In the fast-paced world of industrial operations, where efficiency often drives decisions, the paramount importance of safety can sometimes be overlooked. Activities involving welding, cutting, grinding, or any task that produces heat, sparks, or flame—collectively known as “hot work”—pose significant fire and explosion hazards that can lead to devastating consequences if not properly managed. This is where a robust and well-structured hot work safety program becomes not just a recommendation, but a critical imperative for every organization.
Navigating the complexities of regulatory compliance while ensuring the well-being of your workforce can be a daunting challenge. A comprehensive framework is essential to mitigate these risks effectively, and a dedicated document like an Osha Hot Work Program Template offers an invaluable starting point. It provides a structured approach to hazard identification, risk assessment, and the implementation of controls, transforming a potentially dangerous operation into a controlled and safe process. Let’s delve into why such a program is vital for any workplace where hot work is performed.
Understanding Hot Work and Its Risks
Hot work encompasses a wide array of activities that have the potential to ignite fires or cause explosions. These can range from routine maintenance tasks like arc welding to more specialized operations such as torch cutting or soldering. The common thread among them is the generation of heat, sparks, or open flames, which can easily come into contact with combustible materials present in almost any work environment.
The risks associated with hot work are multifaceted. Beyond the immediate danger of fire, there’s also the potential for severe burns, exposure to hazardous fumes, and even structural damage to facilities. In confined spaces, these risks are amplified, as proper ventilation can be challenging, leading to the accumulation of flammable vapors or toxic gases. A clear understanding of these inherent dangers is the first step toward building an effective safety strategy.
OSHA’s Stance on Hot Work Safety
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) unequivocally recognizes the severe hazards posed by hot work and has established stringent standards to protect workers. While there isn’t one single “hot work” standard, various regulations, particularly in general industry (29 CFR 1910 Subpart Q – Welding, Cutting and Brazing) and construction (29 CFR 1926 Subpart J – Welding and Cutting), address specific aspects of these operations. These standards mandate employers to take proactive measures, including providing proper training, utilizing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and implementing fire prevention strategies.
OSHA requires employers to assess the work area, ensure fire prevention measures are in place, and often, to issue a hot work permit before operations begin. These regulatory requirements are not mere suggestions; they are enforceable laws designed to prevent injuries, fatalities, and property damage. Failing to comply can result in significant penalties, not to mention the irreparable harm caused by an incident. A well-designed hot work safety program is the cornerstone of meeting these critical legal obligations.
The Indispensable Value of a Hot Work Program Template
For many organizations, creating a comprehensive hot work program from scratch can feel overwhelming. This is precisely where an Osha Hot Work Program Template demonstrates its immense value. It acts as a pre-engineered framework, guiding you through the essential elements required for a compliant and effective safety system. Utilizing a templated approach offers numerous benefits beyond just ticking compliance boxes.
Firstly, it ensures consistency across all hot work operations, regardless of location or crew. Secondly, it significantly reduces the time and resources required to develop a new program, allowing safety managers to focus on implementation and training rather than initial document creation. Thirdly, it serves as an excellent training tool, providing a clear roadmap for employees on safe practices. Ultimately, it’s a proactive measure that drastically enhances workplace safety, minimizes risks, and protects both personnel and assets.
Key Components of an Effective Hot Work Program
A robust hot work safety program must be comprehensive, addressing every facet of a hot work operation from planning to post-work cleanup. While specific details may vary based on industry and specific tasks, certain core components are universally critical. These elements ensure a systematic approach to identifying and controlling hazards before they can lead to an incident.
- **Program Scope and Application:** Clearly defines what activities constitute hot work and where the program applies.
- **Roles and Responsibilities:** Outlines who is responsible for what, including the **permit issuer**, hot work operator, and fire watch.
- **Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment:** Procedures for identifying combustible materials, flammable liquids/gases, and other hazards in the work area.
- **Permit-to-Work System:** A formal process for authorizing hot work, detailing specific precautions and requirements.
- **Pre-Hot Work Checks:** Guidelines for inspecting the work area, ensuring adequate ventilation, and removing or protecting combustibles.
- **Fire Watch Requirements:** When a fire watch is needed, their duties, equipment, and duration of watch.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):** Specifies the necessary PPE for all personnel involved in hot work operations.
- **Equipment Inspection and Maintenance:** Requirements for inspecting welding equipment, torches, hoses, and gas cylinders.
- **Emergency Procedures:** Clear instructions for responding to fires, injuries, or other incidents.
- **Training and Competency:** Details for ensuring all personnel involved in hot work are properly trained and qualified.
- **Post-Hot Work Cleanup and Inspection:** Procedures for inspecting the work area after operations cease to prevent smoldering fires.
- **Record Keeping:** Requirements for maintaining permits, training records, and inspection logs.
Leveraging Your Hot Work Permit System
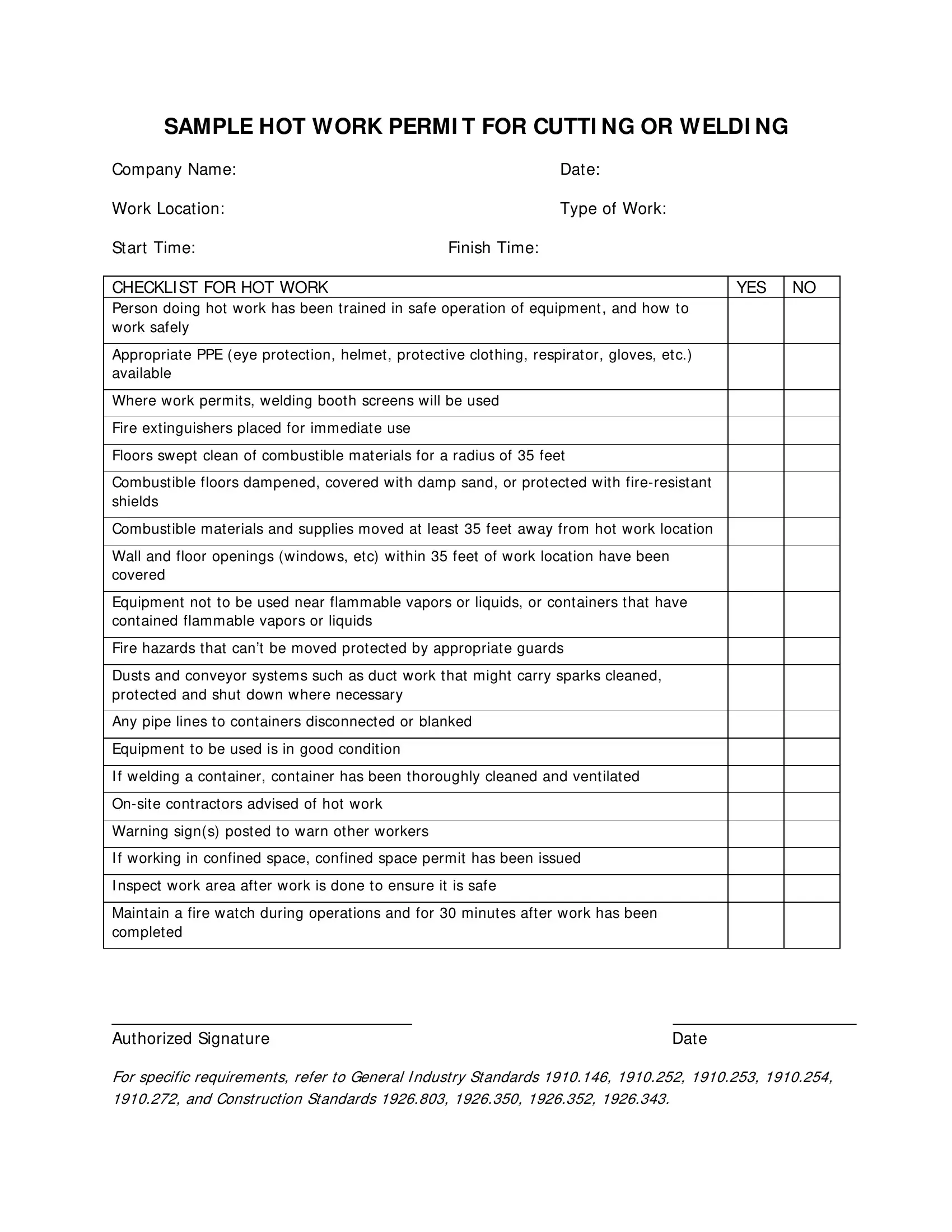
At the heart of any effective hot work safety program is a rigorously implemented hot work permit system. This system isn’t just a piece of paper; it’s a critical control measure that ensures a systematic evaluation of risks and the application of necessary precautions before any heat-producing operation commences. The permit serves as an authorization document, confirming that all required safety checks have been performed and that the work area is deemed safe for hot work.
A well-designed hot work permit typically includes sections for identifying the work location, describing the specific hot work to be performed, listing potential hazards, and detailing the necessary controls and precautions. It also specifies the duration of the permit, the names of the individuals performing the work, and the fire watch personnel. The act of obtaining and reviewing a permit encourages a moment of pause, fostering a culture of deliberate safety over rushed procedures, thereby significantly reducing the likelihood of incidents.
Customizing Your Program for Your Workplace
While a general safety template for hot work provides a strong foundation, true effectiveness comes from tailoring it to your specific operational environment. No two workplaces are exactly alike, and the hazards and controls needed will vary greatly between a shipyard, a manufacturing plant, or a small maintenance shop. The goal is to evolve the initial hot work program template into a living document that accurately reflects your unique risks and operational realities.
Begin by conducting a thorough site-specific risk assessment. Identify the types of hot work routinely performed, the common combustible materials present, and any unique environmental factors (e.g., confined spaces, proximity to flammables). Engage your workforce in this process; their hands-on experience can provide invaluable insights into practical challenges and effective solutions. Adjust the language, add specific departmental procedures, and incorporate any unique equipment or processes relevant to your operations. This customization transforms a generic document into a powerful, tailor-made safety management system for hot work.
Implementing and Maintaining Your Hot Work Safety Protocols
Developing a comprehensive set of hot work procedures is only half the battle; successful implementation and ongoing maintenance are equally crucial. A well-written plan gathers dust if it’s not actively put into practice and regularly reviewed. Effective deployment starts with thorough training for all employees involved in hot work, including operators, supervisors, and fire watch personnel. This training should cover the hot work policy, the permit system, proper equipment use, and emergency response.
Regular audits and inspections are vital to ensure compliance and identify any areas for improvement. These checks should assess whether procedures are being followed, equipment is in good working order, and training remains adequate. Furthermore, foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging feedback from employees and investigating all near-misses and incidents. By treating your hot work safety program as an evolving entity, rather than a static document, you ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness in protecting your most valuable assets: your people.
Implementing a comprehensive hot work program is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a fundamental commitment to workplace safety and operational excellence. The inherent risks associated with heat-producing operations demand a proactive and systematic approach, which a well-crafted program facilitates. By providing clear guidelines, assigning responsibilities, and ensuring proper precautions are taken, you create an environment where hot work can be performed safely and efficiently.
Embracing the principles outlined in a robust hot work safety program empowers organizations to mitigate potential hazards, protect their employees, and safeguard their assets from the devastating consequences of uncontrolled fires or explosions. Investing in a strong safety culture, underpinned by comprehensive protocols, ensures not only compliance but also peace of mind, knowing that every measure has been taken to prevent incidents before they occur. Make safety an integral part of your operational DNA, and watch your workplace thrive.