In the fast-paced world of product development and market launches, clarity and alignment are not just buzzwords—they are the bedrock of success. Without a shared understanding of a product’s purpose, target audience, and competitive landscape, even the most innovative ideas can falter. This is where a robust framework for defining marketing objectives becomes indispensable, serving as a critical bridge between product teams and market-facing strategies.
Navigating the complexities of bringing a product to market requires more than just a great idea; it demands meticulous planning, strategic foresight, and seamless cross-functional collaboration. A well-constructed marketing requirements document (MRD) provides this foundational structure, ensuring every stakeholder, from engineers to sales teams, operates from the same playbook. It’s a living blueprint that outlines the market problem a product solves, defines its features from a customer-centric perspective, and establishes the parameters for its successful launch and sustained growth.
Why a Marketing Requirements Document is Indispensable
In the realm of product and marketing strategy, the value of a comprehensive marketing requirements document (MRD) cannot be overstated. It acts as the definitive statement of the market needs a product addresses, detailing the problems customers face and how the proposed solution will meet those needs. This crucial document helps to align internal teams by providing a shared vision and a clear understanding of market opportunities and customer expectations.
Without a structured marketing requirements document, teams risk developing products in a vacuum, leading to offerings that miss the mark with customers or fail to stand out in a crowded market. It prevents costly reworks, minimizes miscommunications, and ensures that development efforts are strategically focused on delivering real market value. An effective MRD template sets the stage for a product that is not only technically sound but also strategically positioned for success.
The Core Benefits of Using a Structured MRD
Adopting a standardized marketing requirements document framework offers a multitude of advantages that cascade across an organization, from early conception to post-launch analysis. It transforms amorphous ideas into actionable plans and fosters a culture of informed decision-making.
- **Enhanced Clarity:** Provides a single source of truth for all market-related product decisions.
- **Strategic Alignment:** Ensures all departments—product, engineering, sales, and marketing—are working towards common goals.
- **Risk Mitigation:** Identifies potential market challenges and competitive threats early in the development cycle.
- **Customer Focus:** Keeps the **user needs** and market problems at the forefront of development.
- **Efficient Resource Allocation:** Directs resources to features and initiatives that offer the highest market impact.
- **Faster Time-to-Market:** Streamlines the development process by minimizing ambiguity and rework.
- **Improved Decision-Making:** Offers data-backed insights for pivotal product and marketing choices.
Key Elements of an Effective Marketing Requirements Document
A comprehensive marketing requirements document outlines critical information necessary for guiding product development and marketing efforts. While the specifics might vary by industry or product, certain core components are universally essential for any strategic marketing requirements plan.
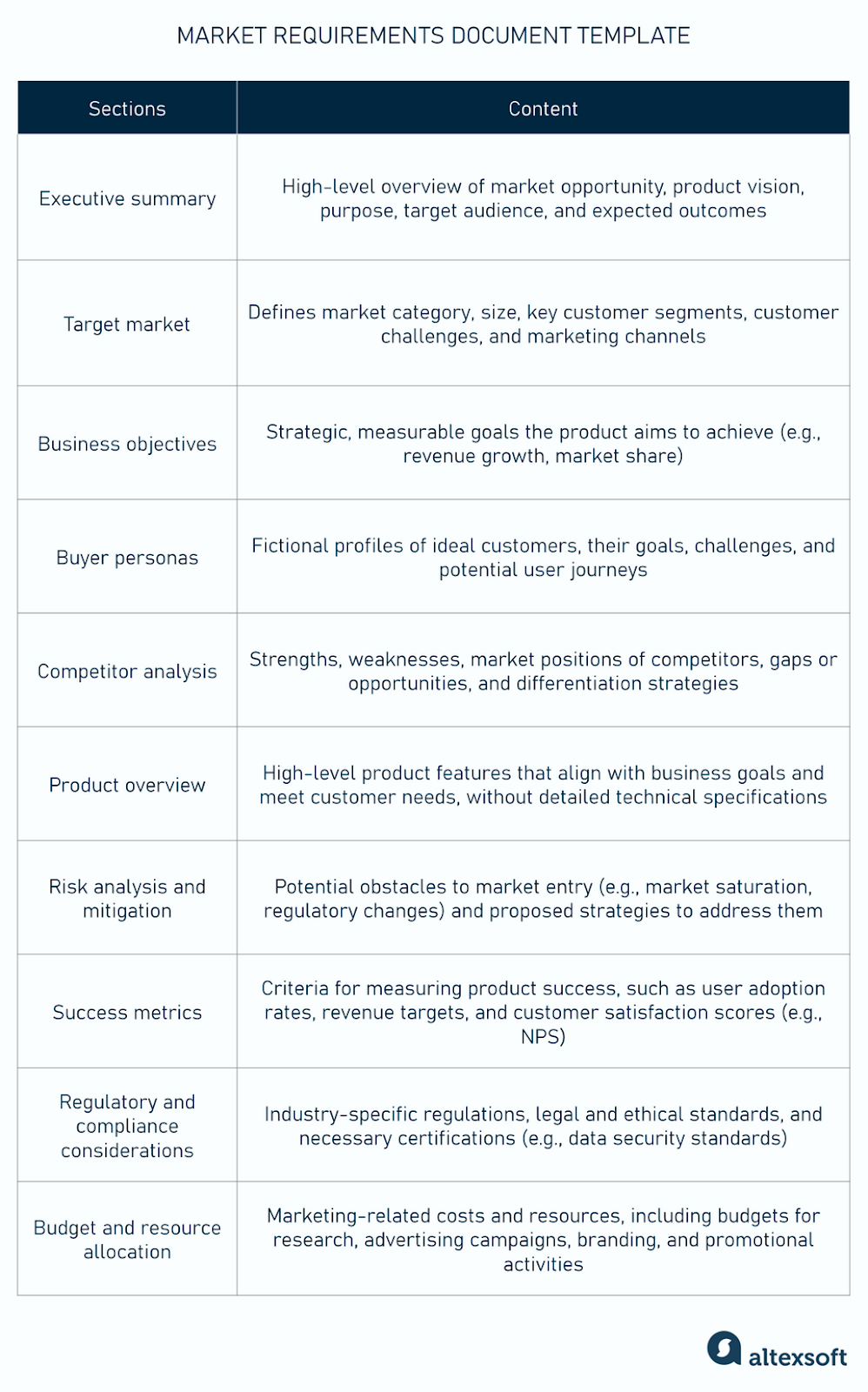
Executive Summary
This section provides a high-level overview of the entire document, summarizing the product vision, target market, and key success metrics. It should be concise and compelling, offering busy stakeholders a quick grasp of the project’s essence and strategic importance.
Market Analysis
A deep dive into the market landscape, including market size, trends, and growth potential. This also encompasses a thorough competitive analysis, identifying direct and indirect competitors, their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. Understanding the market is crucial for defining a product’s unique selling proposition.
Target Audience Profile
Detailed descriptions of the intended customers, often presented as buyer personas. This includes demographic information, psychographics, pain points, needs, and how the product will specifically address these. A clear understanding of the target audience informs every aspect of product design and marketing messaging.
Product Vision and Goals
Articulates the overarching purpose of the product and what it aims to achieve. This includes short-term and long-term objectives, success metrics (KPIs), and how the product aligns with the company’s broader strategic goals. This section establishes the ultimate destination for the product journey.
Features and Functionality (Market View)
Unlike a technical specification, this section describes product features from the perspective of market needs and customer benefits. It details what problems each feature solves for the user, rather than how it will be engineered. Prioritization of features is also critical here, often using a framework like MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have).
Pricing and Packaging Strategy
Outlines the proposed pricing models, tiers, and packaging options, justifying these choices based on market research, competitor pricing, and perceived customer value. This is a critical component for profitability and market penetration.
Go-to-Market Strategy
Details how the product will be launched and introduced to the target market. This includes distribution channels, promotional activities, messaging, and sales enablement plans. It’s the blueprint for how the product will reach and resonate with its audience.
Success Metrics and KPIs
Defines the measurable indicators that will be used to track the product’s performance post-launch. These might include sales volume, customer acquisition cost, retention rates, market share, and customer satisfaction scores. Clear metrics allow for continuous optimization and evaluation.
Crafting Your MRD: A Step-by-Step Guide
Developing an effective marketing requirements document template requires a structured approach to ensure all vital information is captured and clearly communicated. Think of this process as building a narrative around your product’s journey from concept to market impact.
First, start with the problem. Clearly articulate the market problem you are solving and for whom. This sets the foundation for all subsequent requirements. Next, conduct thorough research—both market and customer-facing. Gather data on trends, competitors, and potential users to validate assumptions and uncover critical insights.
Then, define the solution from a market perspective. Focus on what the product does for the customer, not just its technical specifications. Prioritize features based on market demand and strategic importance. Collaborate extensively with product management, engineering, and sales teams to ensure alignment and gather diverse perspectives. A well-rounded marketing requirements document is a collaborative effort, not a solo endeavor.
Finally, iterate and refine. An MRD is a living document; it should be reviewed and updated as new information emerges or market conditions change. This iterative process ensures the document remains relevant and continues to guide the product’s evolution effectively.
Best Practices for Maximizing Your MRD’s Impact
Beyond simply filling out an MRD template, there are strategies to ensure your marketing requirements document becomes a dynamic, impactful tool throughout the product lifecycle. These best practices transform it from a static document into a strategic asset.
One key practice is to maintain a customer-centric focus at all times. Every requirement, feature, and strategic decision documented should trace back to solving a customer problem or fulfilling a customer need. This keeps the product relevant and valuable to its end-users.
Another crucial tip is to keep it concise and clear. While comprehensive, an effective marketing needs document avoids unnecessary jargon or overly technical language that could alienate non-technical stakeholders. Use visuals like diagrams, flowcharts, or wireframes where they can simplify complex ideas.
Furthermore, ensure ongoing communication and collaboration. The MRD should be a shared resource, regularly discussed and reviewed by all involved teams. This fosters a sense of ownership and ensures everyone is updated on any changes or new insights. Make it accessible and encourage feedback to continuously refine the product launch document.
Lastly, treat it as a living document. The market is constantly evolving, and so too should your understanding of its requirements. Schedule regular reviews and updates to your market requirements specification, especially during key project milestones or when significant market shifts occur. This agility helps your product adapt and maintain its competitive edge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between an MRD and a PRD?
An MRD (Marketing Requirements Document) focuses on the *why* and *what* from a market and customer perspective. It describes the market problem, customer needs, and business opportunities. A PRD (Product Requirements Document), on the other hand, delves into the *how*, detailing the technical specifications, functionality, and user experience requirements for the product team to build the solution outlined in the MRD.
Who typically creates the Marketing Requirements Document?
The marketing requirements document is usually owned and primarily authored by product marketing managers or product managers. However, its creation is a collaborative effort, involving input from various departments including sales, engineering, product development, and executive leadership to ensure a holistic view and organizational alignment.
How often should an MRD be updated?
An MRD is a living document and should be updated whenever significant changes occur in the market, customer needs, competitive landscape, or the product’s strategic direction. This could mean quarterly reviews, updates before major development sprints, or as new data and insights become available. Regular maintenance ensures the document remains a relevant and accurate guide.
Can a small startup benefit from using an MRD template?
Absolutely. Even small startups can greatly benefit from a structured marketing requirements document. While they might adapt the template to be less formal or exhaustive, the core principles of defining market problems, target audiences, and product goals are crucial for any size of organization to maintain focus, allocate limited resources effectively, and communicate their vision clearly to investors and early adopters.
Is the MRD only relevant for new products?
While often associated with new product introductions, the marketing requirements document is also highly relevant for existing products undergoing significant updates, feature enhancements, or strategic repositioning. It helps to reassess market fit, identify new opportunities for growth, and guide the evolution of mature products to maintain their competitiveness and relevance in the market.
Leveraging a well-structured Mrd Marketing Requirements Document Template is more than just good practice; it’s a strategic imperative for any organization aiming for sustained success in today’s dynamic marketplace. It brings clarity, fosters alignment, and ensures every effort, from initial concept to final launch, is directed towards delivering maximum value to the customer and achieving commercial objectives.
By investing the time and effort into developing a robust marketing requirements document, companies can minimize risks, optimize resource utilization, and significantly increase their chances of bringing impactful products to market. It serves as your compass, guiding your product journey with precision and purpose. Embrace this powerful tool to transform your product ideas into market-leading realities.


