In the intricate world of modern project development, data stands as the lifeblood of almost every initiative. From customer relationship management systems to complex analytical platforms, the success of any endeavor hinges significantly on the quality, accessibility, and precise understanding of the data it consumes and produces. Yet, all too often, the specific requirements surrounding this crucial asset are left to implicit assumptions or informal discussions, leading to misunderstandings, costly rework, and ultimately, project failure.
This challenge highlights an undeniable truth: explicit definition trumps implicit understanding every time. A well-structured approach to detailing data needs is not just a nice-to-have; it’s a fundamental necessity for aligning business objectives with technical implementation. Whether you’re a project manager striving for clarity, a business analyst ensuring stakeholder alignment, or a developer needing precise specifications, a dedicated framework for documenting data needs is your most reliable ally.
The Unseen Foundation of Successful Projects
Many project teams dive headfirst into development without fully articulating their data requirements, assuming that everyone involved shares a common understanding. This often leads to a “build first, ask questions later” mentality, which invariably results in a system that doesn’t quite meet expectations, or worse, fails to function correctly due to fundamental data mismatches. Without a clear specification of data needs, technical teams might design databases that lack necessary fields, or developers might implement logic based on incorrect data types.
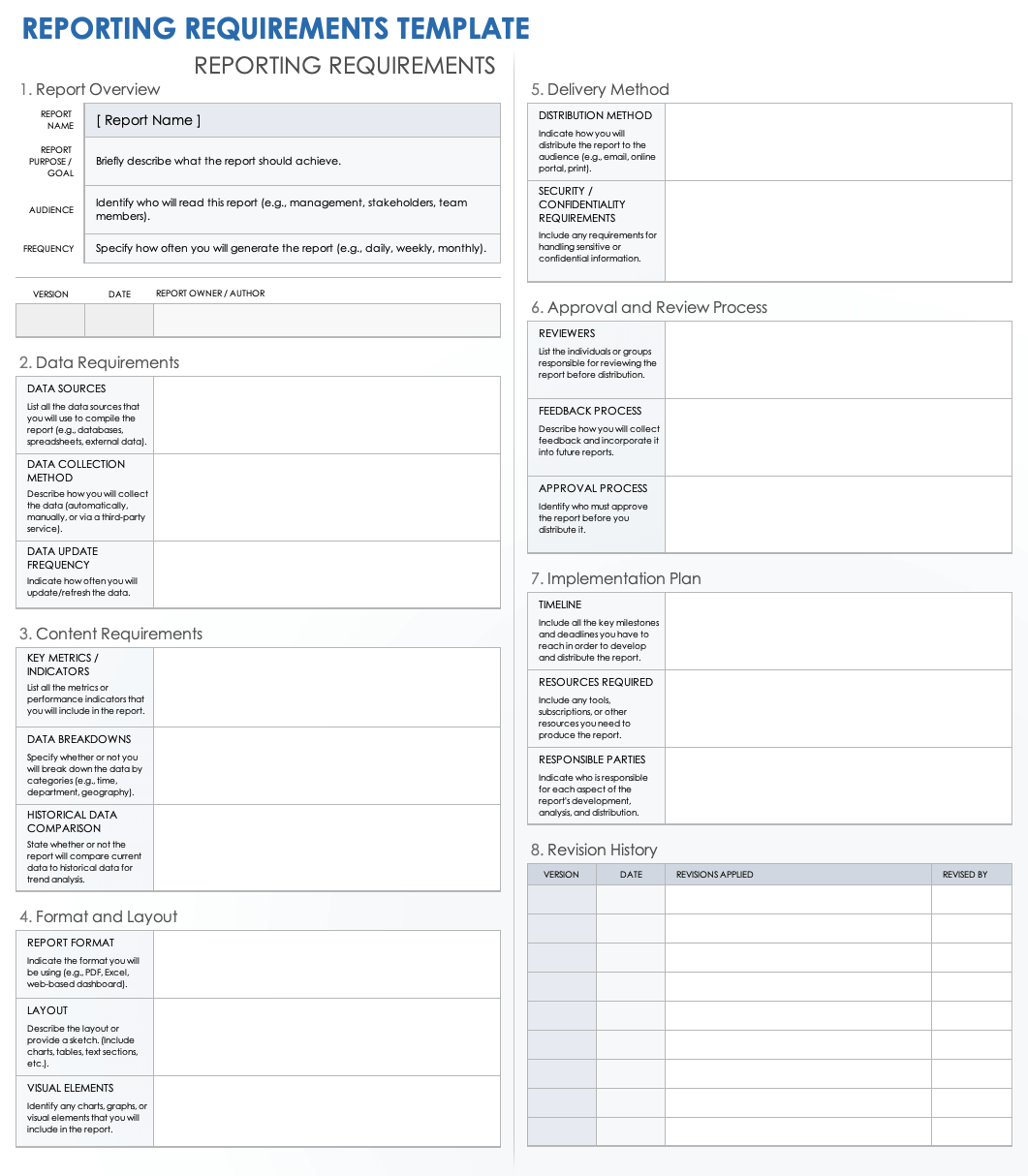
The absence of a robust data specification document creates a communication gap between business stakeholders, who understand the "what" and "why" of the data, and technical teams, who need the precise "how" and "where." This gap can manifest as scope creep, unexpected data quality issues, and prolonged development cycles spent rectifying preventable errors. A properly constructed blueprint for data projects acts as a universal translator, ensuring that everyone involved speaks the same data language, from the initial ideation phase through to deployment and maintenance.
Key Benefits of a Well-Defined Data Requirements Document
Implementing a structured approach to documenting data needs brings a cascade of advantages that directly impact project success and organizational efficiency. It’s an investment that pays dividends in clarity, precision, and reduced risk.
One primary benefit is significantly **improved communication and alignment**. By formalizing data expectations, a data definition blueprint minimizes ambiguity and ensures that all project participants—from business owners to database administrators—have a shared, unambiguous understanding of the data elements, their meanings, and their intended use. This shared understanding prevents costly misinterpretations and fosters better collaboration across diverse teams.
Furthermore, a comprehensive data needs outline leads to **reduced rework and development costs**. When data requirements are clearly articulated upfront, developers can design more accurate data models and build more robust systems from the outset. This pre-emptive clarity drastically cuts down on the need for costly post-implementation modifications or bug fixes related to data discrepancies.
A well-crafted guide to data elements also supports **accurate project scoping and estimation**. With a precise understanding of the data involved, project managers can make more informed decisions about resource allocation, timelines, and potential technical challenges. This foundational insight helps in setting realistic expectations and delivering projects on schedule and within budget.
Finally, a strong data specification ensures **enhanced data quality and integrity**. By defining rules, validations, and constraints at the requirements stage, organizations can build systems that inherently enforce data quality. This leads to more reliable data for reporting, analytics, and operational processes, ultimately empowering better business decisions.
Essential Components of a Robust Data Requirements Document
A comprehensive data requirements document isn’t just a list of fields; it’s a strategic blueprint that describes all aspects of data pertinent to a project. While specific content may vary, certain core elements are universally critical for capturing a complete picture.
- **Project Overview:** A concise summary of the project’s **goals**, **scope**, and how data contributes to achieving the desired business outcomes. This provides crucial context for all subsequent details.
- **Stakeholders and Data Ownership:** Identification of key individuals or departments who will **use**, **provide**, or be **responsible** for the data. This clarifies roles and facilitates future communication.
- **Data Sources:** A description of where the data originates, whether from existing databases, external APIs, user inputs, or third-party vendors. Understanding sources is critical for **integration planning**.
- **Data Elements/Attributes:** This is the heart of the document. For each piece of data, define its:
- **Name:** A clear, unambiguous label.
- **Description:** A detailed explanation of its meaning and purpose.
- **Data Type:** E.g., string, integer, date, boolean.
- **Length/Format:** Specific constraints on its size or structure.
- **Allowed Values:** Lists or patterns for valid entries (e.g., “Male,” “Female” for Gender).
- **Constraints:** Rules like “required,” “unique,” “foreign key reference.”
- **Business Rules:** Any specific logic tied to the data (e.g., “Age must be calculated from Date of Birth”).
- **Data Relationships:** How different data entities relate to each other (e.g., one-to-many, many-to-many), often visualized through **entity-relationship diagrams** (ERDs). This helps in designing robust database schemas.
- **Data Transformations and Derivations:** Details on how raw data will be **processed**, **calculated**, or **converted** before use. This includes aggregation, filtering, or complex calculations.
- **Data Quality Rules:** Explicit rules for ensuring the accuracy, consistency, completeness, and timeliness of data. This covers **validation logic** and error handling procedures.
- **Security and Privacy Requirements:** Guidelines on **data access**, **encryption**, **anonymization**, and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. This is increasingly vital in today’s data landscape.
- **Glossary of Terms:** A dictionary of all technical and business terms used within the document, ensuring consistent language and **understanding**.
Practical Steps for Crafting Your Data Requirements Document
Developing a comprehensive data requirements document is an iterative process that benefits from collaboration and a structured approach. It’s not a one-time task but an evolving asset.
Begin by **initiating and defining the scope** of your data requirements effort. Understand what parts of the system or project your data specification document will cover. Is it for a new application, a data migration, or an analytical report? A clear scope helps prevent overwhelming detail and focuses your efforts.
Next, **gather information** from all relevant stakeholders. Conduct interviews with business users to understand their daily operations, reporting needs, and pain points related to data. Review existing documentation, system specifications, and data models to capture current data definitions and limitations. Facilitate workshops to bridge gaps between business needs and technical possibilities.
Once you have a solid understanding, **document the core data elements and their relationships**. Start with high-level entities and gradually drill down into specific attributes, their characteristics, and associated business rules. Use visual aids like conceptual or logical data models to illustrate relationships and structures, making complex information easier to digest for diverse audiences.
Crucially, **validate and iterate** on your findings. Share drafts of your data specification with stakeholders for feedback. Conduct walkthroughs to ensure that the documented data needs accurately reflect business processes and technical realities. This iterative feedback loop is essential for refining the document and catching potential issues early.
Finally, **obtain formal sign-off**. Once all stakeholders agree that the data needs outline accurately represents their requirements, secure formal approval. This sign-off signifies a shared understanding and commitment to the defined data elements, providing a solid foundation for subsequent development phases.
Customizing Your Approach: Beyond the Template
While a structured approach is invaluable, the rigidity of a one-size-fits-all solution rarely works for every project. The true power of a Data Requirements Document Template lies in its adaptability. It serves as a strong starting point, providing a framework that you can tailor to the unique demands of your specific project, team, and organizational culture.
For smaller projects, you might opt for a more concise data needs outline, focusing only on the most critical data elements and their core attributes. In contrast, large-scale enterprise initiatives will demand a highly detailed and exhaustive data specification, potentially spanning multiple documents or integrated into a broader data governance framework. The key is to find the right balance between comprehensive detail and pragmatic efficiency.
Consider integrating your data definition process with agile methodologies. Instead of a single, monolithic document, you might create an evolving data requirements backlog, defining data elements just-in-time for each sprint or user story. This approach ensures that data specifications remain relevant and responsive to changing project priorities while still maintaining a clear record of data needs.
Furthermore, explore various tools and technologies that can support your data definition efforts. While a simple word processor or spreadsheet can suffice, specialized data modeling tools, requirements management software, or collaborative platforms can enhance efficiency, version control, and stakeholder engagement. The goal is to make the process of defining data specifications as seamless and collaborative as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a data requirements document?
The primary purpose of a data requirements document is to clearly define and communicate the data needs for a project, ensuring all stakeholders have a shared understanding of what data is required, how it will be used, and its characteristics, thereby reducing ambiguity and potential misinterpretations.
Who typically creates and uses a data requirements document?
Business analysts or system analysts often lead its creation, collaborating closely with business stakeholders, data architects, developers, and quality assurance teams. These various groups then use the document as a foundational guide throughout the project lifecycle, from design and development to testing and deployment.
How does a data specification document differ from a functional requirements document?
While a functional requirements document describes *what the system does* or *how it behaves* from a user’s perspective, a data specification document focuses specifically on *what data the system needs* to perform those functions, detailing its structure, meaning, relationships, and associated rules and constraints.
Can a data needs outline be used in agile environments?
Absolutely. In agile environments, a data needs outline can be highly effective. It might be more concise or iterative, evolving with each sprint or iteration. It serves as a living document, ensuring that data definitions and requirements keep pace with incremental development and continuous delivery, often integrated into user stories or epics.
What are the risks of not having a clear data requirements document?
The risks of omitting a clear data requirements document are substantial and include scope creep, inaccurate data models, delayed development schedules, increased rework and costs, poor data quality, systems that fail to meet business objectives, and significant communication breakdowns between technical and business teams.
In an era where data is often cited as the new oil, treating it with the rigor and respect it deserves is paramount for any successful venture. A well-constructed data definition blueprint is not merely bureaucratic overhead; it is an indispensable tool that underpins successful project execution, drives clarity, and minimizes costly errors. It acts as the bridge between abstract business needs and concrete technical implementation, ensuring that the final solution truly serves its intended purpose.
Embracing the principles behind a robust Data Requirements Document Template empowers organizations to build systems that are not only functional but also data-rich, reliable, and aligned with strategic objectives. By investing time upfront in defining data needs, you lay a solid foundation for innovation, efficiency, and sustained success in an increasingly data-driven world. Make the commitment to clarity, and watch your data projects thrive.


