet your business objectives. These are typically organized by business function.
Here are some common functional areas:
- **Sales Force Automation (SFA):** Lead management, opportunity tracking, quote generation, sales forecasting, activity logging.
- **Marketing Automation:** Campaign management, email marketing, lead nurturing, segmentation, marketing ROI tracking.
- **Customer Service & Support:** Case management, knowledge base, self-service portals, service level agreements (SLAs), live chat integration.
- **Reporting & Analytics:** Customizable dashboards, performance metrics, ad-hoc reporting, customer insights.
- **Integration Capabilities:** APIs for connecting with ERP, accounting, marketing, or other essential business systems.
- **User Interface (UI) & User Experience (UX):** Ease of navigation, intuitive design, customization options for user views.
Non-Functional Requirements
These define how the system should perform, not what it should do. This includes aspects like **performance** (response times, scalability), **security** (data encryption, access controls), **reliability** (uptime, disaster recovery), and **usability** (ease of learning, accessibility). Ignoring non-functional requirements can lead to a system that functions correctly but is slow, insecure, or difficult to use.
Integration Requirements
Detail all systems the new CRM must connect with, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, accounting software, email platforms, marketing automation tools, or custom applications. Specify the type of integration needed (e.g., real-time, batch, one-way, two-way) and the data points to be exchanged.
Data Migration Strategy
Outline how existing customer data will be transferred to the new CRM. This includes identifying data sources, defining data cleansing processes, mapping old data fields to new ones, and establishing timelines for migration. This is a critical step to ensure data integrity and avoid disruptions.
Security & Compliance
Specify security protocols, user authentication methods, data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA), and industry-specific compliance standards the CRM must adhere to. This section ensures your customer data remains protected and legally compliant.
User Roles & Permissions
Define different user roles within the organization (e.g., sales representative, marketing manager, customer service agent, administrator) and the specific permissions and access levels associated with each role. This ensures users only see and interact with relevant information.
Reporting & Analytics
Beyond basic reporting, detail specific analytical needs, custom reports, and key performance indicators (KPIs) that the CRM must track and present. This section empowers data-driven decision-making across departments.
Training & Support
While not strictly a system requirement, anticipating the need for user training, ongoing support, and documentation is vital for successful user adoption and long-term system utilization.
Navigating the Requirements Gathering Process
Creating an effective blueprint for CRM implementation requires a systematic approach to gathering and documenting needs. It’s an iterative process that benefits immensely from broad participation and clear communication. The goal is to collect comprehensive, accurate, and unambiguous requirements that truly reflect the organization’s strategic goals and operational realities.
Begin by identifying key stakeholders from all departments that will interact with the CRM – sales, marketing, customer service, IT, and executive leadership. Conduct interviews, workshops, and surveys to solicit input, uncover pain points, and understand desired functionalities. Encourage open dialogue to ensure all perspectives are heard and conflicting requirements are identified and resolved early. Facilitate brainstorming sessions to envision the "future state" and how a new system can empower users.
Once gathered, these requirements must be prioritized. Not all needs are equally critical, and resources are always finite. Utilize methodologies like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) or simple high-medium-low priority rankings. This prioritization guides development, helps in vendor selection, and prevents scope creep by focusing on the most impactful features first. Regularly review and validate the documented requirements with stakeholders to ensure they remain relevant and accurate throughout the project lifecycle.
Tailoring Your Template for Success
While a generic Customer Relationship Management requirements template provides a strong starting point, its true value lies in its adaptability. A successful CRM project isn’t just about implementing software; it’s about aligning technology with your unique business processes, culture, and strategic objectives. This customization phase is where the document truly becomes your organization’s own blueprint.
Consider your industry-specific nuances. A healthcare provider will have different compliance and data privacy requirements than a retail company. Similarly, a small business focused on rapid growth might prioritize agile features and ease of use, whereas a large enterprise might emphasize scalability, complex integrations, and robust security. Take the time to add sections or adjust existing ones to reflect these distinct needs. For instance, if your business relies heavily on field service, ensure specific mobile access and offline capabilities are prominently featured.
Furthermore, think about your company culture. Does your team prefer highly visual dashboards, or are detailed reports more important? Does your sales team need extensive automation for lead routing, or do they thrive on manual control? The template should evolve through internal collaboration, incorporating the language and specific examples relevant to your daily operations. Leveraging a well-structured Crm Requirements Document Template isn’t just about listing features; it’s about strategic planning that encompasses your entire business ecosystem.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, the process of defining requirements can stumble. Awareness of common pitfalls can help you navigate these challenges effectively. One of the most prevalent issues is vague or ambiguous requirements. Phrases like "easy to use" or "fast performance" are subjective; instead, define concrete metrics such as "user can complete XYZ task in less than 3 clicks" or "system response time under 2 seconds for ABC function." Specificity is paramount.
Another significant challenge is scope creep, where new features and functionalities are continuously added throughout the project lifecycle without proper evaluation or adjustment to timelines and budgets. A robust requirements document, regularly revisited and approved by stakeholders, acts as a crucial guardrail against this. It provides a baseline against which all change requests can be evaluated.
Lastly, lack of sufficient stakeholder involvement can lead to a CRM system that meets technical specifications but fails to address the real-world needs of its users. Ensure representation from all affected departments and leadership. Ignoring non-functional requirements in favor of features can also create a technically sound but ultimately unusable system. Prioritize these "how" aspects alongside the "what" to build a truly effective solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary benefit of a CRM requirements document?
The primary benefit is clarity and alignment. It provides a detailed, shared understanding among all stakeholders about what the new CRM system should achieve, how it should function, and the business problems it will solve. This reduces miscommunication and project risks.
Who should be involved in creating this document?
Key stakeholders from all departments that will use or be affected by the CRM should be involved, including representatives from sales, marketing, customer service, IT, operations, and executive leadership. Their diverse perspectives ensure comprehensive coverage of business needs.
How long does it typically take to develop?
The timeline varies significantly based on organization size, project complexity, and stakeholder availability. For a small business, it might take a few weeks; for a large enterprise with complex integrations, it could extend to several months. It’s an investment that pays dividends by preventing costly rework later.
Can small businesses benefit from a CRM requirements document?
Absolutely. While the document might be less extensive than for a large enterprise, even small businesses benefit from clearly defining their needs before investing in a CRM. It helps them choose a system that truly supports their growth and operational efficiency without unnecessary features.
What’s the difference between functional and non-functional requirements?
Functional requirements describe *what* the system does (e.g., “The system shall allow users to log calls”). Non-functional requirements describe *how* the system performs or operates (e.g., “The system shall have a 99.9% uptime” or “The system shall load customer records in under 2 seconds”). Both are crucial for a successful implementation.
Crafting a comprehensive requirements document for your CRM project is a significant undertaking, but it is an investment that yields substantial returns. It’s the foundational step that ensures your organization’s vision for customer engagement is translated into a tangible, effective software solution. By methodically defining your needs, you pave the way for a smooth implementation, enhanced user adoption, and ultimately, a powerful tool that drives business growth and customer satisfaction.
Don’t view the creation of this document as a mere formality; see it as the critical first chapter in your CRM success story. By embracing the disciplined approach offered by a comprehensive Crm Requirements Document Template, your organization can navigate the complexities of CRM implementation with clarity and confidence, ensuring the chosen solution perfectly aligns with your strategic objectives and empowers your teams to excel in every customer interaction. Start documenting your needs today, and build a CRM that truly works for you.


