In the intricate world of project management, where scope creep lurks around every corner and stakeholder expectations can shift like sand, maintaining clarity and control over project requirements is paramount. Without a robust mechanism to connect every requirement to its origin, design, development, and testing, projects risk veering off course, delivering solutions that don’t meet initial needs, or suffering from costly rework. This challenge is precisely why a well-defined Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) becomes not just a useful tool, but an absolute necessity for project success.
Imagine having a clear, verifiable link from the initial business need all the way through to the final product validation. This level of transparency and accountability is what a powerful Pmbok Requirements Traceability Matrix Template offers, serving as the connective tissue that binds your project’s moving parts together. It’s an essential artifact for any project manager striving for precision, alignment, and ultimately, successful delivery in line with the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) principles.
The Cornerstone of Project Clarity: What is a Requirements Traceability Matrix?
A Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) is a document that links requirements to test cases, use cases, design elements, and other project artifacts. Its primary purpose is to ensure that all approved requirements are delivered and tested effectively. By systematically documenting the lifecycle of each requirement, from its source to its implementation and verification, the RTM provides a clear audit trail.
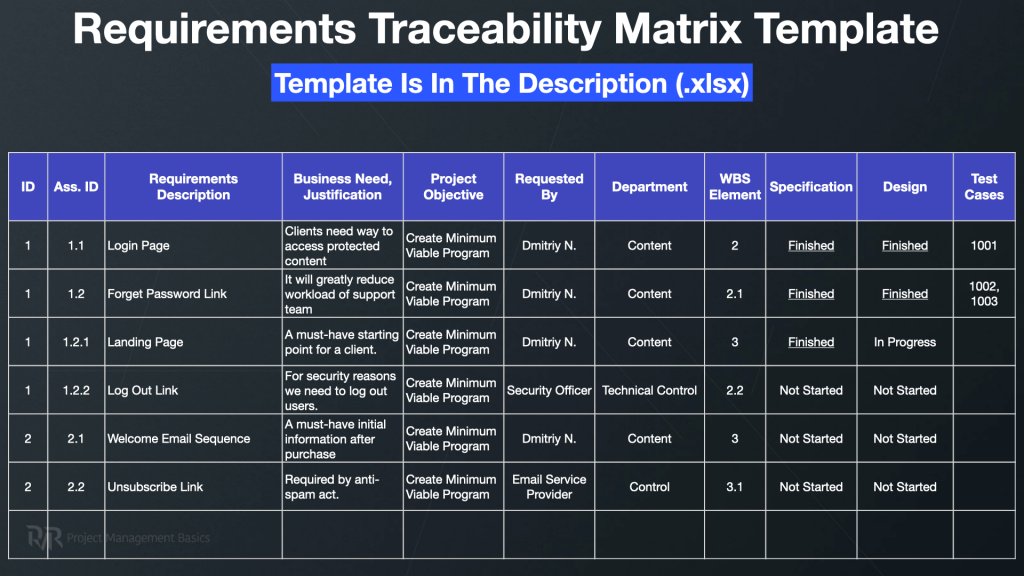
This matrix acts as a bridge, connecting various stages of the project lifecycle. It allows project teams to track the forward and backward traceability of requirements. Forward traceability ensures that every requirement is implemented and tested, while backward traceability confirms that every piece of the solution can be traced back to a specific requirement.
Why the PMBOK Emphasizes Requirements Traceability
The Project Management Institute’s (PMI) PMBOK Guide underscores the critical role of requirements management as a core process within project scope management. It advocates for comprehensive planning, collection, definition, and control of requirements. The Pmbok Requirements Traceability Matrix Template is a direct embodiment of these best practices, providing a structured approach to fulfill PMBOK’s recommendations.
It serves as a key output in the "Collect Requirements" and "Define Scope" processes, ensuring that what the project sets out to achieve is systematically linked to how it will be built and validated. Adopting a structured approach, like utilizing a dedicated Pmbok Requirements Traceability Matrix Template, can significantly elevate your project management practice. It aligns directly with the PMBOK’s emphasis on thorough planning and rigorous execution to minimize risks and enhance project predictability.
Unpacking the Benefits of a Robust Traceability Matrix
Implementing a comprehensive requirements traceability matrix offers a multitude of benefits that resonate throughout the entire project lifecycle, leading to more successful outcomes. This powerful tool significantly enhances communication, reduces risks, and improves overall project quality. Its strategic application helps bridge gaps between various project phases and stakeholders.
For project managers, a well-maintained traceability matrix becomes a single source of truth for requirements status. It helps in making informed decisions, managing changes effectively, and keeping stakeholders aligned. This transparency fosters trust and reduces misunderstandings across the project team and with external parties.
Some key advantages include:
• **Improved Scope Management:** By linking requirements to project deliverables, the matrix helps prevent scope creep and ensures that only approved requirements are addressed. It provides a clear boundary for the project work.
• **Enhanced Quality Assurance:** Connecting requirements to test cases ensures comprehensive testing, verifying that every requirement is adequately tested and validated. This leads to higher quality deliverables and fewer defects post-deployment.
• **Easier Impact Analysis:** When a requirement changes, the traceability matrix allows for quick identification of all affected design elements, code, and test cases. This enables accurate impact assessments and minimizes unintended consequences.
• **Better Risk Management:** Unfulfilled or untested requirements pose significant project risks. The matrix highlights these gaps, allowing teams to proactively address potential issues before they escalate.
• **Clearer Communication and Collaboration:** It provides a common reference point for all stakeholders, fostering a shared understanding of project scope and progress. This reduces ambiguity and promotes better teamwork.
• **Regulatory Compliance and Auditing:** In regulated industries, demonstrating that all requirements have been met and tested is crucial. The traceability matrix provides the necessary documentation for audits and compliance checks.
Key Elements of an Effective Requirements Traceability Template
A highly effective requirements traceability matrix isn’t just a simple spreadsheet; it’s a meticulously organized document designed to capture critical linkages. While specific columns may vary based on project complexity and industry, certain core elements are universally essential for comprehensive tracking. These elements ensure that every aspect of a requirement’s journey is documented and verifiable.
Utilizing a well-structured template ensures consistency and thoroughness across all requirements. It streamlines the process of linking diverse project artifacts, providing a holistic view of how requirements evolve. Here are the fundamental components typically found in a robust traceability matrix:
- **Unique Requirement ID:** A distinct identifier for each requirement, crucial for easy **reference** and tracking.
- **Requirement Description:** A concise explanation of the requirement, outlining what needs to be achieved or what **functionality** is desired.
- **Source of Requirement:** Where the requirement originated (e.g., business analyst, stakeholder, legal mandate, **regulatory body**).
- **Requirement Type:** Categorization (e.g., business requirement, functional, non-functional, **technical**, security).
- **Priority:** The importance of the requirement (e.g., **High**, Medium, Low, Must-Have, Should-Have).
- **Status:** The current state of the requirement (e.g., **Proposed**, Approved, In Progress, Implemented, Tested, Deferred, Rejected).
- **Related Design Documents/Components:** Links to design specifications, architecture diagrams, or specific **system modules** addressing the requirement.
- **Related Test Cases/Scripts:** Identification of the test cases designed to **verify** the fulfillment of the requirement.
- **Verification Method:** How the requirement will be verified (e.g., **User Acceptance Testing (UAT)**, system testing, inspection).
- **Validation Status:** The outcome of the verification process, confirming if the requirement has been successfully **met**.
- **Owner:** The person responsible for the **requirement**.
- **Date Last Modified:** Tracks when the requirement or its status was **last updated**.
Practical Steps to Implement Your Traceability Matrix
Implementing a requirements traceability matrix effectively requires more than just filling out a template; it demands a systematic approach and consistent effort throughout the project lifecycle. A thoughtful implementation strategy ensures the matrix remains a valuable, living document, rather than becoming outdated overhead. By following a structured process, you can maximize its benefits.
Begin by integrating the matrix into your project planning from the outset, rather than adding it as an afterthought. This proactive approach ensures all team members understand its purpose and contribute to its maintenance. It becomes a foundational element of your project documentation, guiding development and testing activities.
1. **Define Your Traceability Scope:** Determine which types of requirements and artifacts you need to trace. Not every single detail might require traceability, but critical business, functional, and non-functional requirements almost always do.
2. **Select or Customize a Template:** Choose a suitable requirements traceability matrix template. It could be a basic spreadsheet or a more sophisticated tool integrated with your project management software. Customize it to include the key elements relevant to your project.
3. **Identify and Document All Requirements:** Systematically collect, analyze, and document all project requirements. Assign unique IDs to each requirement from the very beginning.
4. **Link Requirements to Design Elements:** As design documents are created, link each design component back to the specific requirements it addresses. This ensures that the design is fully aligned with the defined needs.
5. **Develop Comprehensive Test Cases:** Create test cases that directly correspond to each requirement. Ensure that every requirement has at least one test case designed to verify its fulfillment.
6. **Maintain and Update Continuously:** The traceability matrix is a living document. As requirements change, designs evolve, or tests are executed, ensure the matrix is updated promptly. Assign ownership for its maintenance.
7. **Integrate with Change Management:** Link the matrix to your project’s change control process. Any proposed change to a requirement should trigger an update in the matrix and an impact analysis using its data.
8. **Regularly Review with Stakeholders:** Periodically review the matrix with key stakeholders to ensure accuracy and alignment. This promotes transparency and keeps everyone informed about the status of requirements.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While incredibly valuable, a requirements traceability matrix can become a burden if not managed correctly. Awareness of common pitfalls and proactive strategies to avoid them are crucial for its successful implementation. Overlooking these challenges can lead to an outdated, inaccurate, or ignored matrix, negating its potential benefits.
One common mistake is treating the matrix as a one-time setup rather than a dynamic, ongoing process. This often results in the matrix quickly becoming irrelevant as project details evolve. It’s essential to embed its maintenance into daily project activities.
• **Over-Complication:** Trying to trace every single detail can make the matrix unwieldy and difficult to maintain. Focus on critical requirements and linkages that provide the most value for your project’s risk profile. Start simple and expand if needed.
• **Lack of Automation:** Manually updating a large matrix can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Where possible, leverage project management tools or custom scripts to automate parts of the traceability process, especially for status updates.
• **Infrequent Updates:** An outdated matrix is useless. Establish a clear process for regular updates and assign responsibility for maintaining the accuracy of the data. Make it a routine part of project meetings and reviews.
• **Poorly Defined Requirements:** If the initial requirements are vague or ambiguous, the traceability links will also be weak. Invest time in clear, concise, and measurable requirement definitions from the outset.
• **Lack of Team Buy-in:** If the project team doesn’t understand the value of the matrix, they won’t prioritize its maintenance. Educate team members on its benefits and how it helps them in their roles.
• **Disconnected Tools:** Trying to maintain traceability across disparate, unconnected tools can be challenging. Aim for integration between your requirements management, design, and testing tools where feasible.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a Requirements Traceability Matrix?
The primary purpose of an RTM is to ensure that all approved project requirements are fully understood, implemented, and verified throughout the project lifecycle. It creates a clear, documented link from the origin of a requirement to its final validation.
How does a Traceability Matrix relate to PMBOK principles?
A traceability matrix directly supports PMBOK principles by enhancing scope management, ensuring rigorous requirements collection and definition, and providing a structured approach to verify that project deliverables align with stakeholder needs. It’s a key tool for managing project scope and quality.
Can a Requirements Traceability Matrix be used for agile projects?
Absolutely. While often associated with waterfall, an RTM is highly valuable in agile environments too. It helps ensure that user stories or backlog items are linked to features, tests, and business value, providing clarity on scope and sprint goals. It can be adapted to track iteration-level traceability.
What is the difference between forward and backward traceability?
Forward traceability traces requirements forward to design, development, and test cases, ensuring that every requirement is implemented and tested. Backward traceability traces back from test cases, design elements, or code to the original requirements, ensuring that every part of the solution maps back to a defined need.
Who is typically responsible for maintaining the Traceability Matrix?
While the project manager usually oversees it, the responsibility for maintaining the traceability matrix is often shared. Business analysts might manage requirement descriptions, development leads link to design, and QA leads link to test cases. Collaborative effort ensures its accuracy and completeness.
Mastering project requirements is a hallmark of successful project management, and the requirements traceability matrix stands as an unsung hero in this endeavor. It’s more than just a document; it’s a strategic asset that transforms abstract needs into tangible, verifiable outcomes. By diligently applying the principles outlined here, project teams can navigate complexity with greater confidence, delivering solutions that truly meet their intended purpose.
Embrace the power of thorough traceability to elevate your project execution and stakeholder satisfaction. A well-managed traceability matrix not only streamlines development and testing but also fortifies your project against common pitfalls, ensuring that every effort contributes directly to the project’s ultimate success. Invest in a robust approach to requirements tracking, and watch your project clarity and control soar.


