In the bustling world of mobile application development, where ideas can rapidly transform into tangible products, a clear vision is paramount. Without a well-defined roadmap, even the most innovative concepts can get lost in translation, leading to costly reworks, missed deadlines, and a product that ultimately fails to meet user expectations. Imagine embarking on a cross-country road trip without a map or even a destination in mind; that’s akin to building a mobile app without a comprehensive understanding of its purpose, features, and target audience.
This is precisely where a strategic, meticulously crafted product requirements document comes into play. It serves as the single source of truth, a foundational blueprint that aligns every team member—from designers and developers to QA engineers and marketing specialists—towards a common goal. For any organization aiming to deliver exceptional mobile experiences, understanding and effectively utilizing such a document isn’t just helpful; it’s an absolute necessity for navigating the complexities of modern app creation.
The Imperative of a Clear Blueprint
The journey from a nascent idea to a fully functional mobile application is fraught with potential miscommunications and diverging interpretations. Stakeholders might have one vision, designers another, and developers yet a third. This disconnect often leads to scope creep, feature bloat, and a final product that falls short of its original intent. A well-structured product requirements document acts as the ultimate antidote to this chaos, providing a stable anchor in the fluid seas of development.
It doesn’t just list features; it articulates the "why" behind them, connecting each element back to user needs and business objectives. By meticulously detailing every aspect of the app, from user flows to technical specifications, it ensures that all parties involved are singing from the same hymn sheet. This shared understanding minimizes assumptions, reduces the need for constant clarification, and dramatically streamlines the entire development lifecycle, leading to a more efficient and effective build.
What Exactly is a Product Requirements Document (PRD)?
A Product Requirements Document (PRD) is a formal document that outlines the purpose, features, and functionality of a product. In the context of mobile applications, it describes in detail what the app should do, how it should function, and the experience it should provide to the user. A Mobile App Product Requirements Document Template is an especially valuable tool because it provides a structured framework, guiding product managers and teams through the essential considerations specific to mobile environments.
This isn’t merely a laundry list of features. Instead, it’s a living document that captures the product’s vision, defines its scope, and specifies the requirements necessary for its development. It bridges the gap between the business needs and the technical implementation, translating high-level goals into actionable specifications that engineering teams can build upon. By providing this level of detail, it ensures that the final product not only meets business objectives but also delivers a compelling and intuitive user experience.
Core Benefits of a Well-Crafted Mobile PRD
Adopting a systematic approach to documenting your mobile app’s requirements brings a cascade of advantages that reverberate throughout the entire product lifecycle. These benefits extend far beyond simply keeping track of features, fundamentally transforming how teams collaborate and deliver value.
- Enhanced Clarity and Alignment: A robust app requirements document ensures everyone, from executive stakeholders to individual developers, shares a unified understanding of the product. This shared vision minimizes ambiguity and fosters collective ownership.
- Reduced Development Costs and Rework: By defining requirements upfront and thoroughly, teams can catch potential issues and ambiguities before costly development work begins. This proactive approach drastically cuts down on expensive reworks and corrections later in the cycle.
- Faster Time-to-Market: With clear specifications, development teams can work more efficiently, avoiding delays caused by vague instructions or shifting priorities. A precise mobile application design document accelerates the entire build process.
- Improved User Experience: A detailed product spec for mobile apps ensures that features are designed with the end-user in mind, leading to intuitive interfaces and functionalities that genuinely address user needs and pain points.
- Facilitated Testing and Quality Assurance: QA teams can create more comprehensive test plans directly from the documented requirements, leading to more thorough testing and a higher quality final product.
- Streamlined Stakeholder Communication: The product requirements document serves as a central reference point for all discussions, ensuring that decisions are based on a consistent and agreed-upon understanding of the product.
- Simplified Onboarding: New team members can quickly get up to speed on the project by reviewing the comprehensive project outline, reducing ramp-up time and ensuring continuous productivity.
Key Elements of an Effective Mobile App PRD Template
While the specific sections of a product requirements document may vary based on project complexity and organizational culture, a comprehensive Mobile App Product Requirements Document Template typically includes several critical components. These elements ensure that all necessary information is captured, providing a holistic view of the product.
- Executive Summary: A high-level overview of the app, its purpose, and its key features. This section provides a quick understanding for busy stakeholders.
- Vision and Goals: Defines the overarching objective of the app, what problem it solves, and its long-term strategic value to the business and its users.
- Target Audience/User Personas: Detailed descriptions of the intended users, their needs, behaviors, and pain points, which inform design and feature decisions.
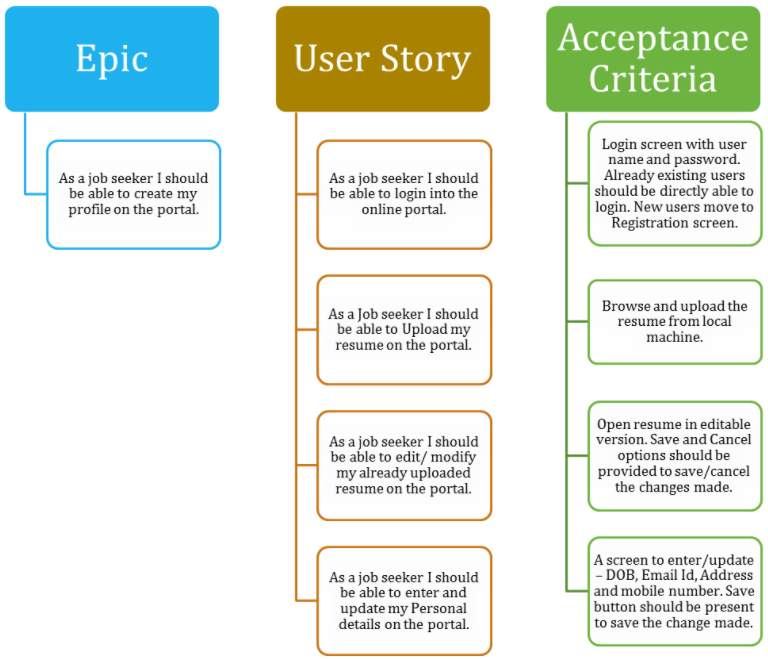
- User Stories and Use Cases: Specific scenarios describing how users will interact with the app to achieve particular goals, often written in the format "As a [user type], I want to [action] so that [benefit]."
- Functional Requirements: A precise breakdown of what the app must do. This includes all user-facing features and internal system functionalities, such as user authentication, data storage, payment processing, or content display.
- Non-Functional Requirements: Criteria that describe how the system performs a function rather than what it does. This covers aspects like performance (speed, responsiveness), scalability (handling increased users), security (data protection), usability (ease of use), and compatibility (OS versions, device types).
- Scope and Features: Clearly delineates what is in scope for the current release and what is explicitly out of scope, preventing scope creep and ensuring focused development. Each feature should be described with its priority.
- UI/UX Design References (Optional but Recommended): Links to wireframes, mockups, design specifications, or prototypes that visually represent the app’s user interface and experience. While not strictly part of the text document, referencing these assets is crucial for a complete understanding.
- Technical Requirements and Architecture (High-Level): An overview of the technical considerations, such as chosen platforms (iOS, Android, cross-platform), backend integrations, APIs, and specific technologies that might impact development.
- Analytics and Tracking: Specifies what data will be collected, how it will be tracked, and what insights are expected, informing future product iterations and business decisions.
- Monetization Strategy: If applicable, outlines how the app will generate revenue (e.g., in-app purchases, subscriptions, ads).
- Future Considerations/Roadmap: A placeholder for potential future features, improvements, or phases, providing context for the current scope and future direction.
Tips for Customizing and Utilizing Your PRD
A product requirements document is not a static artifact; it’s a dynamic tool that should evolve with your project. To truly maximize its value, it needs to be adaptable, accessible, and integrated into your team’s workflow. Here are some practical tips for leveraging your app requirements document effectively.
Firstly, keep it concise and clear. While thoroughness is important, avoid unnecessary jargon or overly technical language that could alienate non-technical stakeholders. Use plain English and aim for precision in every description. Secondly, involve all key stakeholders in the document’s creation and review processes. This fosters a sense of ownership, ensures diverse perspectives are considered, and catches potential issues early on. Product managers, designers, developers, QA, and even marketing should have input.
Thirdly, treat it as a living document. Your app will change, and so too should its defining specification. Implement a robust version control system to track changes and revisions, and establish a process for updates and approvals. Regular reviews are essential to ensure the document remains accurate and relevant. Fourthly, integrate it with your project management tools. Link specific requirements or user stories from your product spec for mobile apps directly to tasks in tools like Jira, Asana, or Trello, ensuring traceability from concept to completion. Lastly, prioritize ruthlessly. Not every feature is equally important. Use the PRD to clearly define priorities, helping your development team focus on what truly matters for each release.
Streamlining Collaboration and Iteration
Beyond its role as a documentation tool, a well-managed mobile app specification document transforms into a powerful catalyst for team collaboration. In an agile environment, where continuous feedback and rapid iteration are key, the PRD provides a stable reference point that keeps everyone aligned while still allowing for flexibility. It serves as the agenda for discussions, the benchmark for feature completeness, and the ultimate source of truth when disagreements arise.
By clearly articulating requirements and their rationale, the document empowers cross-functional teams to work autonomously within defined boundaries. Developers understand what to build, designers know what experience to create, and QA testers have clear criteria for validation. This clarity minimizes communication overhead, reduces handoff friction, and allows teams to deliver incremental value with confidence. As the product evolves, the document becomes a record of decisions made, helping to maintain continuity and institutional knowledge, ensuring that even as team members change, the core vision of the mobile application remains intact.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a PRD necessary for small mobile apps?
Absolutely. Even for small mobile apps, a product requirements document provides immense value by clarifying scope, preventing unnecessary features, and ensuring a focused development effort. It helps avoid misunderstandings and rework, saving time and resources regardless of project size.
How often should a mobile PRD be updated?
A product requirements document for mobile applications should be updated regularly, especially in agile environments. It’s a living document that needs to reflect changes in requirements, design decisions, and scope throughout the development lifecycle. Updates should occur after major feedback sessions, sprint planning, or any significant shift in product direction.
Who is typically responsible for writing the app requirements document?
The Product Manager or Product Owner is usually responsible for initiating and owning the app requirements document. However, its creation is a collaborative effort, involving input from designers, developers, business analysts, marketing, and other stakeholders to ensure all perspectives are captured accurately.
What’s the difference between a PRD and a User Story?
A PRD (Product Requirements Document) is a comprehensive, overarching document that defines the entire product, its vision, goals, and all functional/non-functional requirements. User stories are smaller, more focused descriptions of features from an end-user’s perspective (e.g., “As a user, I want to log in to my account so I can access my profile”). User stories are often *components* of a PRD, helping to detail specific requirements within the larger document.
Can I find a pre-made product requirements document for mobile applications?
Yes, many resources offer templates or examples of product requirements documents for mobile applications. While these can provide a great starting point, it’s crucial to customize any template to fit your specific project, team, and organizational context. The most effective PRD is one tailored to your unique needs.
In the complex tapestry of mobile app development, a robust product requirements document isn’t just a piece of paperwork; it’s the very backbone of successful product delivery. It transforms abstract ideas into concrete specifications, aligns diverse teams, and mitigates the risks inherent in bringing a digital product to life. By investing the time and effort into crafting a thorough and adaptable document, you are not just defining a product, you are investing in clarity, efficiency, and ultimately, the success of your mobile application.
Embrace the discipline of meticulous documentation. Let this guide be the catalyst for creating your next great mobile product, ensuring every line of code, every design element, and every user interaction is purposeful and perfectly aligned with your vision. Begin today to build a clearer path forward, and watch your mobile app aspirations turn into impactful realities.


