In today’s hyper-connected digital landscape, the phrase "data is the new oil" has become a stark reality for organizations of all sizes. Protecting this invaluable asset isn’t just a best practice; it’s a fundamental requirement for business continuity, customer trust, and regulatory compliance. At the heart of this protection lies a robust access control framework, and a well-crafted Logical Access Control Policy Template serves as the bedrock for establishing, enforcing, and managing who can access what, when, and how within your digital ecosystem.
Imagine the sheer complexity of managing user access across countless systems, applications, and data repositories without a clear, consistent set of rules. It’s a recipe for chaos, security vulnerabilities, and potential data breaches. That’s where a Logical Access Control Policy Template steps in, offering a structured approach to define permissions, safeguard sensitive information, and ensure that only authorized individuals have the necessary privileges to perform their duties. It’s not just a document; it’s a proactive shield against unauthorized access, internal threats, and the costly repercussions of security incidents.
Why a Logical Access Control Policy Template is Essential
In an era defined by sophisticated cyber threats and stringent data protection regulations, a Logical Access Control Policy Template is no longer a luxury but a critical necessity. The evolving regulatory landscape, including mandates like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, places significant responsibility on organizations to protect personal and sensitive data. Without a clear and enforceable logical access control policy, meeting these compliance obligations becomes an uphill battle, exposing businesses to hefty fines and reputational damage.
Furthermore, the rising tide of data breaches underscores the importance of a strong security posture. A comprehensive Logical Access Control Policy Template provides a framework for minimizing the attack surface by ensuring the principle of "least privilege" is applied across all user accounts. This means users only get the access they absolutely need to do their jobs, significantly reducing the risk of a breach through compromised credentials or insider threats. It also forms a cornerstone of a robust information security management system, demonstrating due diligence and a commitment to data security to auditors, partners, and customers alike.
Key Benefits of Using a Logical Access Control Policy Template
Adopting a well-designed Logical Access Control Policy Template offers a multitude of tangible benefits that extend far beyond simply ticking a compliance box. Firstly, it brings much-needed standardization and consistency to access management across your entire organization. Instead of disparate, ad-hoc procedures, you establish a unified approach, ensuring everyone understands the rules and expectations for logical access. This uniformity reduces administrative overhead and minimizes human error.
Secondly, a Logical Access Control Policy Template significantly enhances your overall security posture. By clearly defining roles, responsibilities, and access levels, it creates a robust defense against unauthorized access. This proactive stance helps in preventing data theft, intellectual property loss, and system compromise. It also streamlines audit processes, as the clearly documented procedures make it easier to demonstrate compliance with internal policies and external regulations, saving valuable time and resources during audits.
Moreover, such a template facilitates effective risk management. By identifying critical data assets and mapping appropriate access controls, organizations can proactively address potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited. It fosters a culture of security awareness among employees by setting clear expectations and consequences for non-compliance, thereby reducing the likelihood of inadvertent security lapses. Finally, it acts as a foundational element for business continuity, ensuring that even during personnel changes or emergencies, access to critical systems and data is managed systematically and securely.
Customizing Your Logical Access Control Policy Template
While a Logical Access Control Policy Template provides an excellent starting point, it’s crucial to understand that it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Every organization has unique operational requirements, a distinct technological landscape, and varying levels of data sensitivity. Therefore, effective customization is paramount to ensure the policy truly serves your specific needs and context.
Small businesses, for instance, might require a more streamlined policy focusing on core systems and basic user roles, emphasizing ease of implementation and management. In contrast, large enterprises with complex IT infrastructures, multiple departments, and diverse international operations will need a more granular and sophisticated policy. This could involve detailed segmentation of duties, specific provisions for various geographic regions, and integration with advanced identity and access management (IAM) solutions.
Industry-specific regulations also play a significant role in customization. A healthcare provider, for example, must heavily emphasize HIPAA compliance within its Logical Access Control Policy Template, detailing specific controls for protected health information (PHI). Financial institutions will incorporate requirements from FINRA or PCI DSS, while defense contractors will adhere to NIST guidelines. Adapting the template to reflect these specific regulatory landscapes ensures that your access controls are not only effective but also legally compliant, providing a tailored framework that genuinely strengthens your organization’s security and governance.
Important Elements to Include in Your Logical Access Control Policy Template
A truly effective Logical Access Control Policy Template must be comprehensive, covering all critical aspects of managing user access throughout its lifecycle. Here are the essential elements and fields that should be included:
- Policy Statement and Purpose: A clear declaration of the policy’s intent, its scope (e.g., all employees, contractors, systems, data), and the principles it upholds (e.g., least privilege, need-to-know).
- Definitions: A glossary of key terms (e.g., user, system owner, privileged access, multi-factor authentication) to ensure consistent understanding across the organization.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define who is responsible for what, including system owners, data owners, security administrators, managers, and end-users.
- Access Request and Provisioning Procedures: Detailed steps for how access is requested, approved, provisioned, and documented for various systems and data types.
- Access Review and Revalidation: Guidelines for regular reviews of user access rights to ensure they remain appropriate and necessary, especially following job changes or project completion.
- Access Revocation Procedures: A clear process for promptly removing access when an employee leaves the organization, changes roles, or is no longer authorized.
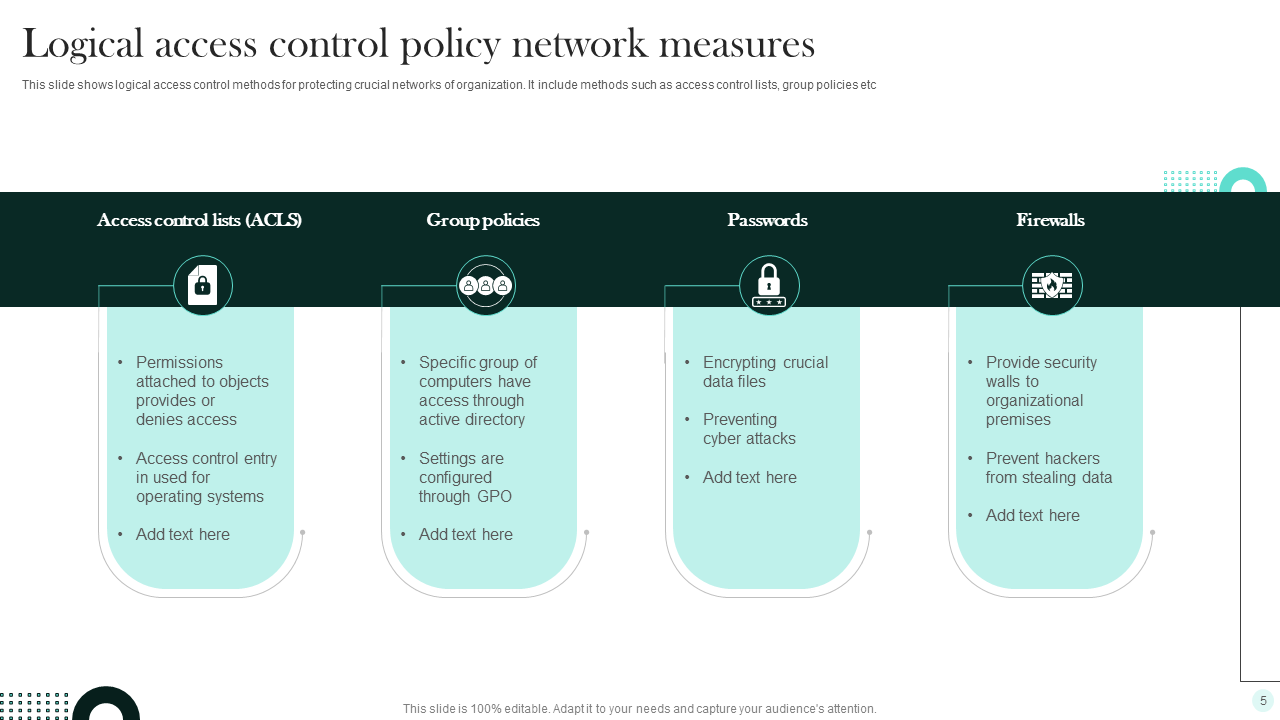
- Password Management Requirements: Specific rules for password complexity, length, history, and regular changes, as well as guidelines for secure storage and handling.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requirements for implementing and using MFA for accessing critical systems and sensitive data, enhancing identity verification.
- Principle of Least Privilege: A strong mandate that users are granted only the minimum necessary access to perform their job functions.
- Segregation of Duties (SoD): Policies designed to prevent a single individual from having control over multiple critical steps in a process that could lead to fraud or error.
- Remote Access: Specific controls and requirements for accessing organizational resources from outside the corporate network, including VPN usage and endpoint security.
- Third-Party and Vendor Access: Clear guidelines and controls for granting and managing access for external parties, ensuring contractual obligations and security standards are met.
- Data Classification Guidelines: How data is categorized (e.g., public, internal, confidential, restricted) and how these classifications dictate access levels.
- Incident Response Integration: How access control policies fit into the broader incident response plan, especially in cases of unauthorized access or breaches.
- Policy Enforcement and Consequences: What actions will be taken in cases of non-compliance, ranging from disciplinary action to legal repercussions.
- Policy Review Cycle: A schedule for regular review and updates to the Logical Access Control Policy Template to ensure it remains current with technological changes and organizational needs.
Tips for Design, Usability, and Implementation
A Logical Access Control Policy Template is only as effective as its adoption and understanding within the organization. Therefore, its design, usability, and implementation strategy are crucial. Firstly, aim for clarity and conciseness. Avoid overly technical jargon where possible, or provide clear explanations. Use plain language that all employees, regardless of their technical background, can understand. Well-structured headings, bullet points, and an intuitive layout can significantly improve readability.
For usability, consider how employees and administrators will interact with the policy. If it’s a digital document, ensure it’s easily searchable and accessible via your intranet or an organizational knowledge base. Version control is paramount; clearly mark the current version, revision history, and approval dates to avoid confusion. If a print version is necessary, ensure it’s legible and distributed to relevant personnel, perhaps as part of new employee onboarding documentation.
Implementation goes beyond simply publishing the document. It requires a comprehensive training and awareness program. Conduct mandatory training sessions for all employees, explaining the "why" behind the policy, not just the "what." Emphasize their role in upholding information security and the importance of adhering to the Logical Access Control Policy Template. Regular refreshers and communication campaigns can reinforce these messages. Finally, integrate the policy into existing HR processes (e.g., onboarding, offboarding, job changes) and IT service management workflows to ensure seamless and consistent application, turning the document into a living, operational standard.
The journey to a robust cybersecurity posture is continuous, and a well-defined Logical Access Control Policy Template is an indispensable milestone on that path. It’s more than just a set of rules; it’s a strategic framework that empowers organizations to manage risk, ensure compliance, and safeguard their most valuable digital assets. By investing time and effort into creating, customizing, and effectively implementing a comprehensive Logical Access Control Policy Template, you are not just protecting data; you are fortifying your business against an ever-evolving threat landscape.
Embrace this essential tool not as a burden, but as a foundational element of your overall information security strategy. A proactive approach to logical access control, guided by a thoughtfully developed Logical Access Control Policy Template, will undoubtedly lead to enhanced operational efficiency, reduced security vulnerabilities, and greater peace of mind in our digital-first world. Make it a priority to review, adapt, and integrate this critical policy into the fabric of your organization’s security culture.


