In the fast-paced world of product development, where innovative ideas often compete with market realities, a clear, shared understanding is not just a luxury—it’s a necessity. Launching a successful product requires more than just a brilliant concept; it demands meticulous planning, deep market insight, and unwavering alignment across every department involved. Without a foundational document to guide this journey, even the most promising endeavors can falter, leading to wasted resources, missed opportunities, and ultimately, products that fail to resonate with their intended audience.
This is where the Market Requirements Document (MRD) steps in as a critical cornerstone. It acts as the compass for your product, articulating the market problems you intend to solve, the needs of your target customers, and the overarching vision for your offering. Far from being a rigid, bureaucratic exercise, a well-crafted MRD serves as a dynamic blueprint, ensuring that everyone—from engineers to marketers to sales teams—is pulling in the same direction, united by a common understanding of what needs to be built and why. It’s the essential bridge between market opportunity and product execution, ensuring that your next big idea truly meets a genuine demand.
What Exactly is a Market Requirements Document?
At its core, a Market Requirements Document is a strategic document that outlines the market needs and business opportunities for a product or service. It defines *what* the market wants and *why* it wants it, rather than *how* the product will be built (that’s typically the domain of a Product Requirements Document or PRD). The primary goal of an MRD is to articulate the problems faced by potential customers and the overarching business goals the product aims to achieve by solving those problems.
It synthesizes research into a cohesive narrative, providing context for the product’s existence and guiding subsequent development efforts. This essential document acts as a foundational agreement among key stakeholders, ensuring that all future decisions are anchored in a solid understanding of market demand and customer value. By focusing on external market factors, it sets the stage for a product that is truly market-driven.
Why Your Product Needs a Solid Market Requirements Document
Implementing a robust Market Requirements Document template offers a multitude of benefits that ripple through the entire product lifecycle. Firstly, it fosters **unparalleled clarity** across cross-functional teams. By clearly defining the problem, target audience, and desired outcomes, it eliminates ambiguity and reduces the chances of misinterpretation that can derail development. This clarity ensures that engineering builds the right solution, marketing communicates the right value, and sales targets the right customers.
Secondly, a well-defined requirements document is instrumental in achieving stakeholder alignment. It serves as a single source of truth that all departments—product, engineering, design, marketing, sales, and even executive leadership—can refer to. This common understanding minimizes internal friction, speeds up decision-making, and ensures that everyone is working towards shared, market-validated goals. Such alignment is crucial for efficient resource allocation and preventing costly reworks.
Furthermore, leveraging a detailed market needs document significantly improves product-market fit. By forcing teams to deeply understand customer pain points and market dynamics before building, it increases the likelihood of creating a product that truly resonates with its audience. This proactive approach helps reduce time-to-market by streamlining the development process, as decisions are based on pre-vetted market intelligence rather than assumptions. Ultimately, an effective requirements framework translates directly into products that are more successful, more profitable, and more impactful in the marketplace.
Key Components of an Effective Market Requirements Document
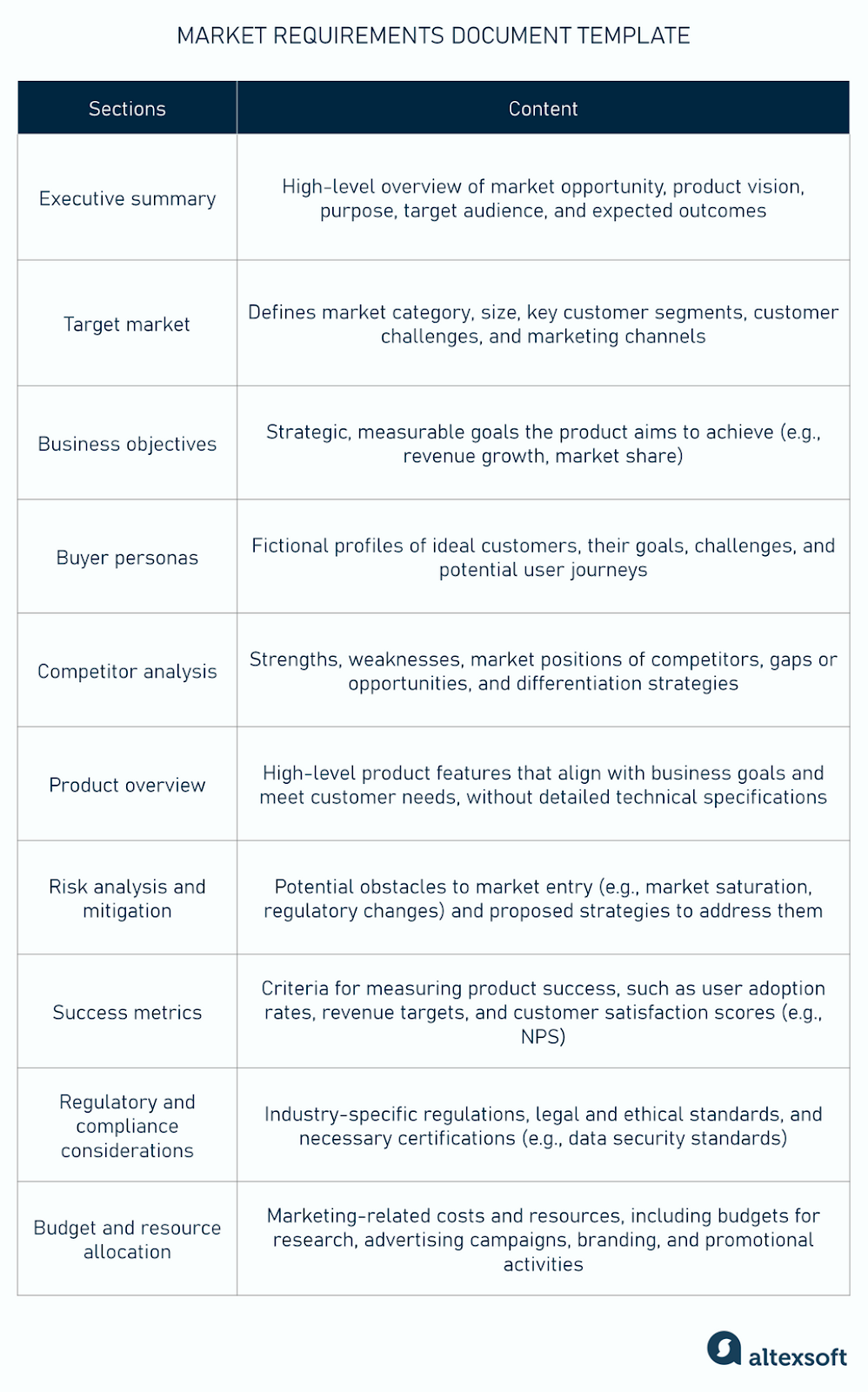
A comprehensive Market Requirements Document is structured to provide a holistic view of the market opportunity and product vision. While specific sections may vary slightly based on industry or company size, a robust requirements definition typically includes the following critical elements:
- **Executive Summary:** A concise overview of the entire document, highlighting the market opportunity, the problem to be solved, and the proposed solution. It should capture the essence of the document for quick executive review.
- **Target Market & Personas:** Detailed description of the ideal customer, including demographics, psychographics, behaviors, and specific pain points. Creating **user personas** brings your target audience to life, making their needs more tangible.
- **Market Problems/Needs:** A deep dive into the specific problems your target customers face that your product aims to address. Each problem should be clearly articulated and supported by market research, customer interviews, or data. This is the **core of the MRD**.
- **Product Vision & Business Goals:** A high-level statement of what the product will achieve and how it aligns with the company’s broader strategic objectives. This includes measurable business goals, such as revenue targets, market share, or customer acquisition metrics.
- **Key Features & Functionality (High-Level):** A conceptual outline of the core capabilities and features required to solve the identified market problems. This section describes *what* the product will do from a user perspective, without detailing technical implementation. For example, “Users must be able to securely log in” rather than “Implement OAuth 2.0.”
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** Important attributes that define the product’s quality and operational characteristics, such as **performance benchmarks**, scalability, security protocols, reliability, and usability standards.
- **Competitive Landscape:** An analysis of existing solutions in the market, identifying direct and indirect competitors, their strengths, weaknesses, and how your proposed product will differentiate itself.
- **Success Metrics & KPIs:** Clearly defined metrics that will be used to measure the product’s success in the market. These could include adoption rates, customer satisfaction scores, retention rates, or specific financial indicators.
- **Go-to-Market Considerations:** A preliminary outline of how the product will be launched and promoted. This might include pricing strategies, distribution channels, and high-level marketing strategies.
Crafting Your Document: Best Practices and Tips
Developing a powerful Market Requirements Document goes beyond simply filling in sections; it requires strategic thought and effective collaboration. Firstly, **start with the “why.”** Before detailing any features, clearly articulate the market problem and customer pain points. This ensures your product is truly solving a need, not just building a feature set. The emphasis should always be on market validation.
Secondly, collaborate widely but designate a single owner. While input from sales, marketing, engineering, and customer support is invaluable, a product manager or designated lead should be responsible for synthesizing this input and owning the document’s coherence and finalization. This prevents the document from becoming a fragmented collection of ideas.
Thirdly, keep it concise and focused on high-level requirements. The MRD is not a technical specification. Avoid getting bogged down in implementation details; instead, describe the desired outcomes and functionalities from a market perspective. Use clear, unambiguous language to minimize misinterpretation. Remember that this product strategy blueprint should be accessible to all stakeholders.
Finally, treat it as a living document. The market is constantly evolving, and your MRD should reflect these changes. Schedule regular reviews and be prepared to iterate based on new market intelligence, competitive shifts, or evolving customer needs. An adaptive requirements definition remains relevant and continues to guide your product effectively over time.
From Concept to Launch: How the MRD Guides Your Journey
The Market Requirements Document isn’t just a static artifact; it’s a dynamic guide that influences every stage of the product development lifecycle. In the initial **ideation phase**, it acts as a filter, helping teams validate new ideas against established market needs and business objectives, ensuring only the most promising concepts move forward. It provides the rationale that fuels initial brainstorms and feasibility studies.
As the product moves into design and development, the MRD serves as the authoritative source for defining the scope and priorities. Product managers use it to inform the creation of more detailed Product Requirements Documents (PRDs) and user stories, while designers refer to it to ensure user interfaces effectively address target user pain points. For engineers, it explains the underlying business context, helping them make more informed technical decisions that align with market goals.
During testing and quality assurance, the market requirements outlined in the document provide a benchmark for evaluating whether the product truly solves the intended problems and meets the expectations of the target market. Even after launch, this comprehensive product planning guide remains relevant, influencing marketing campaigns by providing key messaging points and sales strategies by defining the core value proposition. It’s the consistent thread that connects market opportunity to a successful product in the hands of customers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a Market Requirements Document the same as a Product Requirements Document?
No, while closely related, they serve different purposes. The MRD (Market Requirements Document) focuses on *what* the market wants and *why* (market problems, customer needs, business goals). The PRD (Product Requirements Document) focuses on *how* the product will deliver that value (specific features, functionality, technical details, user stories). The MRD sets the strategic foundation, and the PRD details the tactical execution.
Who is typically responsible for creating an MRD?
Typically, a product manager or product marketing manager is responsible for leading the creation of the Market Requirements Document. They act as the voice of the market and the customer, gathering input from various stakeholders like sales, marketing, customer support, and executive leadership, and then synthesizing this information into the comprehensive market needs document.
How often should an MRD be updated?
An MRD should be considered a living document, not a one-and-done deliverable. It should be reviewed and updated regularly, especially when there are significant shifts in market conditions, competitive landscape, customer feedback, or business strategy. Quarterly or bi-annual reviews are a good practice, but major changes might warrant more frequent updates to keep the product development framework current.
Can a startup benefit from an MRD?
Absolutely. Startups, perhaps even more than established companies, benefit immensely from a clear market requirements definition. It helps validate their core idea, focus limited resources, attract investors by demonstrating market understanding, and avoid building products that no one wants. While it might be less formal than a large enterprise’s MRD, the underlying principles of understanding market problems are critical.
What’s the biggest mistake to avoid when writing an MRD?
The biggest mistake is focusing too much on solutions or technical specifications rather than clearly defining the market problems and customer needs. An MRD that becomes a list of features without a strong “why” behind them loses its strategic value and risks building a product that doesn’t truly solve a market problem. Keep the focus firmly on the market and the customer.
The journey from a nascent idea to a thriving product is fraught with challenges, yet illuminated by clarity. A well-articulated Market Requirements Document is your guiding light, transforming abstract concepts into actionable strategies. It serves as the bedrock upon which successful products are built, ensuring every step, every decision, and every line of code contributes to a solution that genuinely addresses market needs and delights customers.
Embrace the discipline of defining your market requirements thoroughly, and you empower your teams with a shared vision and a clear mission. This comprehensive approach minimizes guesswork, fosters collaboration, and significantly increases your product’s chances of achieving impactful market adoption and sustained success. Don’t just build a product; build the right product, guided by the wisdom of a well-crafted market needs document.


