In the intricate world of industrial operations, construction, and facility management, few tasks carry as many inherent risks as entering a confined space. These environments, often unseen or overlooked by the general public, can quickly turn into deadly traps without meticulous planning and stringent safety protocols. From underground vaults and storage tanks to pipelines and boilers, the dangers range from hazardous atmospheres and engulfment to uncontrolled energy releases.
Navigating these perils isn’t just a matter of common sense; it’s a critical compliance mandate established by regulatory bodies like OSHA, designed to safeguard the lives of the dedicated individuals who perform this essential work. A robust confined space safety program is therefore not merely a bureaucratic checkbox but a foundational pillar of operational integrity and, more importantly, human protection. Developing such a comprehensive program from scratch can be a daunting, time-consuming task, which is precisely where a meticulously crafted framework like a Permit Required Confined Space Program Template becomes an invaluable asset for safety managers, facility owners, and even small businesses.
Understanding the “Why”: The Imperative of Confined Space Safety
The statistics surrounding confined space incidents paint a stark picture: they are frequently fatal, and often, multiple fatalities occur when untrained rescuers attempt to assist. OSHA standards, particularly 29 CFR 1910.146 for General Industry and 29 CFR 1926 Subpart AA for Construction, provide specific, non-negotiable requirements for identifying, evaluating, and controlling hazards associated with permit-required confined spaces. These regulations are not arbitrary; they are born from tragic lessons learned over decades.
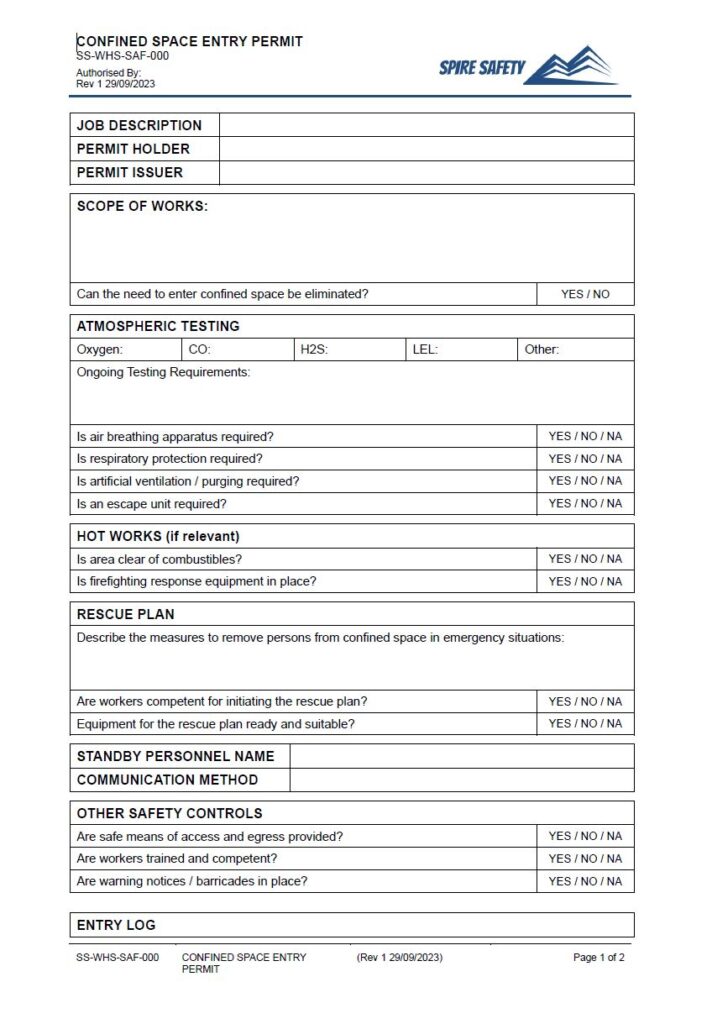
A permit-required confined space (PRCS) is defined by OSHA as a space that has one or more of the following characteristics: contains or has the potential to contain a hazardous atmosphere; contains a material that has the potential for engulfing an entrant; has an internal configuration such that an entrant could be trapped or asphyxiated by inwardly converging walls or by a floor which slopes downward and tapers to a smaller cross-section; or contains any other recognized serious safety or health hazard. The very nature of these spaces demands a structured, systematic approach to ensure that every entry is preceded by a thorough risk assessment, hazard control, and a well-defined plan for safe entry and exit, including emergency procedures.
The Anatomy of a Robust Confined Space Entry Program
An effective confined space entry program extends far beyond a simple checklist; it is a holistic management system designed to anticipate, prevent, and respond to potential hazards. Its primary goal is to ensure that every entry into a hazardous space is performed under strictly controlled conditions, minimizing risk to the entrant and ensuring their safe return. This requires a proactive approach that integrates hazard identification, detailed procedures, appropriate equipment, and comprehensive training.
A well-structured program also establishes clear roles and responsibilities for everyone involved, from the entry supervisor to the authorized entrant and the attendant. It mandates precise atmospheric testing protocols, secure isolation methods for energy sources, and readily available emergency rescue plans. Without such a cohesive framework, organizations risk not only severe penalties from regulatory bodies but, more significantly, the lives and well-being of their workforce.
Key Elements of an Effective Permit-Required Confined Space Program Template
Developing a comprehensive confined space program involves integrating numerous critical components. A robust Permit Required Confined Space Program Template serves as a foundational guide, ensuring no vital element is overlooked. Here are the core components that any effective template should address:
- **Identification and Evaluation:** Thorough procedures for identifying all confined spaces within a facility or on a job site, classifying them as permit-required or non-permit, and evaluating all potential hazards associated with each specific space.
- **Written Program:** A clear, detailed document outlining the employer’s overall strategy for managing confined space entry, including roles, responsibilities, and procedures.
- **Permit System:** Establishment of a formal, written permit system that authorizes entry only after all specified conditions have been met and documented. This includes defining the information required on the permit, such as the date, duration, purpose of entry, authorized entrants, attendant, entry supervisor, hazards, control measures, and rescue services.
- **Authorized Entrants:** Procedures for designating authorized entrants, ensuring they are properly trained, understand the hazards, and know how to use personal protective equipment (PPE).
- **Attendants:** Responsibilities of the attendant, including continuous monitoring of authorized entrants, maintaining communication, performing non-entry rescue, and summoning emergency services. Attendants must never enter the confined space.
- **Entry Supervisor:** Clearly defined duties of the entry supervisor, who is responsible for verifying that all entry requirements have been met, authorizing entry, and terminating entry operations when necessary.
- **Hazard Control Measures:** Specific methods for controlling identified hazards, including ventilation, purging, inerting, lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures, and other isolation techniques to prevent energy release or material ingress.
- **Atmospheric Monitoring:** Requirements for testing the atmosphere within the confined space before entry and continuously during entry for oxygen content, flammable gases/vapors, and potential toxic contaminants. This includes calibration and use of appropriate monitoring equipment.
- **Rescue and Emergency Services:** Detailed plans for emergency response, including designated rescue procedures (non-entry vs. entry rescue), availability of retrieval systems, and coordination with local emergency services.
- **Training:** Comprehensive training programs for all personnel involved in confined space operations, tailored to their specific roles and responsibilities, ensuring they understand the hazards, procedures, and proper use of equipment.
- **Equipment:** Specification and maintenance requirements for all necessary equipment, including atmospheric monitors, ventilation equipment, PPE, retrieval systems, and communication devices.
- **Program Review and Update:** Protocols for periodically reviewing the effectiveness of the program, especially after any incidents or changes in operations, to ensure continuous improvement and compliance.
Benefits of Utilizing a Permit Required Confined Space Program Template
Leveraging a well-designed confined space safety template offers a multitude of advantages that streamline safety management and reinforce compliance. It transforms a potentially overwhelming task into a manageable process, providing a clear roadmap for organizations of all sizes. The value it brings extends across operational efficiency, risk management, and the overall safety culture.
Firstly, a comprehensive template significantly reduces the time and effort required to develop a safety program from scratch. Instead of spending countless hours researching regulations and drafting policies, safety professionals can use a pre-structured framework that already incorporates the essential elements of OSHA compliance. This efficiency allows teams to focus more on site-specific hazard assessments and training, rather than administrative overhead.
Secondly, it ensures consistency and thoroughness. A template provides a standardized structure, ensuring that all critical aspects of a confined space entry program are addressed uniformly across different sites, departments, or projects. This standardization minimizes the risk of overlooking a vital safety step, which could have catastrophic consequences. It acts as a detailed checklist, guiding users through every necessary component, from hazard identification to emergency response.
Furthermore, a robust permit-required confined space program template enhances compliance with regulatory requirements. By aligning with OSHA standards, the template helps organizations meet their legal obligations, thereby avoiding costly fines, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. It provides a defensible document that demonstrates due diligence in protecting workers. This proactive approach not only satisfies regulatory mandates but also builds a stronger, more responsible safety posture.
Finally, and most importantly, it significantly improves worker safety. By providing clear procedures, defining roles, and mandating specific hazard controls, a template directly contributes to a safer working environment. It equips workers and supervisors with the knowledge and tools necessary to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and respond effectively in emergency situations, ultimately saving lives.
Implementing and Customizing Your Confined Space Safety Template
While a template provides an excellent foundation, its true value lies in its effective implementation and customization to fit the unique realities of your specific worksite. No two facilities or projects are identical, and therefore, a generic confined space entry program will always fall short without tailored adjustments. The process of adapting and integrating this framework is crucial for its success.
Begin by conducting a thorough, site-specific hazard assessment for every potential confined space. This step moves beyond the template’s general guidelines, requiring detailed analysis of specific materials, processes, energy sources, and environmental conditions present within your operation. Document these findings meticulously, as they will directly inform the specific control measures and procedures outlined in your customized program.
Next, integrate the customized confined space management system into your existing safety management framework. This ensures cohesion across all safety protocols, preventing isolated policies that might be overlooked or contradict other procedures. Effective integration means that the confined space program becomes a natural, seamless part of daily operations, not an add-on. Regular training for all affected personnel—entrants, attendants, supervisors, and rescue teams—is paramount. This training must cover the specific hazards identified, the detailed procedures for entry, the use of all required equipment, and emergency protocols. Practical drills and exercises using your customized plan are invaluable for reinforcing knowledge and building confidence.
Beyond the Document: Fostering a Culture of Safety
A meticulously documented confined space program, even one built from a stellar template, is only as effective as the culture that supports it. The written procedures are the blueprint, but human vigilance, commitment, and continuous improvement are the builders. Fostering a strong safety culture means that safety is not just a set of rules but a deeply ingrained value shared by everyone within the organization, from the executive suite to the front-line worker.
Leadership commitment is the cornerstone of this culture. When management consistently champions safety, provides necessary resources, and leads by example, it signals to the entire workforce that safety is a non-negotiable priority. Worker involvement is equally critical; those who perform the work often have invaluable insights into potential hazards and practical solutions. Encouraging open communication, feedback, and active participation in safety discussions empowers employees to take ownership of their safety and the safety of their colleagues. Regular review meetings, incident investigations focused on learning rather than blame, and continuous training are all mechanisms to keep the safety program vibrant and responsive.
Ultimately, the goal is to create an environment where every individual feels empowered to identify and address hazards, where safety is integrated into every decision, and where no task is ever so urgent that it bypasses established safety protocols. This goes beyond mere compliance; it’s about cultivating a workplace where the well-being of every person is paramount, ensuring that everyone goes home safely at the end of the day.
The diligent implementation of a comprehensive permit-required confined space program is more than a regulatory obligation; it is a profound commitment to protecting the lives and well-being of your most valuable asset: your workforce. The complexities of confined space entry demand meticulous planning, unwavering adherence to safety protocols, and a proactive approach to hazard mitigation. By leveraging a robust framework, organizations can lay a strong foundation for a safety program that stands up to scrutiny and, more importantly, keeps people safe.
Adopting a high-quality confined space program template empowers organizations to efficiently develop, customize, and maintain a safety system that meets and exceeds industry standards. It provides clarity in hazardous environments, ensures compliance, and significantly reduces the potential for tragic accidents. Invest in this critical tool, personalize it to your operations, and foster a safety culture that truly values every individual’s life.