In the highly regulated world of medical device development, precision isn’t just a virtue; it’s a mandate. Every design choice, every component, and every line of code carries the weight of patient safety and regulatory compliance. At the heart of successfully navigating this intricate landscape lies a foundational document, one that acts as the North Star for your entire development journey: the Product Requirements Document (PRD). It’s not merely a list of features but a comprehensive blueprint defining what your medical device will be, how it will function, and what problems it will solve, all while adhering to the strictest quality and safety standards.
For both startups bringing groundbreaking innovations to market and established firms enhancing existing product lines, a robust PRD is indispensable. It bridges the gap between initial concept and final product, ensuring that all stakeholders—from engineers and designers to regulatory affairs and marketing teams—are aligned. This critical document clarifies expectations, minimizes misinterpretations, and provides a traceable link between user needs, system requirements, and verification activities, ultimately streamlining the path to market approval and successful commercialization.
The Unseen Blueprint: Why a PRD is Non-Negotiable for Medical Devices
Developing any medical device is a complex undertaking, rife with technical challenges and stringent regulatory hurdles. Without a clear, well-defined set of requirements, projects can easily derail, leading to costly redesigns, delays, and even regulatory non-compliance. A comprehensive product requirements document for medical devices serves as the single source of truth, articulating every facet of the device from a technical, operational, and regulatory perspective. It crystallizes the “what” before the “how,” providing a solid foundation before design and development even begin in earnest.
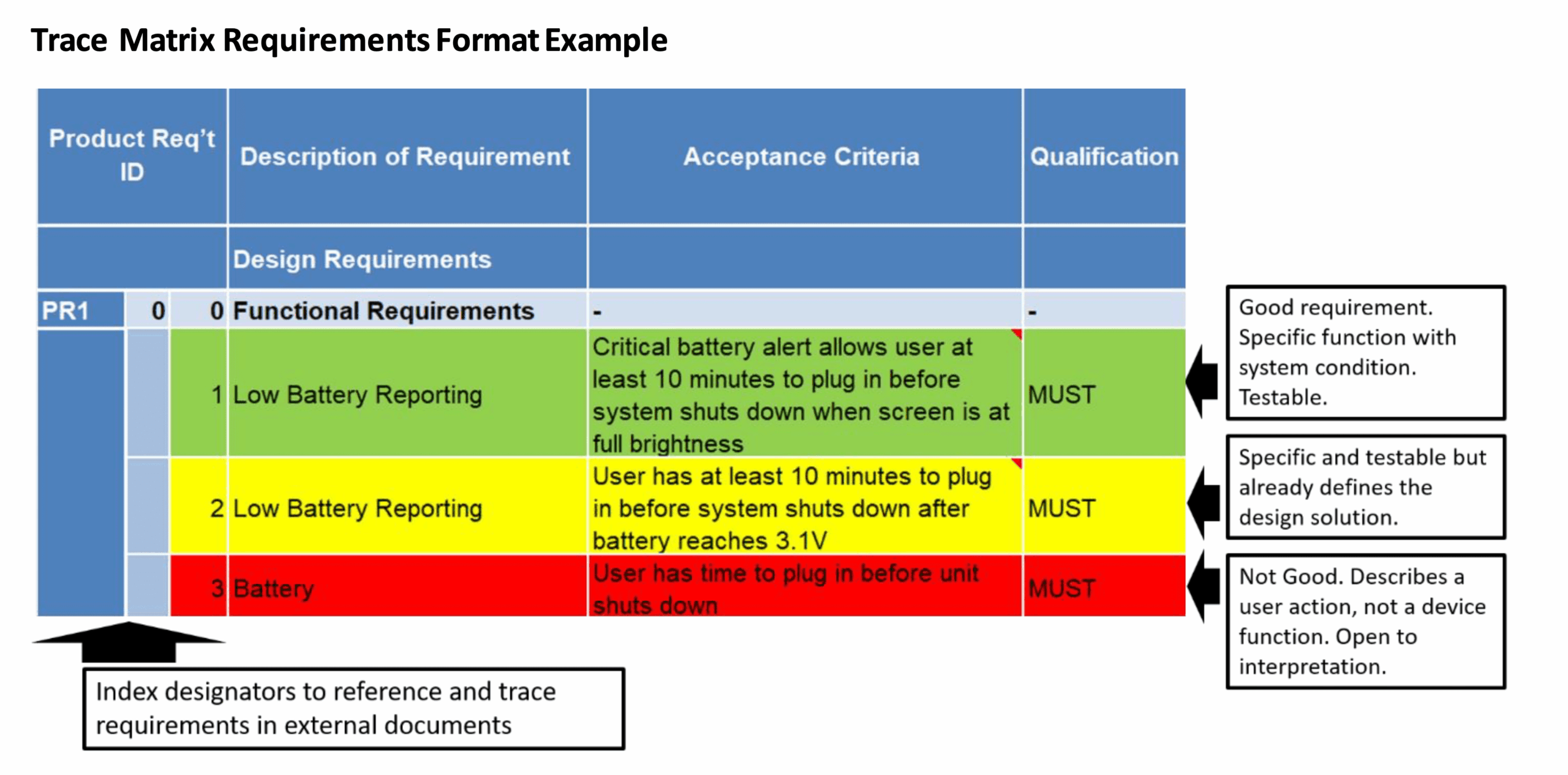
This detailed specification is particularly crucial in the medical sector because of the inherent risks involved. Unlike consumer electronics, medical devices directly impact human health, making errors potentially catastrophic. Regulatory bodies like the FDA in the United States demand meticulous documentation and traceability to ensure that devices are safe and effective. A well-structured PRD directly supports these requirements, acting as a living document that evolves with the project while maintaining an unbroken thread from initial user needs through design validation.
Core Benefits of a Structured Product Requirements Document
Implementing a robust product requirements specification offers a multitude of advantages that extend across the entire medical device lifecycle. From fostering clear communication to mitigating risks and accelerating market entry, its impact is profound and far-reaching. Embracing a disciplined approach to defining requirements can transform a potentially chaotic development process into a streamlined, predictable, and compliant one.
- Enhanced Clarity and Alignment: A clear set of requirements ensures everyone involved understands the device’s purpose, functionality, and constraints. This eliminates ambiguity and fosters consensus among cross-functional teams, reducing miscommunications and rework.
- Risk Mitigation: By meticulously documenting all product requirements, potential risks related to performance, safety, and regulatory compliance can be identified and addressed early in the development cycle, long before they become critical issues.
- Streamlined Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory bodies require demonstrable evidence that a device meets its intended use and safety standards. A well-maintained device requirements document provides a traceable link between user needs, design inputs, and verification activities, simplifying audits and submissions.
- Efficient Development and Resource Allocation: With precise requirements, development teams can work more efficiently, knowing exactly what needs to be built. This optimizes resource utilization, reduces scope creep, and keeps the project on schedule and within budget.
- Improved Product Quality: A thorough medical product documentation process leads to a better-designed product that more accurately meets user needs and performs reliably, enhancing patient outcomes and user satisfaction.
- Easier Testing and Validation: Defined requirements provide clear criteria for testing and validation activities, ensuring that the device is thoroughly vetted against its specified performance and safety parameters.
Key Elements of an Effective Medical Device PRD
While the specifics may vary depending on the device’s complexity and classification, an effective Medical Device Product Requirements Document Template typically encompasses a comprehensive range of sections. These sections collectively define the device, its environment, its users, and the regulatory framework it must operate within. Structuring these elements thoughtfully is paramount for clarity and utility.
- **Introduction and Purpose:** Briefly describe the device, its intended use, and the problem it aims to solve. This sets the stage for the entire document, providing context for all subsequent requirements.
- **Scope:** Clearly define what the device will and will not do. This prevents scope creep and ensures focus on essential functionalities.
- **User Needs (or Voice of Customer):** Detail the needs, goals, and pain points of the intended users (patients, clinicians, caregivers). These are often expressed qualitatively and form the basis for functional requirements.
- **Intended Use and Indications for Use:** Specific statements defining the precise medical conditions or purposes for which the device is intended. This is a critical regulatory statement.
- **Functional Requirements:** Describe what the device must *do*. These are often broken down into features and sub-features, detailing inputs, outputs, data processing, and user interactions.
- **Performance Requirements:** Specify *how well* the device must perform. This includes metrics for speed, accuracy, reliability, response time, and capacity, often quantifiable and testable.
- **Usability Requirements:** Detail how easily and effectively users can operate the device, including aspects like human-machine interface (HMI), learnability, intuitiveness, and error handling.
- **Safety Requirements:** Outline all measures to ensure the device is safe for its intended use, addressing potential hazards, failure modes, and risk control measures. This is paramount for medical devices.
- **Security Requirements:** For connected devices, this covers data protection, access control, cybersecurity measures, and compliance with privacy regulations like HIPAA.
- **Environmental Requirements:** Specify the conditions under which the device must operate and be stored, such as temperature, humidity, light, vibration, and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC).
- **Maintenance Requirements:** Define needs for calibration, serviceability, repair, and potential software updates, ensuring the device remains functional over its lifespan.
- **Regulatory and Compliance Requirements:** List all applicable standards (e.g., ISO 13485, IEC 62304), regulations (e.g., FDA 21 CFR Part 820), and directives specific to the target markets. This section is often detailed and references external documents.
- **Interoperability Requirements:** If the device interacts with other systems or devices, specify communication protocols, data formats, and compatibility standards.
- **Labeling and Packaging Requirements:** Describe necessary information on the device itself, its packaging, and accompanying documentation (user manuals, quick start guides).
- **Traceability Matrix:** While often a separate document, a PRD usually establishes the framework for tracing requirements to design inputs, test cases, and verification activities. This is crucial for regulatory submissions.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape with Your PRD
For medical device manufacturers, the product requirements document isn’t just a development tool; it’s a critical piece of the regulatory puzzle. In the United States, the FDA’s Quality System Regulation (21 CFR Part 820) mandates robust design controls, and your PRD forms the bedrock of these controls. It acts as the primary record for design inputs, which are the requirements that completely define a device. Every subsequent stage of design and development must trace back to these inputs, demonstrating that the final product consistently meets its initial specifications.
Similarly, international standards like ISO 13485:2016 (Medical devices – Quality management systems – Requirements for regulatory purposes) place strong emphasis on documenting requirements, planning, and design control. A well-executed PRD, especially when informed by a comprehensive medical device product requirements document template, directly facilitates compliance with these standards by providing a structured framework for capturing all necessary information. It aids in developing the design history file (DHF) and ultimately streamlines the submission process for market authorization, whether that’s a 510(k), PMA, or CE Mark.
Customizing Your Approach: Beyond the Template
While a robust medical device product requirements document template provides an excellent starting point, it’s crucial to remember that it is a tool, not a rigid constraint. Every medical device is unique, with varying levels of complexity, risk classification, and intended use. Therefore, customization is not just recommended, but essential. Adapt the template to fit the specific needs of your project, your organization’s quality system, and the regulatory nuances of your target markets.
Consider the audience for your device requirements document. Will it primarily be used by engineers, or does it need to be accessible to marketing and sales teams? Tailor the language and level of detail accordingly. For lower-risk devices, certain sections might be less extensive, while high-risk, complex devices will demand excruciating detail in areas like safety, cybersecurity, and performance. Involving a multidisciplinary team from the outset—including regulatory affairs, quality assurance, engineering, and clinical specialists—will ensure the template evolves into a document that truly serves your project’s distinct requirements.
Best Practices for Developing and Maintaining Your Medical Device PRD
Creating an effective device requirements document is an iterative process that benefits from careful planning and continuous refinement. Adopting best practices throughout its lifecycle ensures it remains a valuable and accurate resource. This proactive approach supports not only the initial development but also the long-term maintenance and evolution of your medical product documentation.
- Start Early, Iterate Often: Begin drafting your requirements as soon as the concept takes shape. The PRD is a living document; expect to refine and update it as your understanding of the device and its environment evolves.
- Engage Stakeholders Broadly: Involve representatives from all relevant departments—R&D, quality, regulatory, marketing, clinical, and even potential users—to ensure all perspectives are captured and buy-in is secured.
- Focus on Clarity and Unambiguity: Each requirement should be clear, concise, verifiable, and unambiguous. Avoid vague language that could lead to misinterpretation. Use objective criteria whenever possible.
- Ensure Traceability: Establish clear links between user needs, functional requirements, design inputs, verification plans, and test cases. This is non-negotiable for regulatory compliance and effective change management.
- Manage Changes Rigorously: Implement a formal change control process for your medical device PRD. Any modifications must be reviewed, approved, documented, and communicated to all affected stakeholders.
- Version Control: Utilize robust version control systems to track all revisions. This ensures that everyone is working with the most current information and provides an audit trail of changes over time.
- Regular Review and Updates: Schedule periodic reviews of the PRD throughout the product lifecycle, especially at key project milestones. This ensures its continued accuracy and relevance as the project progresses.
- Utilize Tools: Consider using requirements management software, particularly for complex devices, to manage traceability, version control, and stakeholder collaboration more efficiently than manual methods.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a medical device PRD?
The primary purpose of a medical device PRD (Product Requirements Document) is to comprehensively define all the requirements for a medical device. It serves as the authoritative source detailing what the device must do, how it will perform, and what standards it must meet, ensuring alignment among development teams and compliance with regulatory bodies.
Who typically contributes to a product requirements document?
A product requirements document is typically a collaborative effort. Key contributors include product managers, system engineers, regulatory affairs specialists, quality assurance professionals, clinical experts, human factors engineers, and software/hardware developers. Each brings a unique perspective to ensure the document is holistic and accurate.
How does a PRD differ from a design specification?
A PRD defines *what* the medical device needs to achieve from a user, business, and regulatory perspective, focusing on the problem to be solved and the desired outcomes. A design specification, in contrast, details *how* those requirements will be met, outlining the technical solutions, architecture, components, and implementation specifics. The PRD is an input to the design specification.
Is a template truly necessary for small medical device companies?
Yes, even for small medical device companies, utilizing a medical device product requirements document template is highly beneficial. It provides a structured framework, ensuring no critical aspects are overlooked, streamlining the documentation process, and making it easier to meet regulatory requirements without expending excessive resources on creating a format from scratch.
How often should a medical device PRD be updated?
A medical device PRD should be updated whenever there are changes to user needs, functional requirements, performance specifications, or regulatory guidance that impact the device. It’s a living document that needs regular review, especially at key project milestones, to ensure it always reflects the current state of the product definition and development.
Crafting a comprehensive and compliant product requirements document for your medical device is far from a mere administrative task; it is a strategic imperative. It stands as the cornerstone of successful medical device development, ensuring that innovation is pursued with diligence, safety is paramount, and regulatory pathways are navigated efficiently. By investing in a well-structured document, perhaps beginning with a robust medical device product requirements document template, you are not just listing requirements—you are laying the groundwork for a product that truly makes a difference in healthcare.
Embrace the power of detailed documentation to transform your medical device concept into a tangible, high-quality solution. A thoughtful and meticulously maintained PRD will not only guide your development team but also serve as a testament to your commitment to excellence, patient safety, and regulatory adherence, ultimately paving the way for a smoother journey from design bench to patient bedside.


