Working in confined spaces presents some of the most challenging and potentially life-threatening environments in industrial and commercial settings. These are not merely cramped areas; they are locations with limited entry and exit, not designed for continuous human occupancy, and often harbor serious hazards that can quickly become catastrophic. From oxygen deficiency and toxic gas exposure to engulfment and mechanical hazards, the risks are profound and demand an unwavering commitment to safety. This is precisely why the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates stringent regulations for employers whose workers enter such spaces.
Navigating these regulations can feel like a daunting task, especially when trying to ensure every detail is covered to protect your team and maintain compliance. The good news is that foundational tools exist to streamline this complex process. A well-constructed framework, often starting with a robust confined space safety plan, serves as the bedrock for effective hazard control and worker protection. It’s more than just a document; it’s a living blueprint for preventing accidents, saving lives, and fostering a culture of safety within your organization.
Understanding Confined Spaces and OSHA’s Mandate
Before diving into program development, it’s crucial to grasp what constitutes a confined space under OSHA’s purview. OSHA defines a "confined space" as an area that is large enough for an employee to enter and perform assigned work, has limited or restricted means for entry or exit, and is not designed for continuous employee occupancy. Think tanks, vessels, silos, storage bins, hoppers, vaults, pits, manholes, tunnels, equipment housings, and pipelines.
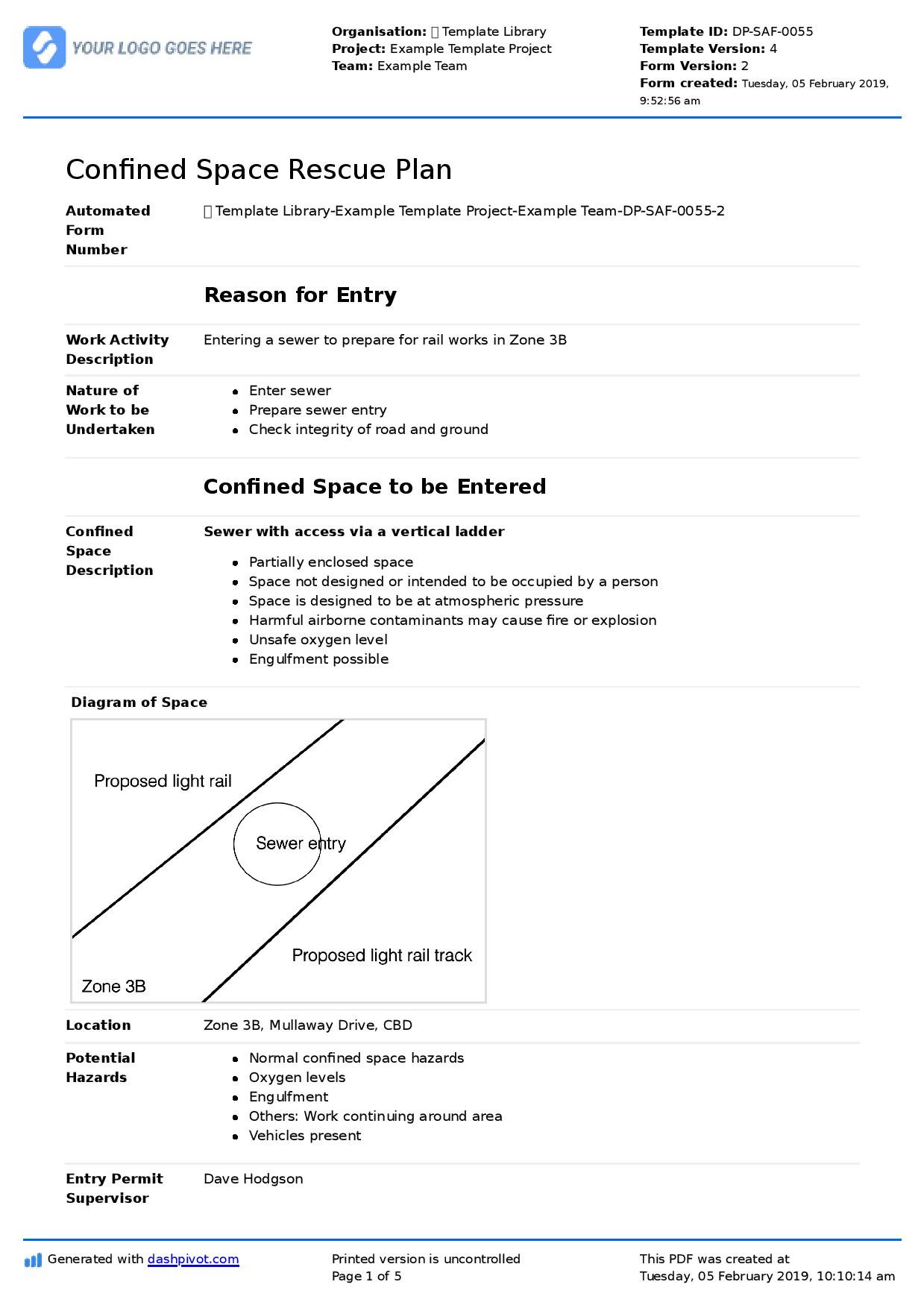
The even more critical category is a "permit-required confined space" (PRCS). These spaces have one or more of the following characteristics: they contain or have a potential to contain a hazardous atmosphere; they contain a material that has the potential for engulfing an entrant; they have an internal configuration such that an entrant could be trapped or asphyxiated by inwardly converging walls or by a floor which slopes downward and tapers to a smaller cross-section; or they contain any other recognized serious safety or health hazard. OSHA’s standard, 29 CFR 1910.146, specifically addresses these hazardous environments, outlining detailed requirements for entry. This comprehensive regulation is designed to prevent fatalities and serious injuries that tragically still occur too frequently in these high-risk areas.
Why a Robust Confined Space Entry Program is Non-Negotiable
Developing and rigorously implementing a comprehensive entry program for confined spaces isn’t just about ticking boxes for regulatory compliance; it’s a fundamental commitment to worker well-being and operational integrity. The direct benefits are multifaceted. Foremost, it significantly reduces the likelihood of accidents, injuries, and fatalities by proactively identifying and controlling hazards before entry occurs. This proactive approach protects your most valuable asset: your employees.
Beyond the humanitarian aspect, a strong confined space safety plan offers substantial organizational advantages. It helps avoid costly OSHA citations, which can carry significant fines and damage a company’s reputation. It also minimizes potential liability in the event of an incident, demonstrating due diligence and a commitment to established safety protocols. Furthermore, a clear and consistently applied permit space program improves operational efficiency by standardizing procedures, reducing downtime associated with unsafe practices, and fostering a more organized and predictable work environment. It’s an investment that pays dividends in both safety and bottom-line stability.
Key Elements of an Effective Confined Space Program
A truly effective program for managing confined space entry must be comprehensive, covering every aspect from initial assessment to post-entry review. It needs to be a living document, frequently reviewed and updated. Here are the core components you’d expect to find within a well-structured confined space program:
- **Hazard Identification and Evaluation:** Thoroughly assessing each confined space to determine if it is permit-required and identifying all potential hazards (atmospheric, engulfment, mechanical, etc.).
- **Written Program Document:** A clear, concise, and accessible document outlining policies, procedures, and responsibilities for all confined space entry operations. This is the heart of your safety program for restricted spaces.
- **Permit System:** Establishing a formal written permit system for all permit-required confined space entries, including details like purpose of entry, authorized entrants, attendants, entry supervisor, hazards, control measures, and duration.
- **Training:** Comprehensive training for all personnel involved in confined space operations, including authorized entrants, attendants, entry supervisors, and rescue personnel. Training must cover their specific duties and the hazards involved.
- **Equipment:** Providing and ensuring proper use of necessary equipment, such as atmospheric testing devices, ventilation equipment, personal protective equipment (PPE), communication systems, and rescue equipment.
- **Attendants:** Assigning a trained attendant who remains outside the permit space during entry operations, maintaining communication with entrants, and initiating rescue procedures if needed.
- **Entry Supervisor:** Designating an entry supervisor responsible for overseeing the entry operation, verifying the permit is complete, and ensuring all procedures are followed.
- **Rescue and Emergency Services:** Developing and implementing procedures for non-entry or entry rescue, including coordination with local emergency services and providing proper retrieval systems.
- **Contractor Safety:** Procedures for informing contractors about identified hazards and ensuring they follow the employer’s permit space entry procedures or have their own compliant program.
- **Program Review and Revision:** Regularly reviewing the effectiveness of the confined space program, especially after incidents or near-misses, and revising it as necessary.
Leveraging an Osha Confined Space Program Template
While the thought of developing such a comprehensive document from scratch can be overwhelming, the good news is that you don’t have to start from square one. An Osha Confined Space Program Template provides an invaluable starting point, offering a pre-structured framework that aligns with OSHA’s requirements. These templates are designed to incorporate the fundamental elements of 29 CFR 1910.146, giving you a solid foundation upon which to build your specific safety protocols.
Using a template for confined space entry saves considerable time and ensures that critical components are not overlooked. It acts as a detailed checklist, guiding you through the various sections and considerations necessary for a compliant and effective program. Instead of spending hours researching every line of the regulation, you can focus on tailoring the pre-existing structure to your unique operational needs, specific confined spaces, and organizational culture. This strategic approach ensures both efficiency and thoroughness in developing a vital safety document.
Customization: Making the Template Work for *Your* Operation
It’s crucial to understand that an Osha Confined Space Program Template is a starting point, not a final solution. No two workplaces are identical, and therefore, no generic template can perfectly fit every scenario. Effective implementation requires meticulous customization to reflect the specific hazards, equipment, personnel, and procedures unique to your facility. This process involves more than just filling in blanks; it demands a deep understanding of your confined spaces and the work performed within them.
Begin by conducting a detailed inventory and hazard assessment of every confined space at your site. Document their exact locations, dimensions, potential atmospheric hazards, structural integrity issues, internal configurations, and the types of work typically performed inside. Based on this assessment, you will need to adapt the template’s sections on hazard control, equipment requirements, emergency procedures, and training modules. For instance, if your confined spaces are primarily agricultural silos, your program will differ significantly from one designed for petrochemical tanks. Tailoring the program ensures its relevance, maximizes its effectiveness in preventing incidents, and truly makes it a robust compliance document for confined spaces.
Implementation: Bringing Your Program to Life
A meticulously crafted confined space safety plan, no matter how thorough, is only as effective as its implementation. The transition from paper to practice requires a strategic approach. First, disseminate the finalized program document to all relevant personnel, ensuring they understand where to access it and its importance. This means making it readily available, perhaps both physically and digitally.
Next, and perhaps most critically, initiate comprehensive training. Every employee who might interact with confined spaces – whether as an authorized entrant, attendant, entry supervisor, or even those involved in rescue operations – must receive tailored instruction. This training should cover specific procedures, hazard recognition, use of equipment, and emergency protocols. Practical drills and hands-on experience with equipment, such as gas monitors and retrieval systems, are invaluable. Finally, designate clear roles and responsibilities. Everyone involved must know their specific duties and accountabilities within the permit-required confined space program to ensure seamless and safe operations.
Ongoing Management and Continuous Improvement
Establishing your confined space program is an achievement, but maintaining its efficacy is an ongoing commitment. Safety programs are not static; they are dynamic systems that require continuous review and refinement. Regular audits of your permit space entry procedures are essential to identify any deviations from the established plan or new hazards that may have emerged. These audits should assess compliance with written procedures, the condition of equipment, and the effectiveness of training.
Furthermore, a critical aspect of ongoing management is learning from experience. Every confined space entry, whether routine or challenging, offers an opportunity for improvement. After each entry, and especially after any incident, near-miss, or change in operations, conduct a thorough review. Were the procedures effective? Was the equipment adequate? Was the training sufficient? Use this feedback to update your permit-required confined space program, revise training materials, and refine safe work procedures for confined spaces. This commitment to continuous improvement ensures your program remains a robust shield against hazards, continually evolving to meet new challenges and protect your workforce.
Ensuring worker safety in hazardous environments like confined spaces is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a moral imperative. By meticulously developing, customizing, and consistently implementing a comprehensive confined space program, you establish a clear pathway to mitigating risks and preventing devastating incidents. Starting with a solid framework, such as a well-designed Osha Confined Space Program Template, empowers organizations to build robust safety protocols that truly safeguard their employees.
The journey from initial assessment to ongoing program management demands diligence, commitment, and a proactive approach. Investing the time and resources into creating an effective entry program for confined spaces is an investment in human lives, operational continuity, and your company’s reputation. Make it a priority to review your current procedures, enhance your safety plan, and ensure every team member understands their vital role in maintaining a secure working environment.