Developing software for medical devices is a unique challenge, one where precision, safety, and regulatory compliance are not merely goals but absolute necessities. In an industry where errors can have critical, even life-threatening, consequences, establishing a clear, comprehensive, and unambiguous foundation for your software development is paramount. This foundational document, often guided by a structured framework, serves as the blueprint that ensures every line of code contributes to a safe, effective, and compliant medical product.
This isn’t just about ticking a box; it’s about fostering clarity, reducing risk, and streamlining the entire development lifecycle. From concept to post-market surveillance, a well-crafted software requirements specification document ensures that all stakeholders—engineers, quality assurance, regulatory teams, and even marketing—are aligned on what the software must do, how it should behave, and under what conditions. A robust Medical Device Software Requirements Specification Template provides that essential structure, empowering teams to navigate the complexities of healthcare technology with confidence and control.
Why a Robust Software Requirements Specification is Crucial for Medical Devices
The stakes in medical device development are extraordinarily high. Unlike consumer electronics, a software malfunction in a medical device can directly impact patient health, leading to severe injuries or even fatalities. This inherent risk demands an equally rigorous approach to defining what the software is intended to achieve and how it will operate. A comprehensive software requirements specification for medical devices acts as the single source of truth, minimizing ambiguities and preventing costly misinterpretations that could lead to design flaws or regulatory non-compliance.
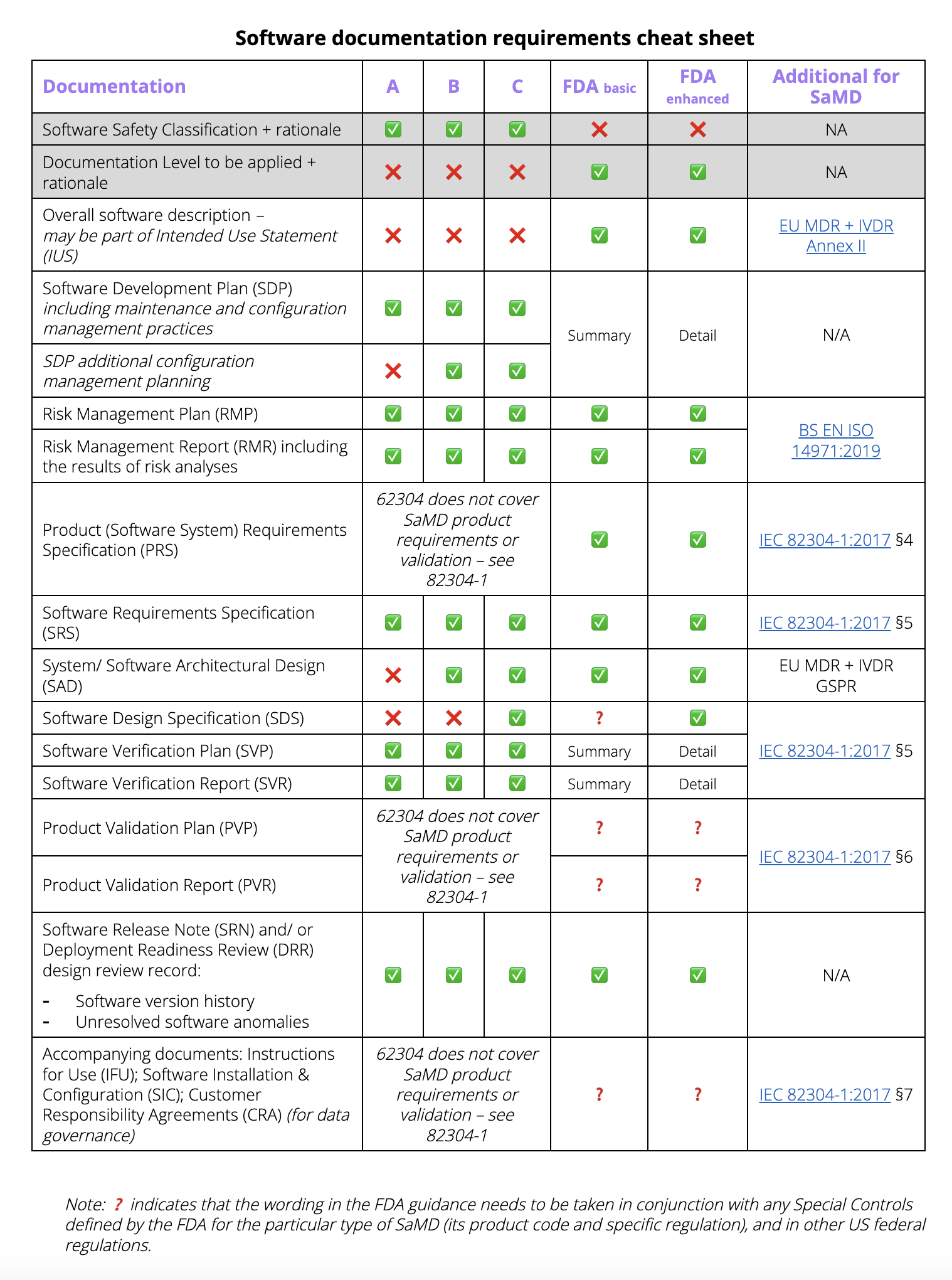
Beyond the immediate safety concerns, a detailed device software specification is indispensable for efficient project management. It provides a baseline for estimating development timelines, allocating resources, and tracking progress effectively. Without this foundational document, projects can drift, scope creep becomes rampant, and teams often find themselves revisiting design decisions, leading to significant delays and budget overruns. Ultimately, this proactive approach underpins the trust placed in medical technology by both healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The Anatomy of an Effective Device Software Specification
While specific content may vary depending on the device’s complexity and risk class, an effective medical device software requirements specification document generally encompasses several key sections designed to provide a holistic view of the software’s functionality and constraints. Adopting a structured framework, often derived from a reliable Medical Device Software Requirements Specification Template, ensures that no critical aspect is overlooked during the design and development phases.
Here are the essential components typically found in a well-structured software specification framework:
- **Introduction:** This section provides an overview of the document’s purpose, scope, and target audience. It also outlines any **definitions, acronyms, and abbreviations** used throughout, ensuring consistent understanding.
- **Overall Description:** Here, the document details the **product perspective**, placing the software within the context of the larger medical device. It defines user characteristics, operating environment, design and implementation constraints, and any assumptions or dependencies.
- **External Interface Requirements:** This crucial part specifies all interfaces the software will have with other systems, hardware, users, and communication protocols. This includes **user interfaces (UI), hardware interfaces, software interfaces**, and communication interfaces.
- **Functional Requirements:** This is the core of the specification, describing **what the software must do**. Each requirement should be clear, verifiable, unambiguous, and testable. These are typically organized by feature or subsystem.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** These define **how the software performs**. This category includes requirements related to performance (e.g., speed, response time), safety, security, reliability, usability, maintainability, and portability. For medical devices, **safety and security requirements** are particularly stringent.
- **Verification Requirements:** This section outlines the methods and criteria for **testing and verifying** that each requirement has been met. This is vital for demonstrating compliance with design inputs.
- **Traceability Matrix:** Although often a separate document, its principles are core. This matrix links requirements to higher-level system needs, design elements, test cases, and validation activities, demonstrating **complete coverage and compliance**.
- **Appendix (Optional):** May include supplementary information such as glossaries, diagrams, or references.
Benefits of Adopting a Standardized Specification Approach
Utilizing a consistent approach to defining your software requirements, often guided by a professional template, offers numerous advantages throughout the product lifecycle. A standardized software development plan for healthcare tech fosters uniformity across projects, making it easier for new team members to onboard and understand existing documentation. This consistency is not just about aesthetics; it’s about establishing a repeatable process that reliably produces high-quality, compliant software.
One of the most significant benefits is enhanced clarity and reduced ambiguity. By following a predefined structure, teams are prompted to consider all necessary aspects, preventing assumptions that can lead to costly rework later. This structured thinking also significantly improves communication among cross-functional teams, ensuring everyone operates from a shared understanding of the software’s intended behavior and limitations. Furthermore, a well-organized requirements specification document facilitates easier reviews and audits, critical for demonstrating regulatory compliance to bodies like the FDA.
Tailoring Your Specification for Specific Projects
While a Medical Device Software Requirements Specification Template provides an excellent starting point, it’s rarely a one-size-fits-all solution. Every medical device project has its unique nuances, from the device’s intended use and risk classification to the specific technologies employed. Therefore, tailoring your requirements specification document to fit the individual needs of your project is essential for its effectiveness.
Consider the complexity and risk level of your device. A low-risk, standalone mobile application might require a less exhaustive level of detail than an implanted, life-sustaining device with intricate hardware interactions. Adapt the template by adding sections relevant to your specific project, such as particular cybersecurity considerations for connected devices, or detailed performance metrics for high-precision instruments. Conversely, remove sections that are not applicable to avoid unnecessary documentation burden. The goal is to make the document comprehensive enough to cover all critical aspects without becoming overly verbose or impractical to maintain.
Best Practices for Developing and Maintaining Your Specification
Creating a robust software requirements specification for medical devices is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. Effective development and maintenance are key to ensuring its continued relevance and utility throughout the product lifecycle. Start with early and continuous stakeholder involvement; engaging clinicians, engineers, quality assurance, and regulatory experts from the outset ensures all perspectives are considered and buy-in is secured.
Implement a strong change control process. Requirements are rarely static, and medical device software requirements can evolve as new insights emerge or regulatory landscapes shift. Any changes must be formally documented, reviewed, approved, and tracked, along with their impact on design, testing, and risk. Utilize version control to manage iterations of the document, ensuring that only the most current and approved version is in use. Finally, ensure traceability from requirements through design, development, testing, and risk management activities. This helps demonstrate that all requirements have been addressed and validated, a cornerstone of regulatory compliance.
Leveraging Tools and Collaboration for Success
In today’s complex development environments, managing a comprehensive software specification framework without the aid of specialized tools can be incredibly challenging. Requirements management software can significantly streamline the process, offering features such as centralized repositories, automated change tracking, impact analysis, and robust reporting capabilities. These tools help teams maintain control over thousands of requirements, ensuring consistency and traceability across large and intricate projects.
Beyond tools, fostering a collaborative environment is paramount. Developing a medical software requirements document is inherently a team effort. Regular cross-functional meetings, clear communication channels, and a culture of open feedback ensure that the specification is accurate, complete, and understood by everyone involved. When teams work in unison, leveraging both advanced tools and effective communication, the resulting design specification for medical products becomes a powerful asset, driving efficiency, quality, and ultimately, patient safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a medical device software requirements specification?
The primary purpose is to define exactly what the software for a medical device must do, how it must behave, and under what conditions, ensuring clarity for developers, guiding testing, and demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements for safety and efficacy.
How does a software requirements specification differ from a design specification?
A software requirements specification (SRS) defines *what* the software needs to do (the “what”), while a design specification details *how* the software will be implemented to meet those requirements (the “how”). The SRS serves as the input for the design specification.
Can a single template fit all medical device software projects?
While a core Medical Device Software Requirements Specification Template provides an excellent starting structure, it should be adapted and tailored for specific projects. Factors like device risk classification, complexity, and unique functionalities necessitate customization to ensure the specification is comprehensive yet efficient.
Who should be involved in creating this specification?
A cross-functional team including software engineers, quality assurance personnel, regulatory affairs experts, clinical representatives, and sometimes even marketing or product management, should collaborate on developing the requirements to ensure all perspectives are captured and validated.
How often should the specification be updated?
The specification should be a living document, updated whenever there are approved changes to the requirements, designs, or regulatory landscape. Any updates must follow a formal change control process, with reviews and approvals by relevant stakeholders to maintain its accuracy and relevance.
Establishing a robust and well-managed software requirements specification is not merely a bureaucratic hurdle; it is a critical investment in the success and safety of any medical device. It serves as the bedrock for quality, ensuring that every design decision and line of code contributes to a product that is not only innovative but also reliably safe and effective for its intended users. This structured approach helps prevent costly errors, accelerates time to market, and builds unwavering confidence in your medical technology.
By embracing the principles of clear, comprehensive requirements definition, guided by a well-structured framework, development teams can navigate the stringent demands of the medical device industry with greater assurance. It empowers organizations to deliver cutting-edge solutions that genuinely improve patient care, reinforcing their commitment to excellence and regulatory adherence in every product they bring to life.


