In today’s data-driven world, organizations grapple with an overwhelming volume of information. The promise of actionable insights often gets lost in a swamp of inconsistent, redundant, and inaccurate data. This “dirty data” isn’t just an inconvenience; it actively erodes trust, impairs decision-making, and significantly inflates operational costs, becoming a silent saboteur of strategic initiatives.
The journey toward effective Master Data Management (MDM) often begins with a critical, foundational step: defining your needs with a robust Master Data Management Requirements Template. This isn’t merely a document; it’s a strategic framework that guides your organization through the intricate process of identifying, standardizing, and governing your most critical data assets. It ensures that everyone, from data architects to business stakeholders, is aligned on what needs to be achieved, why it matters, and how success will be measured.
The Undeniable Need for a Structured MDM Requirements Framework
Implementing a Master Data Management solution is a significant undertaking, impacting processes, technology, and people across the enterprise. Without a clear and comprehensive set of requirements, projects can easily drift off course, suffer scope creep, or fail to deliver the expected value. A well-defined blueprint for your master data strategy acts as your north star, preventing costly missteps and ensuring that your investment yields tangible benefits.
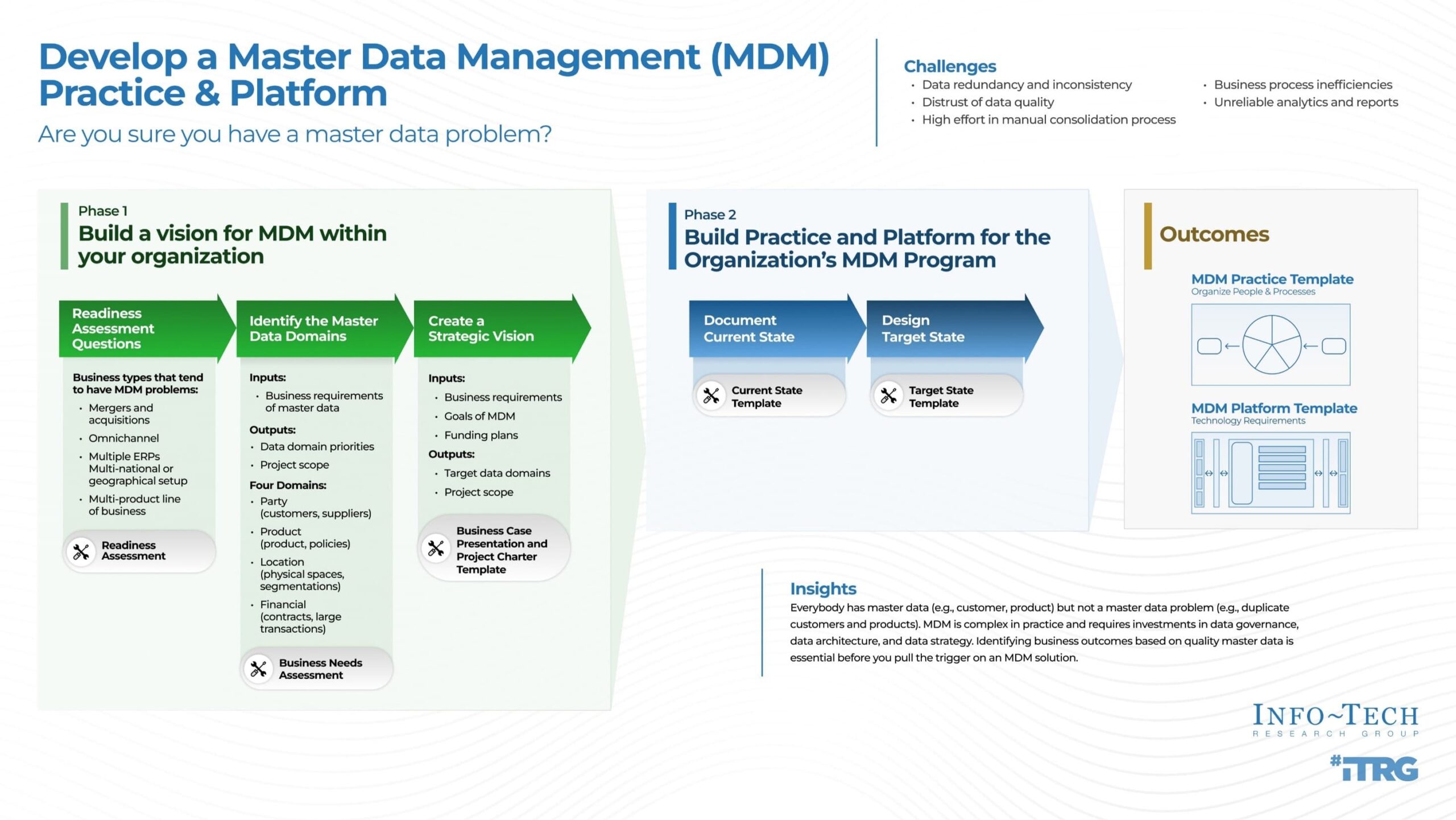
Many organizations jump into MDM initiatives without fully understanding the depth and breadth of their data challenges or the specific business problems they aim to solve. This often leads to solutions that are either over-engineered or insufficient, creating further frustration. A detailed requirements document provides the clarity needed to build an MDM system that truly serves the organization’s strategic goals, laying the groundwork for sustainable data governance.
Key Elements of a Robust Master Data Management Requirements Template
A comprehensive MDM project requires a meticulous approach to requirements gathering. Utilizing a well-structured Master Data Management Requirements Template ensures that no critical aspect is overlooked. Here are the essential components that should form the backbone of your data management requirements document:
- **Executive Summary and Business Justification:** Briefly outline the project’s purpose, scope, and the anticipated **business value**. Clearly state the problems being addressed and the strategic objectives.
- **Scope Definition:**
- **Data Domains in Scope:** Identify which master data domains (e.g., customer, product, supplier, location, asset) are part of this initiative.
- **Business Units/Departments Impacted:** List the internal teams that will be involved or affected by the MDM solution.
- **System Boundaries:** Define which source systems will feed data into the MDM hub and which consuming systems will receive master data.
- **Business Requirements:** Detail the **”what”** from a business perspective.
- **Problem Statements:** Specific challenges currently faced due to poor master data.
- **Desired Outcomes:** Measurable business benefits expected (e.g., reduced operational costs, improved customer satisfaction, faster time-to-market).
- **Critical Success Factors (CSFs):** Key elements that must be in place for the project to be deemed successful.
- **Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):** Metrics to track progress and measure success post-implementation.
- **Functional Requirements:** Describe the **”how”** the system should behave.
- **Data Acquisition:** How will data be ingested from source systems (batch, real-time, APIs)?
- **Data Standardization and Harmonization:** Rules for formatting, cleansing, and transforming data.
- **Data Matching and Merging (Survivorship):** Algorithms for identifying duplicate records and rules for creating a “golden record.”
- **Data Governance Workflow:** Processes for data stewardship, approval, and exception handling.
- **Data Distribution:** How master data will be disseminated to consuming applications.
- **Data Quality Rules and Monitoring:** Specific checks and reports to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
- **User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX):** Requirements for MDM user portals, dashboards, and reporting.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** Address system qualities and constraints.
- **Performance:** Response times, data processing throughput.
- **Scalability:** Ability to handle increasing data volumes and user loads.
- **Security:** Access controls, data encryption, audit trails.
- **Reliability and Availability:** Uptime targets, disaster recovery plans.
- **Usability:** Ease of learning and use for different user roles.
- **Maintainability:** Ease of support and upgrades.
- **Integration:** Specific protocols and technologies for connecting with other systems.
- **Technical Requirements:** Specific technology choices or constraints.
- **Platform and Infrastructure:** On-premise, cloud, specific operating systems, databases.
- **Development Standards:** Coding languages, architectural patterns.
- **Data Model Requirements:** High-level overview of entities, attributes, and relationships.
- **Data Governance and Stewardship Requirements:**
- **Roles and Responsibilities:** Clear definition of data owners, stewards, and custodians.
- **Data Policies:** Rules for data creation, modification, deletion, and usage.
- **Change Management:** Process for evolving data definitions and rules.
- **Reporting and Analytics Requirements:** What reports, dashboards, or data extracts are needed to monitor MDM effectiveness and data quality?
- **Training and Support Requirements:** Needs for user training, documentation, and ongoing support.
Benefits of a Well-Defined Requirements Structure
Adopting a comprehensive Master Data Management Requirements Template isn’t just a best practice; it’s a strategic imperative that yields numerous benefits across the organization. Foremost, it significantly **reduces project risk**. By clearly articulating what needs to be built and why, you minimize misunderstandings, prevent scope creep, and ensure that the solution aligns perfectly with business objectives from the outset. This clarity acts as a powerful shield against costly rework and delays.
Furthermore, a well-structured set of requirements enhances stakeholder alignment and communication. It provides a common language and a single point of truth for all parties involved, from technical developers to executive sponsors. This shared understanding fosters collaboration and ensures that everyone is working towards the same vision, leading to smoother project execution and greater buy-in. It also empowers your teams to make informed decisions by providing a robust framework for evaluating potential solutions and vendors.
Crafting Your Own Master Data Solution Blueprint
Developing an effective blueprint for your master data needs involves more than just filling out a form; it’s a dynamic process of discovery and collaboration. Start by engaging key business stakeholders early and often. Their insights into day-to-day operations and strategic objectives are invaluable for identifying critical data domains and business problems. Facilitate workshops and interviews to uncover pain points and desired outcomes, ensuring that the collected business requirements are comprehensive and truly reflect operational realities.
Translate these business needs into tangible functional and non-functional requirements. This requires a strong understanding of both business processes and technological capabilities. Prioritize these requirements based on business impact, feasibility, and dependencies. Not everything can be built at once, so an effective master data strategy outline will guide you in phasing the implementation, delivering value iteratively. Remember, this document is a living artifact; it should be reviewed and refined throughout the project lifecycle to adapt to evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even with a solid framework, MDM initiatives can stumble. One common pitfall is the **”big bang” approach**, attempting to solve all master data problems for all domains across the entire enterprise in a single, massive project. This often leads to overwhelming complexity and lengthy timelines, resulting in fatigue and budget overruns. Instead, adopt an iterative, phased approach, starting with a critical data domain that offers immediate business value and then expanding.
Another frequent error is underestimating the human element. MDM isn’t just a technology project; it’s a significant change management effort. Failing to secure strong executive sponsorship, involve data stewards early, or invest in comprehensive user training can derail even the most technically sound master data platform specifications. Focus on communication, education, and fostering a data-driven culture to ensure user adoption and sustained success. Don’t forget to define clear data governance requirements upfront, establishing ownership and accountability from day one.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of defining MDM requirements?
The primary goal is to clearly articulate the business needs, functional capabilities, and technical specifications required for an MDM solution to effectively address an organization’s master data challenges. This clarity ensures that the solution built aligns with strategic objectives, mitigates project risks, and delivers measurable business value. It acts as a foundational guide for the entire MDM implementation journey.
Who should be involved in developing the master data management requirements?
A diverse group of stakeholders should be involved, including business users (who understand data usage and pain points), data owners and stewards (who are accountable for data quality), IT professionals (architects, developers, security experts), project managers, and executive sponsors. Their collective input ensures a holistic view of the master data initiative requirements.
How often should master data management requirements be reviewed and updated?
Requirements should be considered living documents. They should be reviewed at key project milestones, during iterative development cycles, and whenever there are significant changes in business processes, data sources, or strategic objectives. Regular review ensures that the MDM solution remains relevant and continues to meet evolving organizational needs.
Can a single template serve all MDM projects?
While a core master data management requirements template provides an excellent starting point, it should always be customized to fit the specific needs, scope, and complexity of each individual MDM project. Different industries, organizational structures, and data domains will require unique considerations and detailed specifications. A flexible framework allows for adaptation while maintaining a structured approach.
Master Data Management is more than just a technological investment; it’s a fundamental shift towards treating data as a strategic asset. By meticulously defining your data management requirements, you equip your organization with the clarity and foresight needed to navigate this complex landscape successfully. This disciplined approach ensures that your MDM initiative not only meets but exceeds expectations, transforming fragmented data into unified, trusted intelligence.
Embracing a structured methodology for outlining your master data needs will accelerate your journey towards data mastery. It’s an investment in precision that pays dividends in operational efficiency, informed decision-making, and a sustained competitive advantage. Start building your comprehensive blueprint today, and lay the groundwork for a future where clean, consistent data fuels every facet of your enterprise.