The silent hum of electricity powers our modern world, driving industries, illuminating workplaces, and enabling countless tasks. Yet, this indispensable force also harbors a significant potential for danger. Every year, workers across the United States face severe injuries, and even fatalities, due to electrical accidents. These incidents range from electric shock and electrocution to arc flashes and fires, often stemming from inadequate safety practices or a lack of proper planning.
For any organization utilizing electrical equipment, establishing a comprehensive and effective electrical safety program isn’t merely a recommendation; it’s a critical imperative. It’s about protecting lives, complying with stringent regulations set forth by agencies like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and fostering a culture where safety is paramount. The journey to a safer electrical environment often begins with a structured approach, and for many, an Osha Electrical Safety Program Template offers a foundational blueprint to build upon.
The Unseen Hazard: Why Electrical Safety is Non-Negotiable
Electricity, by its very nature, is invisible, odorless, and silent, making its hazards particularly insidious. According to OSHA, electricity causes hundreds of fatalities and thousands of injuries annually in the workplace. These aren’t just statistics; they represent lives irrevocably altered and businesses facing significant operational disruptions, legal repercussions, and severe financial penalties.
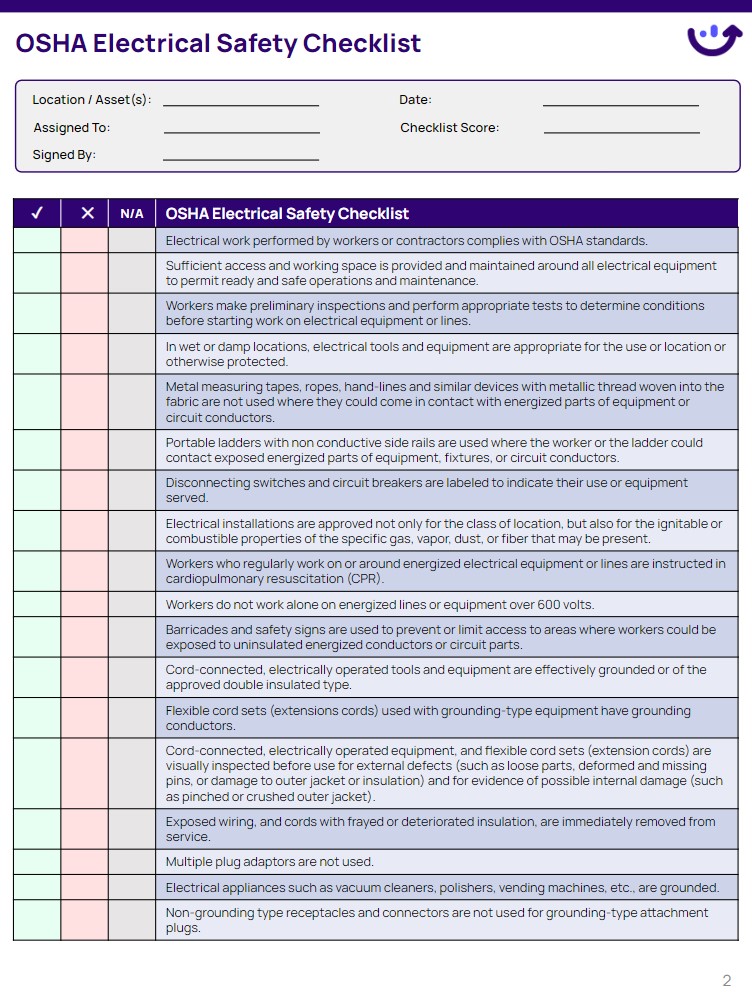
Common electrical hazards include contact with live parts, inadequate wiring, overloaded circuits, damaged insulation, improper grounding, and the misuse of flexible cords. Beyond the immediate danger of shock or electrocution, arc flash incidents, though less common, can unleash extreme heat and pressure, causing catastrophic burns and other injuries from a safe distance. Therefore, proactively addressing these risks through a robust electrical safety program is not just a regulatory requirement, but a moral and operational necessity.
Understanding OSHA’s Stance on Electrical Safety
OSHA takes electrical safety very seriously, outlining clear standards that employers must adhere to. The primary regulations governing workplace electrical safety are found in 29 CFR 1910 Subpart S, specifically Sections 1910.301 through 1910.399. These standards cover everything from design safety standards for electrical systems to safe work practices and maintenance requirements.
Beyond these general industry standards, OSHA frequently references and indirectly mandates compliance with the National Fire Protection Association’s (NFPA) NFPA 70E, "Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace." While not an OSHA standard itself, NFPA 70E provides detailed practical guidance on how to comply with OSHA’s broader electrical safety requirements, particularly concerning safe work practices, lockout/tagout procedures, and arc flash prevention. Employers are expected to identify electrical hazards, implement control measures, and train employees to work safely around electricity.
Building Your Foundation: Core Elements of an Electrical Safety Program
A comprehensive electrical safety program serves as your organization’s blueprint for managing electrical risks. It should be a living document, regularly reviewed and updated, rather than a static piece of paper. When constructing or refining your program, a structured framework, such as an Osha Electrical Safety Program Template, can help ensure all critical components are addressed.
Here are the essential elements that should be integrated into any effective workplace electrical safety plan:
- **Clear Scope and Responsibilities:** Define who is responsible for what, from management to individual employees. This includes designated safety officers, supervisors, and qualified electrical workers.
- **Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment:** Establish procedures for systematically identifying potential electrical hazards (e.g., exposed wiring, overloaded circuits, lack of proper grounding) and assessing the associated risks (e.g., shock, arc flash, electrocution). This involves regular inspections and incident reporting.
- **Safe Work Practices:** Detail specific procedures for working safely near or on electrical equipment. This includes requirements for de-energizing equipment, lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures, and establishing electrically safe work conditions.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):** Specify the types of electrical PPE required for various tasks, such as arc-rated clothing, insulating gloves, and eye protection. Include guidelines for selection, use, inspection, and maintenance of PPE.
- **Electrical Equipment Maintenance and Inspection:** Outline schedules and procedures for the routine inspection, testing, and maintenance of all electrical equipment, tools, and wiring to ensure they remain in safe operating condition.
- **Training and Qualification:** Describe the training requirements for all employees who work with or near electrical equipment. Differentiate between qualified and unqualified persons and define the specific training each group must receive. This includes refresher training.
- **Emergency Procedures:** Establish clear protocols for responding to electrical accidents, including first aid, rescue procedures, and contacting emergency services. Ensure all employees know these procedures.
- **Arc Flash Analysis and Labeling:** Implement a system for conducting arc flash hazard analyses to determine arc flash boundaries and required PPE levels. Ensure equipment is properly labeled with this crucial information.
- **Documentation and Record-Keeping:** Detail requirements for maintaining records of hazard assessments, training, equipment inspections, maintenance, and incident investigations.
- **Continuous Improvement:** Include provisions for regularly reviewing the effectiveness of the electrical safety framework, conducting audits, investigating incidents, and implementing corrective actions to continually enhance safety performance.
Beyond the Basics: Customizing Your Electrical Safety Framework
While a general safety program template provides a strong starting point, true effectiveness comes from tailoring it to your specific operational environment. No two workplaces are exactly alike, and the electrical hazards faced by a manufacturing plant differ significantly from those in an office building or a construction site. This customization is where the power of a comprehensive electrical safety plan truly shines.
Begin by performing a thorough site-specific risk assessment. What types of electrical equipment are used? Are there unique environmental factors, such as wet locations or explosive atmospheres? What is the skill level of your workforce? Involve employees who work directly with electricity in this process; their insights are invaluable. They can identify practical challenges and propose realistic solutions that might be overlooked in a top-down approach. Your customized electrical safety framework should reflect these nuances, clearly addressing the particular hazards and specific equipment present in your facility.
Putting it into Practice: Implementation and Maintenance
Developing a detailed safety program is only half the battle; effective implementation is key to preventing accidents. Once your robust electrical safety program is drafted, the next crucial step is to integrate it into daily operations. This involves several critical phases.
Firstly, training is paramount. All employees, from management to frontline workers, must understand their roles and responsibilities within the program. Qualified persons performing electrical work require specialized, in-depth training on safe work practices, arc flash hazards, and lockout/tagout procedures. Unqualified persons need to be aware of general electrical hazards and understand when to report unsafe conditions or avoid certain areas. Regular refresher training is essential to reinforce knowledge and address any changes in equipment or procedures.
Secondly, documentation must be meticulously maintained. This includes records of training, equipment inspections, hazard assessments, LOTO permits, and incident investigations. Good record-keeping not only demonstrates compliance but also provides valuable data for continuous improvement.
Thirdly, regular audits and inspections are vital. These periodic reviews ensure that the program is being followed, identifies any deviations or new hazards, and assesses the overall effectiveness of your electrical safety management system. Findings from audits should lead to corrective actions and updates to the program. Finally, fostering a culture of safety is perhaps the most important element. This means leadership actively championing safety, encouraging open communication about hazards, and empowering employees to stop work if they perceive an unsafe electrical condition.
The ROI of Safety: Benefits Beyond Compliance
Implementing a thorough electrical safety program, guided perhaps by an Osha Electrical Safety Program Template, involves an investment of time, effort, and resources. However, the returns on this investment extend far beyond simply avoiding OSHA fines. The benefits are multifaceted, impacting every aspect of your organization.
Foremost is the prevention of injuries and fatalities. A safe workplace protects your most valuable asset—your people. This directly translates to reduced worker’s compensation claims, lower insurance premiums, and fewer lost workdays. Beyond the financial, there’s the profound moral satisfaction of knowing you’ve created a work environment where employees feel secure and valued.
A strong commitment to workplace electrical safety also enhances employee morale and productivity. When employees feel safe, they are more focused, engaged, and productive. They trust their employer, leading to higher retention rates and a more positive work environment. Furthermore, consistent adherence to safety protocols often results in improved operational efficiency. Fewer incidents mean less downtime for investigations, repairs, and accident recovery, allowing operations to run more smoothly and predictably. Ultimately, a proactive approach to managing electrical risks bolsters your company’s reputation as a responsible and ethical employer.
Embracing a comprehensive electrical safety strategy is more than a compliance checklist; it’s a strategic business decision that safeguards your workforce, strengthens your operations, and contributes to long-term success. By diligently applying a structured framework and continuously adapting it to your unique environment, you build a resilient safety culture that protects everyone, every day. It transforms potential danger into managed risk, allowing your business to thrive securely.