In the intricate world of project management, where stakes are high and success hinges on precision, the clarity of project requirements stands as a foundational pillar. Without a well-defined understanding of what needs to be built or achieved, even the most skilled teams can find themselves adrift, grappling with scope creep, budget overruns, and ultimately, stakeholder dissatisfaction. This universal challenge underscores the critical need for meticulous documentation that leaves no room for ambiguity.
For project management professionals, particularly those pursuing or holding the prestigious Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, mastering the art of requirements documentation is not merely a best practice; it is a strategic imperative. This is precisely where a robust Pmp Requirements Documentation Template becomes an invaluable asset. It’s more than just a form; it’s a structured approach that guides teams through the complexities of gathering, analyzing, and formalizing project needs, ensuring everyone is aligned from conception to delivery.
Why Comprehensive Requirements Documentation is Non-Negotiable
The journey from a project idea to a tangible outcome is fraught with potential missteps. One of the most common pitfalls arises from inadequate or poorly communicated requirements. Imagine a builder starting construction without detailed blueprints – the result would be chaos, costly rework, and a structure that barely resembles the client’s vision. The same principle applies to projects across any industry.
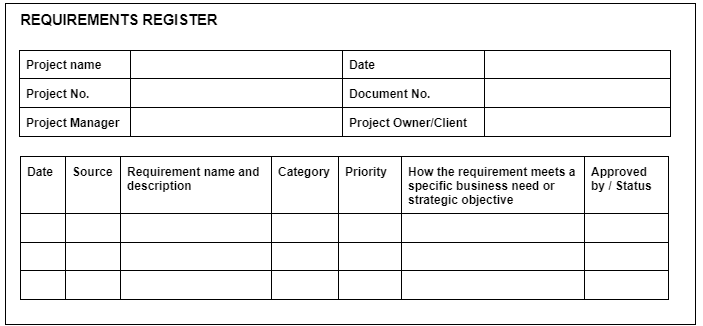
Effective requirements documentation serves as the blueprint for your project. It minimizes assumptions, clarifies expectations, and provides a single source of truth for all stakeholders. This clarity is crucial for mitigating risks such as scope creep, where undocumented changes subtly expand the project’s boundaries, or resource misallocation, which can lead to missed deadlines and increased costs. By thoroughly documenting every aspect of what the project aims to deliver, teams can ensure that development efforts are consistently aligned with organizational goals and stakeholder needs, establishing a strong foundation for successful project execution and control.
The Core Benefits of a Structured Approach
Adopting a standardized project requirements template offers a multitude of advantages that extend far beyond simply recording information. It instills discipline and consistency in the requirements management process, which is vital for complex endeavors. This structured methodology translates directly into improved project outcomes and enhanced team efficiency.
A well-utilized template helps to forge consensus among diverse stakeholder groups, ensuring that everyone involved shares a common understanding of the project’s objectives and deliverables. It provides the essential groundwork for accurate scope definition, enabling more precise estimates for budget, schedule, and resource allocation. Furthermore, detailed documentation significantly aids in the development of robust test plans and quality assurance processes, as testers can directly validate whether implemented features meet the specified criteria. Ultimately, comprehensive requirements serve as a critical reference point for change management, preventing unauthorized modifications and facilitating controlled adjustments throughout the project lifecycle.
Key Elements of Effective Requirements Documentation
A comprehensive requirements gathering document goes beyond a simple list of features. It systematically captures various facets of project needs, providing a holistic view that supports effective planning and execution. While each project is unique, a well-designed project requirements template typically includes several core components that ensure all critical aspects are addressed.
Here are the essential elements commonly found in robust requirements specification:
- **Project Overview and Purpose:** A high-level summary defining the project’s vision, objectives, and its alignment with strategic business goals. This sets the context for all subsequent details.
- **Stakeholder Identification:** Listing all individuals or groups impacted by the project, along with their roles, responsibilities, and influence levels. Understanding who needs what is paramount.
- **Business Requirements:** Describes the high-level needs of the organization, outlining what the business aims to achieve. These often drive the project’s justification and ultimate value.
- **Functional Requirements:** Details what the system or product *must do*. These specify behaviors, actions, and features that the solution will provide to users.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** Specifies *how* the system should perform, focusing on quality attributes like **performance**, security, usability, reliability, scalability, and maintainability.
- **Use Cases or User Stories:** Descriptions of how users will interact with the system to achieve specific goals, often written from the perspective of an end-user. This provides a user-centric view.
- **Assumptions and Constraints:** Clearly states any assumptions made during requirements definition and any limitations or restrictions that may impact the project.
- **Glossary:** Defines key terms and acronyms used within the documentation to ensure clarity and consistency in language.
- **Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM):** A table that links requirements to design, development, and testing artifacts. An RTM ensures that all requirements are addressed throughout the project and facilitates **impact analysis** for changes.
Customizing Your Requirements Template for Success
While a good **Pmp Requirements Documentation Template** provides a solid foundation, it’s crucial to understand that no single template fits every project perfectly. The true value lies in its adaptability. A rigid, one-size-fits-all approach can be as detrimental as having no documentation at all, leading to unnecessary overhead for simple projects or insufficient detail for complex ones. The key is to tailor the structure and depth of your requirements documentation to align with the specific characteristics of your project.
Consider the project’s size, its inherent complexity, the industry it serves, and the methodology being employed (e.g., Agile, Waterfall, Hybrid). For smaller, less complex projects, a streamlined version of a project requirements template might suffice, focusing on critical functional and non-functional aspects without excessive detail. Conversely, large-scale, highly regulated projects will necessitate comprehensive documentation, including detailed legal, compliance, and security requirements. Scalability is paramount; your template should be robust enough to handle intricate details but flexible enough to be simplified when appropriate. Furthermore, integrating the template with collaboration tools and version control systems can significantly enhance its utility, allowing for seamless team contributions and a clear history of changes.
Integrating Requirements with the Project Lifecycle
Effective requirements documentation is not a one-time event at the beginning of a project; it is an ongoing process that is deeply woven into the fabric of the entire project lifecycle. From the initial stages of project initiation to its eventual closure, the evolving set of requirements acts as a constant guide, influencing decisions and shaping deliverables. In the planning phase, detailed requirements form the bedrock for developing the project schedule, budget, and resource plan, ensuring that all efforts are aligned with stakeholder expectations.
During project execution, these documented requirements serve as a benchmark against which progress is measured and work is validated. For monitoring and control, they are essential for identifying deviations, managing changes, and ensuring that the project remains on track to deliver its intended value. Even in iterative or Agile methodologies, where requirements may emerge incrementally, a template for project requirements provides a structured way to capture user stories, epics, and acceptance criteria, maintaining a living document that adapts with each sprint. A robust requirements management plan ensures that as the project evolves, so too does the understanding and articulation of its needs, facilitating informed decision-making at every stage.
Tips for Maximizing Template Utility
Leveraging a project requirements template effectively requires more than just filling in blanks; it demands a strategic approach to requirements gathering and ongoing management. To truly unlock the full potential of your documentation efforts, consider these practical tips designed to enhance clarity, collaboration, and control throughout your project. Implementing these best practices will not only improve the quality of your requirements but also streamline your entire project management process.
- **Engage Stakeholders Early and Often:** Involve key stakeholders from the outset. Their input is invaluable for accurately defining needs and securing buy-in. Continuous engagement helps to clarify ambiguities and manage expectations.
- **Keep it Concise and Clear:** Avoid jargon and overly technical language where possible. Use simple, unambiguous terms to describe requirements, making them understandable to all audiences.
- **Utilize Visual Aids:** Incorporate diagrams, flowcharts, wireframes, and prototypes to supplement textual descriptions. Visuals can often convey complex information more effectively than words alone, especially for functional requirements.
- **Establish a Review and Approval Process:** Define a clear process for reviewing, refining, and formally approving requirements. This ensures that all parties agree on the documented needs before development proceeds.
- **Maintain Traceability:** Ensure that each requirement can be traced to its source (e.g., business need, stakeholder request) and linked to corresponding design elements, test cases, and project deliverables. This is crucial for verifying completion and managing changes.
- **Regularly Update and Manage Changes:** Requirements are rarely static. Implement a robust change management process to formally propose, review, approve, and communicate any modifications to the requirements documentation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between business and functional requirements?
Business requirements describe the high-level objectives or needs of the organization that the project aims to address, focusing on *why* the project is being undertaken. For example, “Increase customer satisfaction by 15%.” Functional requirements, on the other hand, specify *what* the system or product must do to meet those business needs, detailing specific behaviors or capabilities. An example might be, “The system must allow users to track their order status in real-time.”
How does requirements documentation support Agile projects?
In Agile projects, requirements documentation typically takes the form of user stories, epics, and acceptance criteria. While less formal than traditional Waterfall documentation, these elements still serve to define what needs to be built. They are often captured and managed in tools that facilitate collaboration and continuous refinement, evolving with each sprint. The emphasis is on “just enough” documentation to guide development and support communication, with a focus on delivering working software incrementally.
Who is responsible for documenting project requirements?
While the project manager ultimately oversees the requirements process, the actual documentation is often a collaborative effort. Business analysts typically play a primary role in eliciting, analyzing, and documenting requirements. However, active participation from stakeholders, subject matter experts, development teams, and quality assurance personnel is crucial for ensuring accuracy and completeness. The project manager ensures that the process is followed and that requirements align with project objectives.
Can a generic requirements template be used for any industry?
A generic requirements template can serve as a strong starting point for projects across various industries, providing a foundational structure for capturing essential information. However, it will almost certainly require customization to address the specific nuances, regulatory compliance needs, terminology, and technical demands unique to a particular industry or project type. For instance, a template for a healthcare IT project would need sections for HIPAA compliance, while a construction project template would focus on building codes and materials specifications. Adaptability is key.
Meticulous requirements documentation is undeniably one of the most powerful tools in a project manager’s arsenal. It transforms vague ideas into concrete plans, aligning stakeholders and guiding teams toward a shared vision of success. By investing in a well-structured approach, such as leveraging a comprehensive project requirements template, organizations can drastically reduce rework, mitigate risks, and enhance the overall quality of their deliverables.
Embracing this discipline not only streamlines project execution but also fosters a culture of clarity and accountability within project teams. For any professional striving for excellence in project management, mastering the art of articulating and managing requirements is a testament to their commitment to delivering value. Make robust requirements documentation the cornerstone of your next project, and witness the profound impact it has on achieving your strategic objectives.


