In the ever-evolving landscape of digital threats, maintaining a robust cybersecurity posture is not just a best practice; it’s a fundamental necessity. Organizations of all sizes face constant bombardment from vulnerabilities, exploits, and sophisticated cyberattacks that can compromise data, disrupt operations, and erode trust. One of the most effective, yet often overlooked, defenses against these threats is a well-defined and consistently executed patch management strategy. For many, the challenge lies in crafting a policy that is comprehensive, actionable, and aligned with industry best practices.
This is precisely where a Patch Management Policy Template Nist becomes an invaluable asset. Leveraging the rigorous and widely respected guidelines from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), such a template provides a structured foundation for developing an organizational policy that minimizes security gaps and strengthens overall resilience. It’s a critical tool for IT managers, security officers, compliance teams, and anyone responsible for safeguarding digital assets, offering a clear roadmap to effectively manage the lifecycle of software and system updates.
Why a Patch Management Policy Template NIST is Essential in Today’s Threat Landscape
The digital world moves at an astounding pace, and with every new software release or operating system update comes the potential for newly discovered vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals are relentlessly searching for these weaknesses, often exploiting them within hours or days of their public disclosure. Without a structured and proactive approach to applying patches, organizations leave gaping holes in their defenses, inviting costly breaches and operational disruptions.
A Patch Management Policy Template Nist provides the framework needed to address these challenges head-on. It ensures that an organization’s approach to vulnerability management is not reactive or ad-hoc, but rather systematic and integrated into its core IT operations. Adhering to NIST guidelines, such as those found in NIST SP 800-40, provides a gold standard for digital hygiene and operational security. This isn’t just about applying fixes; it’s about establishing a repeatable, auditable process that demonstrates due diligence and commitment to data security, which is increasingly critical for regulatory compliance across various industries.
Consider the growing landscape of regulatory requirements like HIPAA for healthcare, PCI DSS for financial transactions, GDPR for data privacy, or the emerging CMMC framework for the defense industrial base. Each of these mandates a strong security posture, with patch management often explicitly or implicitly listed as a core requirement. A NIST-aligned policy template helps organizations not only meet these requirements but also demonstrate a mature and responsible approach to protecting sensitive information and maintaining system integrity. It’s an investment in preventative security, significantly reducing the likelihood and impact of successful cyberattacks.
Key Benefits of Adopting a NIST-Aligned Patch Management Policy Template
Implementing a Patch Management Policy Template Nist offers a multitude of benefits that extend far beyond simply fixing bugs. It fundamentally transforms an organization’s approach to cybersecurity, making it more resilient and efficient.
Firstly, it significantly improves the overall security posture. By standardizing the process for identifying, evaluating, testing, and deploying patches, organizations can systematically reduce their attack surface. This proactive approach ensures critical vulnerabilities are addressed promptly, closing potential entry points for malware, ransomware, and other malicious threats. It’s a cornerstone of effective risk management, safeguarding sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
Secondly, a well-defined policy streamlines IT operations. Rather than chaotic, emergency patching, teams can follow a clear, documented procedure. This leads to more efficient resource allocation, less downtime caused by unpatched systems or botched updates, and clearer roles and responsibilities. The predictability offered by the Patch Management Policy Template Nist reduces operational friction and allows IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives rather than constant firefighting.
Moreover, leveraging a NIST-aligned template provides robust compliance assurance. Regulators and auditors often look for evidence of structured security controls. A policy built on NIST best practices demonstrates a commitment to recognized security standards, making audits smoother and reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties. It provides concrete documentation of an organization’s efforts to protect its information assets, enhancing its reputation and trustworthiness among customers and partners.
Finally, a strong patch management policy contributes to business continuity. By minimizing the risk of security incidents, it reduces potential financial losses from data breaches, legal fees, and reputational damage. It ensures that systems remain available and operational, supporting uninterrupted business processes and maintaining productivity across the enterprise.
Customizing Your Patch Management Policy Template NIST for Unique Organizational Needs
While a Patch Management Policy Template Nist provides an excellent foundational structure, it’s crucial to recognize that no two organizations are exactly alike. Customization is not just recommended; it’s essential to ensure the policy is effective, practical, and truly serves the unique needs and risk profile of your specific environment.
Organizations vary widely in size, from small businesses with a handful of employees to large enterprises with complex, global IT infrastructures. A small business might integrate patch management directly into routine IT tasks, while a large enterprise will require a dedicated team, sophisticated automation tools, and multi-tier approval processes. The template needs to be adapted to reflect the scale of operations, the availability of resources, and the existing IT policy framework.
Industry-specific regulations also play a significant role in how a Patch Management Policy Template Nist should be tailored. A financial institution, for example, might have stringent requirements for patch validation and change control due to PCI DSS, while a healthcare provider will prioritize data privacy under HIPAA, requiring careful consideration of how patches impact systems containing protected health information. The template should be modified to explicitly address these sector-specific compliance obligations and integrate them seamlessly into the patching workflow.
Furthermore, an organization’s technical environment—whether it’s predominantly on-premise, cloud-based, or a hybrid model—will dictate specific elements of the policy. Cloud patching might leverage different tools and processes compared to on-premise servers. Similarly, the types of systems (e.g., critical production servers, development environments, user workstations, IoT devices) will have varying patch frequency and urgency requirements. The template should be flexible enough to encompass these technological nuances, ensuring that the policy remains relevant and actionable across all assets.
Finally, an organization’s unique risk appetite and corporate culture must be reflected. Some organizations may accept a higher level of risk in exchange for faster deployment of new features, while others prioritize stability and security above all else. The Patch Management Policy Template Nist should be adapted to align with these strategic priorities, ensuring that the policy is not just a bureaucratic document but a living guide that supports the organization’s overarching goals.
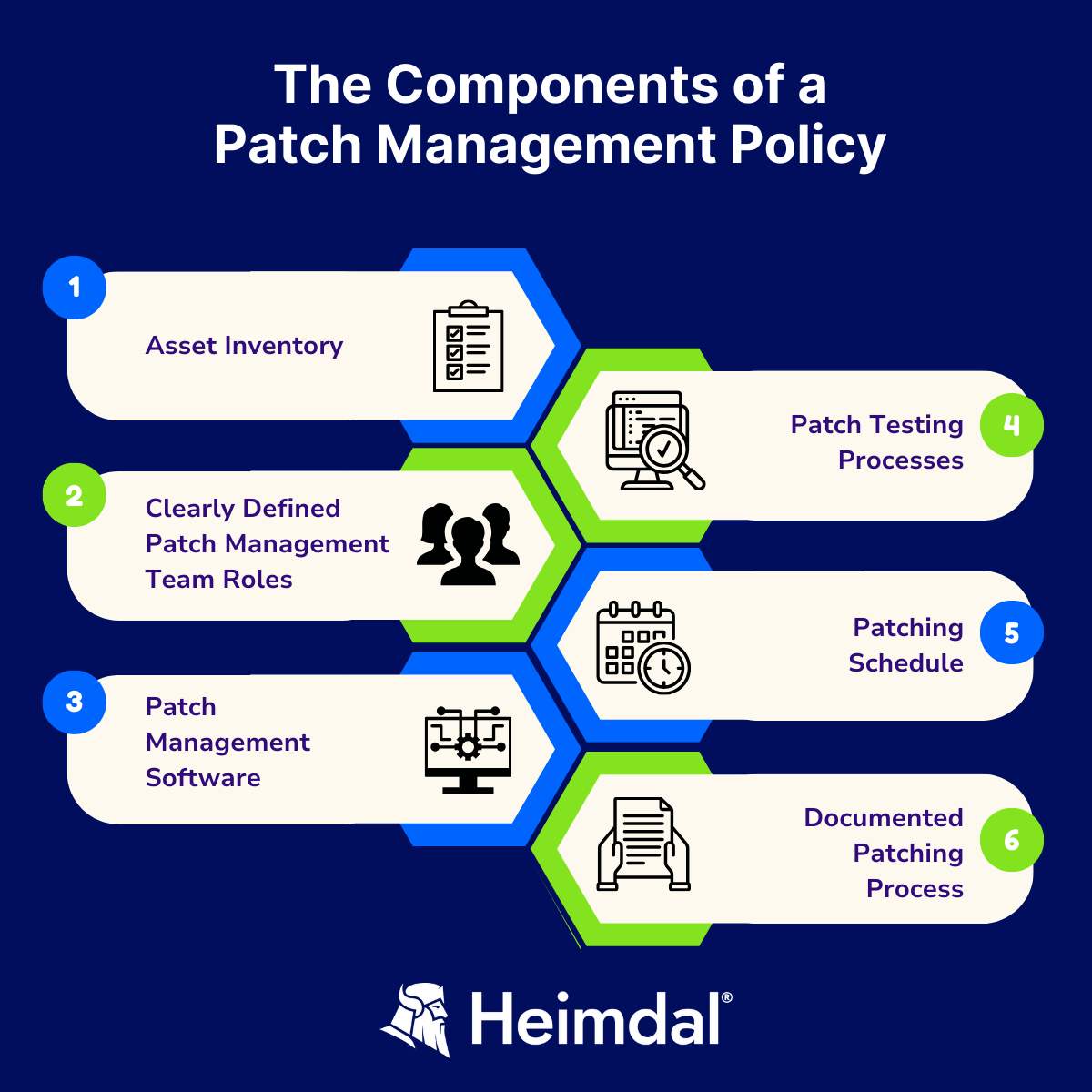
Core Elements to Include in Your Patch Management Policy Template NIST
A robust Patch Management Policy Template Nist must be comprehensive, leaving no critical aspect of the patching lifecycle unaddressed. While customization is key, several core elements form the backbone of any effective policy. These components ensure a holistic and systematic approach to maintaining system integrity and data security.
- Policy Scope: Clearly define what systems, applications, and devices are covered by the policy. This might include operating systems, business applications, firmware, network devices, and even mobile endpoints, ensuring every relevant asset is accounted for.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Outline who is responsible for each stage of the patch management process. This includes system owners, IT security teams, network administrators, application owners, and executive leadership, clearly assigning duties for identification, testing, deployment, and oversight.
- Patch Identification and Assessment: Describe the process for identifying new patches and vulnerabilities. This involves subscribing to vendor alerts, using vulnerability scanners, and leveraging threat intelligence feeds. It also includes methods for assessing the criticality of patches based on factors like severity, exploitability, and impact on business operations.
- Patch Testing and Validation: Detail the procedures for testing patches in a non-production environment before deployment. This section should cover test environments, success criteria, and rollback procedures in case of adverse effects. It’s crucial for preventing operational disruptions.
- Patch Deployment Procedures: Outline the methodology for deploying patches, including scheduling, communication strategies, and sequencing of updates. This might involve different approaches for critical servers versus end-user workstations, and specify automated versus manual deployment.
- Patch Verification and Monitoring: Describe how to verify that patches have been successfully applied and that systems are functioning correctly post-deployment. This includes logging, auditing, and continuous monitoring for any new issues.
- Configuration Management Integration: Explain how patch management integrates with the organization’s broader configuration management practices, ensuring that changes are tracked and documented.
- Exception Handling and Remediation: Establish a clear process for handling exceptions where a patch cannot be applied immediately (e.g., due to compatibility issues) and define compensating controls or remediation plans.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Mandate detailed documentation of all patch management activities, including dates, versions, responsible parties, and any issues encountered. This is vital for auditing and continuous improvement.
- Policy Review and Update: Specify a regular schedule for reviewing and updating the Patch Management Policy Template Nist itself to ensure it remains relevant, effective, and aligned with evolving threats and technologies.
- Communication Plan: Outline how stakeholders will be informed about upcoming patches, potential downtime, and any completed changes. This ensures transparency and minimizes user impact.
- Training and Awareness: Include provisions for training personnel on the importance of patch management and their specific roles within the policy.
Tips for Designing, Implementing, and Maintaining Your Patch Management Policy Template NIST
Developing a comprehensive Patch Management Policy Template Nist is only the first step. For it to be truly effective, it must be designed for usability, implemented thoughtfully, and maintained diligently over time.
When designing your policy, prioritize clarity and conciseness. Avoid overly technical jargon where plain language will suffice, ensuring that all relevant personnel, from IT specialists to executive leadership, can understand its core tenets. Use clear headings, bullet points, and flowcharts where appropriate to enhance readability. Remember, a policy that isn’t understood won’t be followed. Consider creating both a detailed technical document and a high-level executive summary, especially for a large organization, to cater to different audiences. For digital implementation, ensure the document is easily searchable and accessible within your internal knowledge base or document management system, potentially using version control to track changes.
Implementation requires a strategic approach. Start by gaining stakeholder buy-in from the outset, particularly from executive management, who can champion its importance and allocate necessary resources. Pilot the policy in a limited, non-production environment to identify any unforeseen challenges or areas for refinement before a full rollout. Provide thorough training to all personnel involved in the patch management process, emphasizing their specific roles and responsibilities. Integrate the Patch Management Policy Template Nist with existing IT service management (ITSM) frameworks or operational security procedures, such as incident response plans, to ensure seamless execution.
Maintaining the policy is an ongoing commitment. Establish a regular review cycle, ideally annually or whenever significant changes occur in your IT infrastructure, regulatory landscape, or threat environment. This review should include an assessment of the policy’s effectiveness, feedback from the teams executing it, and an analysis of any security incidents that occurred. Use lessons learned to update and refine the policy, ensuring it remains a living document that adapts to evolving needs. Regularly audit compliance with the policy to ensure it’s being followed consistently across the organization. This continuous improvement loop is vital for keeping your patch management strategy robust and responsive to new challenges.
The journey to a truly secure digital environment is ongoing, and a well-crafted patch management strategy is arguably one of its most critical components. By leveraging a Patch Management Policy Template Nist, organizations gain a powerful advantage, transforming a potentially chaotic process into a structured, proactive defense mechanism. It’s more than just a document; it’s a strategic framework that integrates best practices into the very fabric of your IT operations.
Adopting and customizing a NIST-aligned patch management policy not only fortifies your defenses against the relentless tide of cyber threats but also instills confidence in your data security posture. It streamlines operations, ensures compliance with essential regulations, and ultimately contributes to greater business continuity and resilience. Consider this template not as a burden, but as an indispensable tool for achieving a more secure, efficient, and trustworthy digital presence.


