In the intricate landscape of modern healthcare, where patient care intersects with stringent regulatory requirements and technological advancements, the integrity and accessibility of health information are paramount. Navigating this complexity demands not just robust systems, but also clear, comprehensive guidelines that dictate how health data is managed, protected, and utilized. This is precisely where a well-crafted Legal Health Record Policy Template becomes an indispensable asset, serving as the foundational blueprint for an organization’s approach to information governance and patient privacy.
Imagine a world where every piece of patient information, from the initial consultation note to the final discharge summary, is handled with consistent precision, adhering to both internal best practices and external legal mandates. A Legal Health Record Policy Template transforms this vision into reality, providing a standardized framework that mitigates risk, ensures compliance, and fosters an environment of trust. Healthcare providers, legal counsel, compliance officers, and IT professionals alike stand to benefit immensely from such a document, as it clarifies roles, defines procedures, and ultimately safeguards the sensitive data at the heart of patient care.
Why a Legal Health Record Policy Template is Essential in Today’s Context
The digital transformation sweeping through healthcare, coupled with an ever-evolving regulatory environment, makes a robust Legal Health Record Policy Template more critical than ever. We’re living in an era dominated by electronic health records (EHRs), telehealth services, and sophisticated data analytics, all of which generate vast amounts of protected health information (PHI). Without a definitive policy, organizations face significant risks related to data breaches, non-compliance fines, and erosion of patient trust.
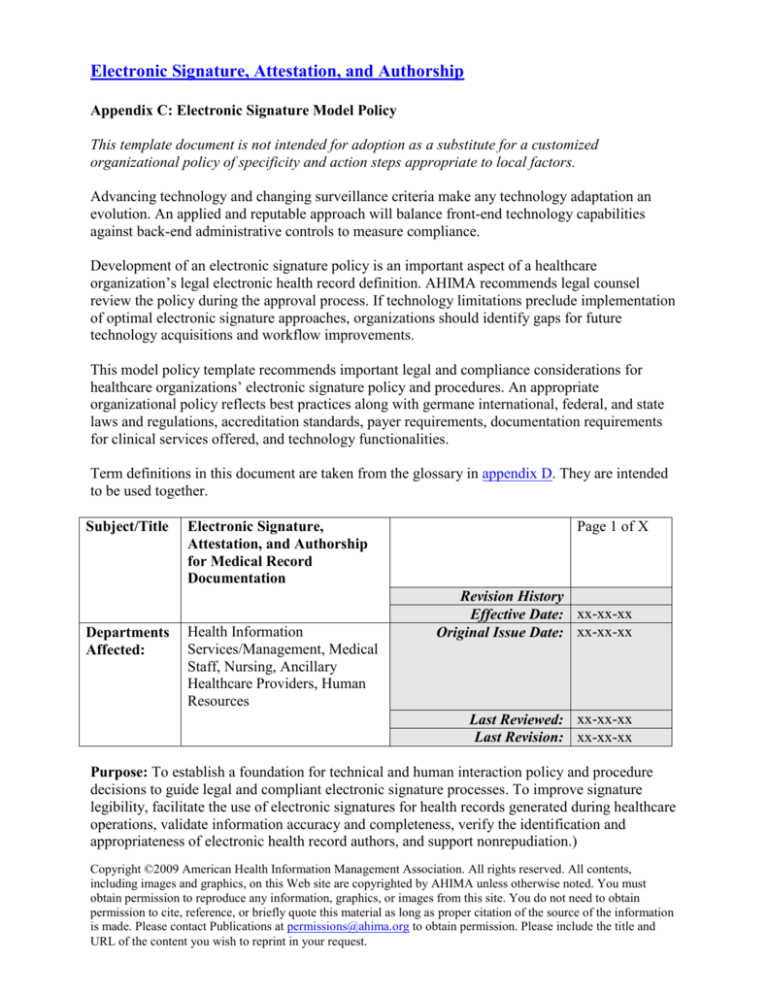
Consider the implications of HIPAA and HITECH Acts in the United States, which impose strict rules on the privacy and security of PHI. A Legal Health Record Policy Template acts as your organization’s internal compass, guiding all staff members on their legal obligations and ensuring that compliance is not just an aspiration but a tangible, repeatable process. It addresses the challenges posed by fragmented data sources, varying state laws concerning record retention, and the increasing demand for interoperability, providing clarity amidst potential confusion.
Key Benefits of Using a Legal Health Record Policy Template
Adopting and diligently implementing a Legal Health Record Policy Template offers a multitude of strategic and operational advantages. Foremost among these is the standardization of record-keeping practices across all departments and care settings. This consistency is vital for patient safety, accurate billing, and seamless care coordination, ensuring that everyone accessing health data understands what constitutes the official legal record.
Beyond standardization, a robust Legal Health Record Policy Template significantly enhances risk management. By clearly defining what information comprises the legal health record, how it’s maintained, and who can access it under what circumstances, organizations can proactively minimize the likelihood of data breaches, accidental disclosures, or legal challenges arising from incomplete or inaccurate records. It provides a defensible position in litigation and simplifies audit processes, demonstrating a commitment to patient privacy and data security. Furthermore, it streamlines training for new and existing staff, clearly outlining their responsibilities regarding information governance and compliance with workplace rules.
How a Legal Health Record Policy Template Can Be Customized and Adapted
No two healthcare organizations are identical, which is why the inherent adaptability of a Legal Health Record Policy Template is one of its greatest strengths. While the core principles of information governance remain universal, the specific operational nuances of a large hospital system will differ significantly from a small specialty clinic, a telehealth provider, or a long-term care facility. The template serves as a robust starting point, offering a comprehensive framework that can be meticulously tailored to an organization’s unique structure, services, and technological infrastructure.
Customization might involve integrating specific state-level regulations that go beyond federal HIPAA requirements, or adapting sections to reflect the particular EHR system in use. For example, a facility specializing in mental health might have additional considerations for highly sensitive information, while a research institution would need to incorporate policies related to de-identified data and research protocols. The flexibility of a Legal Health Record Policy Template allows for the inclusion of specific departmental procedures, unique data elements, or particular legal obligations tied to grants or partnerships, ensuring the policy is truly reflective of the organization’s real-world operations.
Important Elements That Should Be Included in a Legal Health Record Policy Template
A truly effective Legal Health Record Policy Template must be comprehensive, covering all critical aspects of health information management from creation to destruction. Each section should be clearly defined and meticulously detailed to leave no room for ambiguity.
Here are the important elements or fields that should be included:
- Policy Statement and Purpose: A concise declaration of the policy’s intent, emphasizing compliance, patient privacy, and data integrity.
- Scope: Clearly delineate who and what the policy applies to (e.g., all employees, contractors, volunteers, all forms of health information – electronic, paper, verbal).
- Definitions: A glossary of key terms (e.g., Legal Health Record, Protected Health Information (PHI), Designated Record Set, Custodian of Record, Electronic Health Record (EHR)).
- Components of the Legal Health Record: A detailed list of what specific documents and data elements constitute the official legal health record for the organization. This often includes clinical notes, lab results, imaging reports, billing records, and more.
- Record Creation and Documentation Standards: Guidelines on accurate, timely, legible, and complete documentation, including authorship, authentication, and correction procedures.
- Record Integrity and Authentication: Policies for ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and trustworthiness of health information, including electronic signatures and audit trails.
- Access, Disclosure, and Use: Rules governing who can access the legal health record, under what circumstances, and for what purposes, aligning with HIPAA’s Privacy Rule. This includes patient rights to access their own records.
- Record Amendment and Correction: Procedures for how patients can request amendments to their health information and how corrections are made to the record.
- Record Retention and Destruction: Adherence to federal and state statutes, as well as accreditation standards, regarding the length of time records must be kept and secure methods for their destruction.
- Security and Confidentiality: Measures to protect the legal health record from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure, encompassing both physical and technical safeguards as per HIPAA’s Security Rule.
- Legal Holds and Litigation: Procedures for preserving records in anticipation of or during litigation, ensuring no destruction or alteration occurs.
- Information Governance and Oversight: Designating roles and responsibilities for policy maintenance, compliance monitoring, and staff training.
- Training and Education: Requirements for staff training on the Legal Health Record Policy Template and related information governance principles.
- Non-Compliance and Sanctions: Consequences for violating the policy, including disciplinary actions.
- Policy Review and Updates: A schedule for regular review and revision of the policy to ensure it remains current with regulatory changes and organizational practices.
Tips on Design, Usability, and Implementation
A policy, however well-written, is only as effective as its implementation. When designing and deploying your Legal Health Record Policy Template, focus heavily on usability and accessibility to ensure it becomes a living document rather than just a binder on a shelf. For both print and digital versions, clarity and conciseness are paramount.
Use clear, straightforward language, avoiding excessive jargon where possible. Employ headings, subheadings, bullet points, and numbered lists to break up text and make it easy to digest. For digital versions, ensure the document is easily searchable and accessible via your internal network or compliance portal. Consider creating executive summaries or quick reference guides for specific roles, distilling the most critical information relevant to their daily tasks. Implementation should be accompanied by comprehensive training programs, not just a one-time overview. Regular refresher courses and ongoing communication about policy updates are essential. Establish clear communication channels for staff to ask questions or report concerns, fostering a culture of compliance and continuous improvement.
In the complex tapestry of modern healthcare, the Legal Health Record Policy Template stands as a beacon of clarity and control. It’s more than just a document; it’s a commitment to safeguarding patient data, upholding legal and ethical standards, and ensuring the operational excellence of your organization. Investing time and resources into developing, customizing, and rigorously implementing such a policy is not merely a compliance task, but a strategic imperative.
By embracing a well-structured Legal Health Record Policy Template, healthcare providers can navigate the intricate world of information governance with confidence, protect their patients’ most sensitive data, and build an unshakeable foundation for trust and accountability. It’s an essential tool that underpins all aspects of patient care, operational efficiency, and legal defensibility in an ever-changing digital health landscape. Consider it the bedrock of your information governance strategy – an invaluable asset for today and the future.