In the intricate dance of manufacturing and supply chain management, precision is not just a virtue—it’s a necessity. Businesses worldwide grapple with the challenge of ensuring they have the right materials, in the right quantities, at the right time, without tying up excessive capital in inventory or, conversely, facing costly production delays due to shortages. This delicate balance often determines the thin line between profitability and missed opportunities, especially in today’s fast-paced, demand-driven markets.
Navigating this complexity effectively is where a robust framework for materials management becomes indispensable. Far from being a mere spreadsheet, a well-structured material requirement planning template serves as the backbone for operational efficiency, translating customer demand into a concrete plan for procurement and production. It’s a vital tool for manufacturers, distributors, and any business reliant on a steady flow of components, empowering them to forecast needs, optimize stock levels, and ultimately, meet customer expectations with unwavering reliability.
Understanding Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
Material Requirements Planning, or MRP, is a production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Most MRP systems are software-based, but at their core, they rely on a logical, structured approach to planning. The fundamental purpose of MRP is to ensure that materials are available for production and products are available for delivery, to maintain the lowest possible material and product levels in inventory, and to plan manufacturing activities, delivery schedules, and purchasing activities.
Essentially, MRP takes a "master production schedule" (MPS) – which outlines what products are to be manufactured and when – and breaks it down into the specific components and raw materials needed. It then calculates when these components and raw materials must be ordered or produced to meet the MPS. This process prevents stockouts, minimizes holding costs, and streamlines the entire production workflow, from initial order to final product shipment. It’s a proactive rather than reactive approach to inventory and production management.
The Power of an Effective MRP Template
While full-fledged MRP software systems are common in larger enterprises, many small to medium-sized businesses, or even specific departments within larger organizations, can benefit immensely from a well-designed Material Requirement Planning Template. This template provides a structured yet flexible framework that mimics the core logic of MRP software, allowing users to manually input data and generate critical insights. It democratizes the power of sophisticated planning, making it accessible and adaptable to various operational scales.
An effective MRP template isn’t just a data entry sheet; it’s a strategic asset. It helps visualize demand, calculate lead times, and project material needs, giving decision-makers a clear roadmap for procurement and production. By simplifying complex calculations into an intuitive format, it reduces the likelihood of human error, improves communication across departments, and enables more informed purchasing decisions. This transparency fosters greater control over the supply chain and significantly enhances operational agility.
Key Elements of a Robust Planning Document
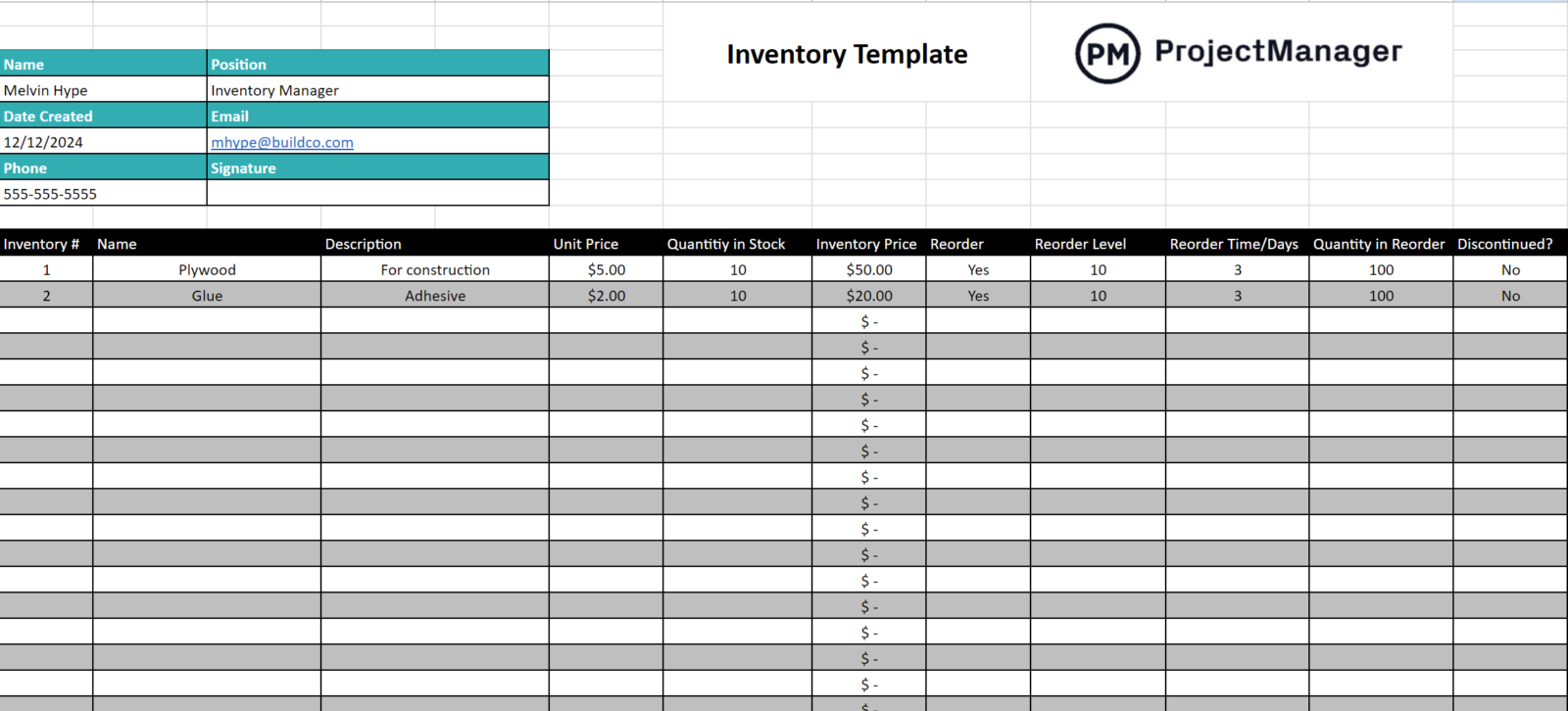
A truly useful materials planning document incorporates several crucial data points and calculation areas to function effectively. Without these components, the template would lack the necessary intelligence to provide accurate and actionable insights for resource allocation and scheduling. Understanding these elements is the first step toward customizing or developing a truly impactful tool for your operations.
Here are the essential components typically found in a comprehensive materials management framework:
- Master Production Schedule (MPS): This defines the quantity of finished products required and their scheduled completion dates. It’s the primary input that drives all subsequent material calculations.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): A detailed list of all raw materials, sub-assemblies, and components required to produce one unit of a finished product. Each item typically includes its quantity per unit of the parent item.
- Inventory Records: Current stock levels for all raw materials and components, including any allocated or reserved stock, as well as lead times for their procurement.
- Lead Times: The time required to obtain a material after an order is placed, whether through purchasing from a supplier or internal manufacturing.
- Safety Stock: An additional quantity of an item held in inventory to reduce the risk of stockouts due to variations in demand or supply.
- Order Quantities: The optimal or standard batch size for ordering or producing a particular item.
- Net Requirements: The actual quantity of materials needed for production, calculated after considering existing inventory and scheduled receipts.
- Planned Order Releases: The recommended dates and quantities for placing purchase orders or starting production orders to meet net requirements.
Benefits of Implementing a Materials Planning Tool
Adopting a systematic approach to material planning, even through a simplified production planning aid, yields a multitude of benefits that resonate throughout the entire organization. These advantages extend beyond mere inventory control, influencing financial health, customer satisfaction, and overall business competitiveness. It’s a foundational step towards operational excellence that provides tangible returns.
One of the most immediate benefits is reduced inventory costs. By accurately forecasting needs, businesses can avoid overstocking expensive components, freeing up capital that would otherwise be tied up in idle inventory. This also minimizes the risk of obsolescence and reduces warehousing expenses. Furthermore, a precise planning spreadsheet helps prevent production delays and stockouts, ensuring that all necessary components are available exactly when they are needed.
Moreover, a well-managed component requirement planner leads to improved customer service. By consistently meeting production schedules and delivery promises, businesses build trust and reliability with their clientele. It also fosters better communication and coordination across departments, aligning procurement, production, and sales teams around a single, unified plan. Ultimately, a strong supply chain planning tool drives enhanced operational efficiency and profitability, making the entire manufacturing process smoother and more cost-effective.
How to Use and Customize Your Inventory Planning Template
Leveraging an inventory planning template effectively requires a systematic approach, starting with accurate data input and moving through logical steps to generate actionable insights. The beauty of a template lies in its adaptability, allowing you to tailor it precisely to your business’s unique operational nuances and product catalog. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution but a powerful framework to be personalized.
Begin by populating the core data: enter your Master Production Schedule (MPS) with planned finished product quantities and dates. Next, input your Bill of Materials (BOM) for each product, ensuring all components and their respective quantities are listed accurately. Crucially, update your current inventory levels and lead times for every raw material and component. Regularly audit these numbers to ensure their accuracy, as outdated information can lead to significant planning errors.
To customize your stock management blueprint, consider adding columns for supplier information, minimum order quantities, or reorder points specific to your procurement policies. You might also integrate conditional formatting to highlight items nearing low stock or requiring immediate orders. For businesses with fluctuating demand, building in a buffer for safety stock calculations can provide an extra layer of protection against unexpected spikes or supply disruptions. Regularly review and refine the template based on your operational experience to continuously improve its utility and accuracy.
Choosing the Right Format for Your Production Planning Aid
The format of your production planning aid can significantly impact its usability and the efficiency of your planning process. While the underlying logic of Material Requirements Planning remains consistent, how you structure and present that information can make a world of difference. The choice often depends on your company’s size, existing software, and the complexity of your product offerings.
For many small to medium-sized businesses, a spreadsheet-based template (like Excel or Google Sheets) is often the most practical and accessible starting point. These platforms offer robust calculation capabilities, customizable cells, and the flexibility to integrate various data points. They are relatively easy to set up and modify without specialized IT knowledge. Another option might be a database-driven application for more complex needs, offering greater data integrity and scalability, though typically requiring more technical expertise to build and maintain.
Regardless of the chosen format, ensure that the interface is intuitive and easy to navigate. Cluttered or overly complex templates can lead to errors and resistance from users. Prioritize clear labeling, consistent data entry fields, and automated calculations where possible. A well-designed resource planning tool, regardless of its technical sophistication, should serve as a clear and unambiguous guide for your procurement and production teams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of using a Material Requirements Planning Template?
The primary goal is to ensure that all necessary materials and components are available when needed for production, while simultaneously keeping inventory levels as low as possible. This balances avoiding stockouts and production delays with minimizing holding costs and wasted capital.
How often should I update the data in my MRP template?
The frequency of updates depends on your business’s volatility and production schedule. For highly dynamic environments, daily or weekly updates of inventory levels and demand forecasts might be necessary. For more stable operations, monthly updates could suffice. The key is to keep the data current enough to support accurate planning decisions.
Can a spreadsheet-based planning template replace full MRP software?
While a spreadsheet-based materials planning template can be highly effective for smaller operations or specific planning tasks, it generally cannot fully replace comprehensive MRP software. Full MRP software offers greater automation, integration with other business systems (like accounting or CRM), advanced forecasting capabilities, and scalability that manual templates often lack. It is, however, an excellent starting point and a valuable tool for many businesses.
What challenges might I face when implementing a new production planning aid?
Common challenges include ensuring data accuracy and completeness, getting buy-in and training for all users, accurately estimating lead times, managing supplier variability, and dealing with unexpected demand fluctuations. Consistency in data entry and a commitment to regular updates are crucial for overcoming these hurdles.
Is this template suitable for service-based businesses?
While the core concept of a Material Requirement Planning Template is rooted in manufacturing and tangible goods, the principles of resource planning can be adapted. Service-based businesses might use similar frameworks to plan for human resources, equipment, or specific tools required for service delivery, though the specific elements would differ from raw materials and components.
Mastering your material flow is not merely an operational task; it’s a strategic imperative that underpins your ability to deliver on promises and compete effectively. A well-implemented Material Requirement Planning Template provides the clarity, control, and foresight needed to transform complex supply chain challenges into predictable and manageable processes. It empowers businesses to move beyond reactive problem-solving toward proactive strategic planning, ensuring that every component is accounted for and every production target is within reach.
By embracing this powerful planning tool, businesses can unlock significant efficiencies, reduce costs, and enhance their responsiveness to market demands. It’s an investment in precision that pays dividends in streamlined operations, improved cash flow, and ultimately, a more robust and reliable path to customer satisfaction and sustained growth. Start building your foundation for operational excellence today.