In today’s interconnected business landscape, the reliance on third-party vendors, suppliers, and service providers is not just a convenience, but a fundamental operational necessity. From cloud computing platforms and SaaS applications to outsourced IT support and payment processors, external entities often handle, process, or have access to an organization’s most sensitive data. This intricate web of relationships, while enabling innovation and efficiency, simultaneously introduces significant information security risks that can compromise data integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
Navigating these complex risks requires more than just ad-hoc checks; it demands a structured, comprehensive approach. This is precisely where a robust Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template becomes an invaluable asset. It serves as the bedrock for establishing clear expectations, enforcing security standards, and mitigating potential vulnerabilities across your vendor ecosystem, benefiting CISOs, IT risk managers, procurement departments, and legal teams alike in their quest for robust organizational security.
Why an Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template is Essential Today
The modern enterprise operates in an environment rife with evolving cyber threats and stringent regulatory demands. Data breaches originating from third-party vendors are unfortunately common, often making headlines and causing significant financial and reputational damage. An Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template addresses this critical vulnerability head-on, providing a proactive framework to manage vendor-related risks.
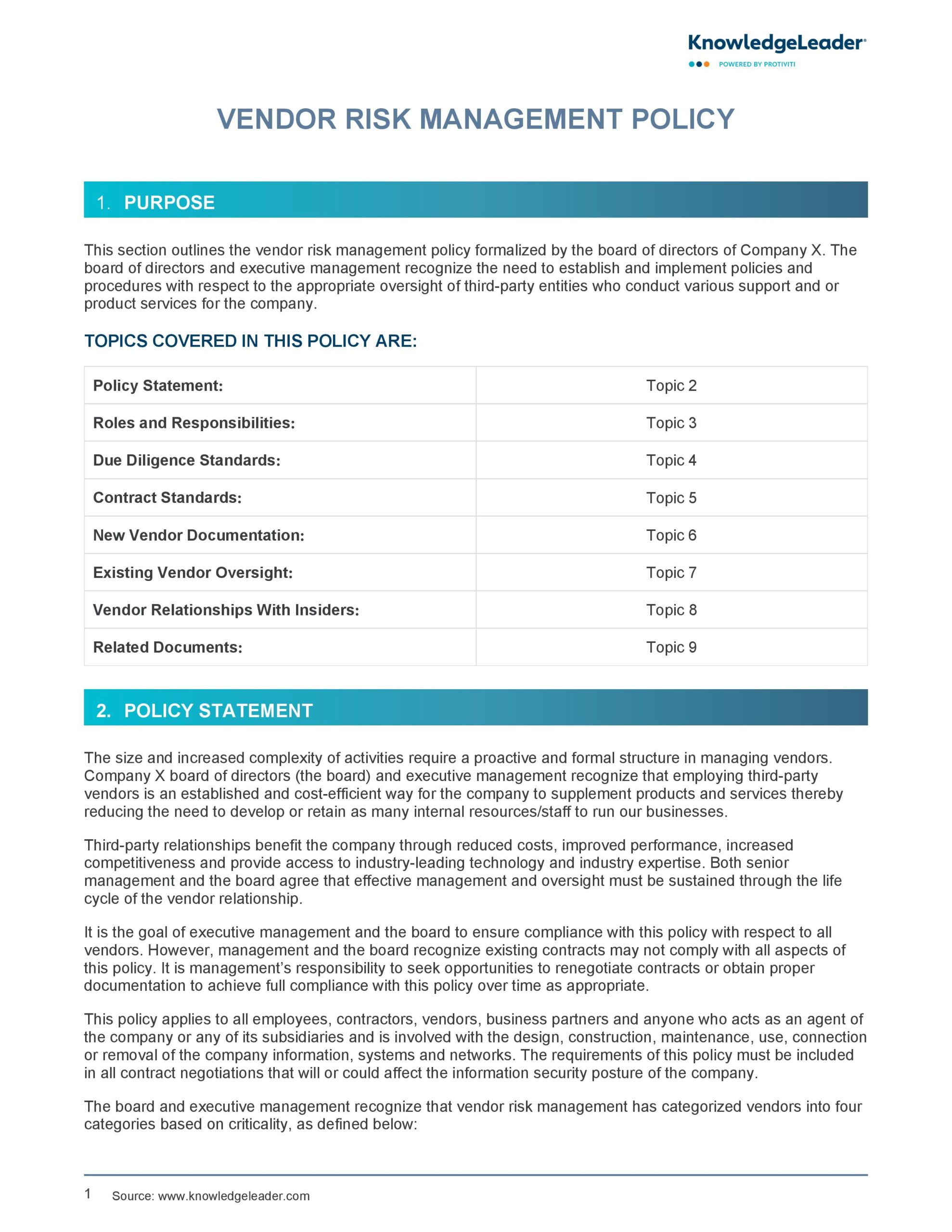
Consider the ever-growing list of compliance obligations, from GDPR and CCPA to HIPAA and the NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulation. Organizations are increasingly held accountable not only for their own security posture but also for that of their entire supply chain. A well-defined policy template acts as your compliance blueprint, ensuring that all third-party engagements align with these demanding regulatory requirements and internal security standards, thereby significantly reducing your exposure to potential fines and legal repercussions. Without such a framework, organizations face a reactive stance, trying to plug holes after incidents occur, rather than preventing them.
Key Benefits of Utilizing an Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template
Adopting a standardized Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template offers a multitude of strategic and operational advantages. Firstly, it fosters consistency in how all vendors are evaluated, onboarded, monitored, and offboarded. This uniformity eliminates guesswork and ensures that every third-party relationship adheres to the same stringent security baseline, regardless of the service they provide or the department they interact with.
Moreover, a well-crafted policy template acts as a powerful risk mitigation tool. It formalizes due diligence processes, ensuring that potential vendors undergo thorough security assessments before any data exchange or system integration takes place. This proactive vetting drastically reduces the likelihood of partnering with entities that pose unacceptable security risks. Furthermore, it clarifies contractual obligations, embedding critical data protection clauses and incident response protocols directly into agreements, providing a clear legal basis for accountability. The result is a more resilient security posture, streamlined vendor management, and enhanced trust among stakeholders and customers, knowing their data is handled with care.
Customizing Your Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template for Unique Needs
While an Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template provides a foundational structure, its true power lies in its adaptability. No two organizations are exactly alike; differences in size, industry, regulatory landscape, and risk appetite necessitate thoughtful customization. A small startup might focus on core cloud vendor security, while a large financial institution will require extensive controls for multiple types of service providers and adherence to specific financial regulations.
Tailoring your Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template involves adjusting various sections to reflect your company’s specific context. For instance, the scope section might be expanded or narrowed to include or exclude certain types of vendors. Your risk assessment methodology will need to align with your internal risk management framework and appetite. Furthermore, the policy should incorporate references to your existing internal security policies, data classification standards, and incident response plans. This ensures that the vendor management policy is not an isolated document but an integral, harmonized component of your broader information security program and overall compliance framework.
Important Elements to Include in Your Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template
A comprehensive Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template should cover the entire lifecycle of a vendor relationship, from initial engagement through termination. Here are the critical elements and fields that should be included:
- Policy Statement and Purpose: Clearly articulate the policy’s objective, which is typically to protect organizational information assets and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations when engaging with third-party vendors.
- Scope: Define which vendors and types of services are covered by the policy. This might include all third parties with access to sensitive data, IT systems, or critical business processes.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly assign who is accountable for each stage of the vendor management process, including ownership from legal, procurement, IT, and information security teams.
- Vendor Risk Assessment and Classification: Outline the methodology for assessing vendor risk levels (e.g., critical, high, medium, low) based on factors like data access, criticality of service, and potential impact of a breach.
- Due Diligence Procedures: Detail the steps for evaluating potential vendors prior to engagement, including security questionnaires, audits, background checks, and review of certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2).
- Contractual Requirements: Specify the mandatory security clauses to be included in all vendor contracts, such as data protection obligations, incident notification timelines, right-to-audit clauses, and liability limits.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Performance Management: Describe how vendor security performance will be continuously monitored, including periodic reviews, vulnerability assessments, and performance metrics (SLAs).
- Incident Response and Breach Notification: Establish clear protocols for how vendors must respond to security incidents involving your data, including notification timelines, communication channels, and cooperation requirements.
- Vendor Offboarding and Termination: Detail the process for securely concluding vendor relationships, including data return/destruction, access revocation, and confirmation of security posture post-contract.
- Training and Awareness: Outline requirements for vendor personnel to undergo security awareness training relevant to their access and responsibilities.
- Policy Review and Updates: Specify a regular schedule for reviewing and updating the Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template to ensure it remains current with evolving threats and regulatory changes.
- Exceptions Process: Describe the procedure for requesting and approving exceptions to the policy, along with clear documentation requirements.
- Definitions: Provide a glossary of key terms used throughout the policy for clarity and consistency.
Design, Usability, and Implementation Tips for Your Policy Template
Even the most comprehensive Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template will be ineffective if it’s not user-friendly and practically implementable. Design and usability are crucial for ensuring adoption and adherence across the organization. Start by structuring the document logically with clear headings and subheadings, making it easy to navigate. Use straightforward, unambiguous language, avoiding overly technical jargon where possible, so that it’s understandable to both security professionals and business stakeholders.
For digital implementation, consider hosting the policy on an accessible internal portal or knowledge base, allowing for easy search and version control. Ensure it’s compatible with various devices for on-the-go access. If a print version is necessary for official sign-offs or compliance audits, ensure it has a professional layout, clear page numbering, and designated areas for signatures and dates. Beyond the document itself, effective implementation requires robust communication and training. Develop a rollout plan that includes awareness sessions for relevant departments, ensuring they understand their roles and the importance of adhering to the Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template. Regular reviews and updates, coupled with mechanisms for feedback, will keep the policy alive and relevant, transforming it from a static document into an active tool for risk management.
Embracing a well-crafted Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template is more than just a compliance checkbox; it’s a strategic investment in your organization’s resilience and trustworthiness. In an era where data breaches can severely impact reputation and bottom line, having a clear, actionable framework for managing third-party risks is non-negotiable. It transforms reactive firefighting into proactive risk mitigation, giving you greater control over your extended digital perimeter.
By integrating this indispensable tool, your organization can foster stronger, more secure relationships with its vendors, ensuring that the benefits of external partnerships are realized without compromising your vital information assets. Consider making the development and implementation of a tailored Information Security Vendor Management Policy Template a top priority—it’s a foundational step towards building an unassailable security posture in an increasingly interconnected world.


