In today’s interconnected digital landscape, data is both a powerful asset and a significant liability. Organizations across the United States are grappling with an ever-evolving patchwork of data privacy regulations, from federal mandates to state-specific laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and emerging privacy acts in Virginia, Colorado, and beyond. This complex environment demands more than just reactive compliance; it calls for a proactive, forward-thinking approach to how personal information is handled at every stage.
This is precisely where a robust Privacy By Design Policy Template becomes not just helpful, but absolutely critical. It serves as the foundational blueprint for embedding privacy considerations into the very core of your systems, processes, and products, rather than tacking them on as an afterthought. Whether you’re a startup developing a new app, an established enterprise launching a new service, or a public sector entity managing citizen data, understanding and implementing the principles outlined in a comprehensive Privacy By Design Policy Template can safeguard your operations, build consumer trust, and ensure long-term legal and ethical compliance.
Why a Privacy By Design Policy Template Is Essential in Today’s Context
The digital age has brought unprecedented opportunities for innovation and connection, but it has also amplified the risks associated with data handling. High-profile data breaches are a constant reminder of the vulnerabilities organizations face, leading to significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and a profound erosion of consumer confidence. A well-articulated Privacy By Design Policy Template helps mitigate these risks by institutionalizing a proactive stance on data protection.
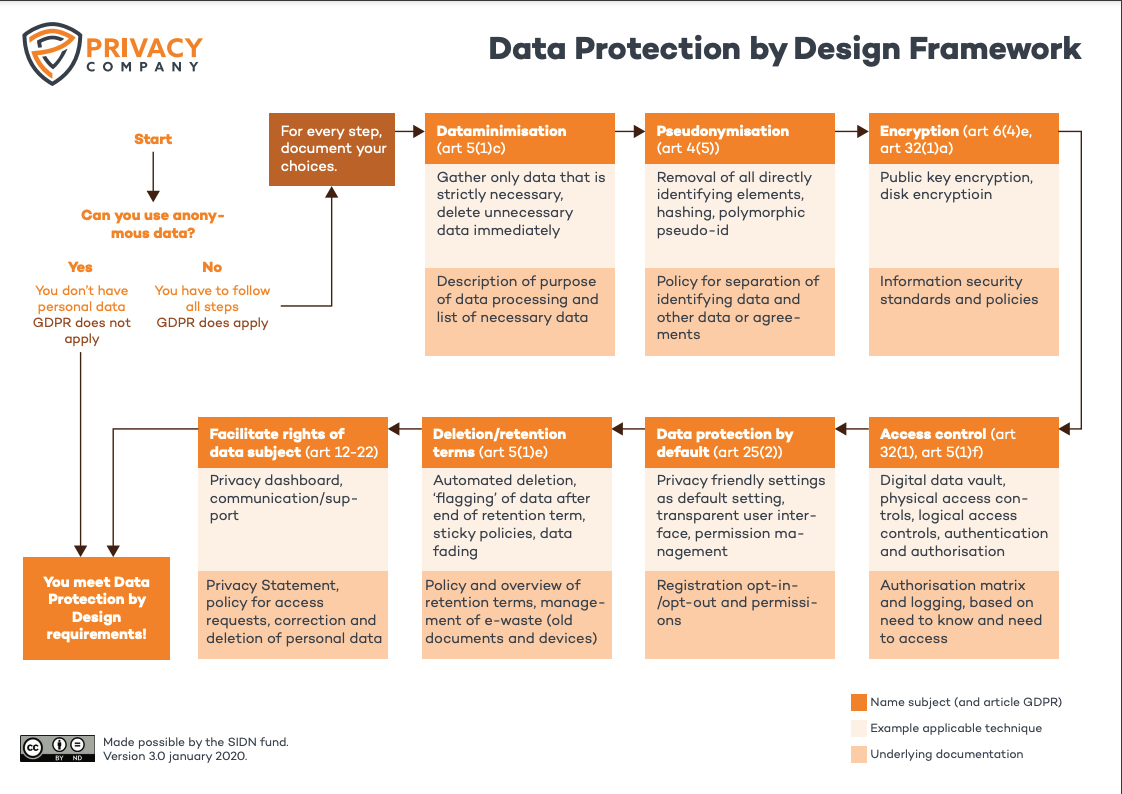
This proactive approach is increasingly mandated by law. Regulators are moving away from mere disclosure requirements towards requiring demonstrable accountability and built-in protections. Laws like the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) explicitly champion Privacy by Design as a core principle, influencing legislative trends worldwide, including here in the US. Implementing a Privacy By Design Policy Template demonstrates an organization’s commitment to these principles, showing due diligence and fostering a culture of respect for individual privacy rights, which can be invaluable during audits or in the event of an incident. It moves data security from an IT problem to an enterprise-wide strategic imperative.
Key Benefits of Using a Privacy By Design Policy Template
Adopting a comprehensive Privacy By Design Policy Template offers a multitude of strategic and operational advantages that extend far beyond simply avoiding penalties. It transforms privacy from a burden into a powerful differentiator. One primary benefit is enhanced compliance; by embedding privacy requirements from the outset, organizations can more easily meet the intricate demands of various data protection laws, reducing the risk of costly violations and legal disputes.
Furthermore, a strong Privacy By Design Policy Template fosters greater consumer trust and loyalty. In an era where individuals are increasingly concerned about how their data is used, organizations that visibly prioritize privacy stand out. This can translate into a significant competitive advantage, attracting customers who value data stewardship and building a reputation for ethical data practices. It also leads to more efficient and effective risk management, as potential privacy vulnerabilities are identified and addressed early in the development lifecycle, preventing more expensive fixes down the line. Finally, it drives innovation by encouraging teams to think creatively about how to build privacy-enhancing features into new products and services, often leading to more robust and user-friendly solutions.
How a Privacy By Design Policy Template Can Be Customized or Adapted
The beauty of a robust Privacy By Design Policy Template lies in its inherent flexibility. While the core principles of Privacy by Design remain consistent, its application must be tailored to the unique context of each organization. Customization begins by considering your industry sector; a healthcare provider handling sensitive patient information will require different emphasis and specific controls than an e-commerce platform processing transaction data, or a SaaS company managing customer accounts.
The size and global reach of your organization also dictate adaptation. A small startup might integrate these principles into agile development cycles, whereas a multinational corporation will need to account for varying international privacy standards within their Privacy By Design Policy Template. Specific data types processed, such as biometric data, financial records, or children’s data, demand heightened scrutiny and specialized safeguards. Moreover, the template should be adaptable to different phases of the data lifecycle—from collection and storage to processing, sharing, and eventual deletion. By thoughtfully adjusting the scope, responsibilities, and control mechanisms within the Privacy By Design Policy Template, organizations can create a living document that is both comprehensive and highly relevant to their specific operational realities and regulatory obligations.
Important Elements or Fields That Should Be Included in a Privacy By Design Policy Template
A truly effective Privacy By Design Policy Template provides a structured framework that guides decision-making and ensures consistency across all initiatives. To achieve this, several key elements and fields must be meticulously detailed:
- Policy Statement and Objectives: A clear declaration of the organization’s commitment to Privacy by Design principles and the overarching goals it aims to achieve through this policy.
- Scope: Defining what the policy applies to (e.g., all new systems, products, services, processes, and major changes to existing ones) and who it applies to (e.g., all employees, contractors, third-party vendors).
- Privacy By Design Principles: Explicitly listing and explaining the seven foundational principles (proactive not reactive, privacy as the default, privacy embedded into design, full functionality, end-to-end security, visibility and transparency, respect for user privacy) and how they are to be applied.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly assigning who is accountable for implementing and overseeing Privacy by Design throughout the organization, including data privacy officers, legal teams, product managers, and engineering leads.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Outlining how privacy considerations will be integrated at each stage of data processing: collection, use, retention, disclosure, and destruction.
- Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) / Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): Detailing the requirements for conducting these assessments, including when they are necessary, the methodology to be used, and how findings will be addressed.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Establishing a framework for identifying, assessing, and mitigating privacy-related risks, along with procedures for ongoing monitoring.
- Data Security Measures: Specifying the technical and organizational controls to protect personal data, such as encryption, access controls, pseudonymization, and anonymization techniques.
- Transparency and User Control: Describing how individuals will be informed about data practices and how their rights (e.g., access, rectification, erasure) will be honored.
- Training and Awareness: Requiring regular training programs for all relevant personnel to ensure understanding and adherence to the Privacy By Design Policy Template.
- Policy Review and Updates: Establishing a schedule and process for regularly reviewing and updating the Privacy By Design Policy Template to reflect changes in technology, law, and organizational practices.
- Incident Response: Briefly outlining how privacy breaches or incidents will be handled in alignment with the proactive principles of the policy.
- Compliance and Reporting: Documenting mechanisms for monitoring compliance with the policy and reporting on its effectiveness.
Tips on Design, Usability, and Implementation
Developing a comprehensive Privacy By Design Policy Template is just the first step; its true value comes from its practical application and integration into daily operations. For both print and digital versions, ensure the document is designed for maximum usability. Use clear, concise language, avoiding jargon where possible, so that it’s accessible to a wide audience within your organization, not just legal or technical experts. Employ headings, subheadings, bullet points, and tables to break up text and improve readability.
Digitally, consider making the Privacy By Design Policy Template searchable and easily navigable through an internal knowledge base or intranet. This allows teams to quickly find relevant sections when initiating new projects or making design decisions. Integrating the policy into existing project management tools and development methodologies (like Agile sprints or DevOps pipelines) can make it a natural part of the workflow rather than an additional burden. Regular training sessions, workshops, and clear communication channels are vital for fostering a culture where privacy by design is not just a policy document, but a deeply ingrained organizational practice. Provide practical examples and case studies relevant to your business to illustrate how the principles apply in real-world scenarios.
Ultimately, a Privacy By Design Policy Template is more than a legal document; it’s a strategic declaration of your organization’s commitment to ethical data stewardship. By embedding privacy into the very fabric of your operations, you build a stronger, more resilient enterprise. It’s about designing products and services with trust and security as foundational elements, ensuring customer data is respected and protected from the earliest stages of conception.
Embracing the principles laid out in a Privacy By Design Policy Template isn’t just about meeting compliance obligations; it’s about staying ahead of regulatory trends, mitigating reputational risks, and fostering innovation. It empowers your teams to build better, more privacy-preserving solutions, creating a significant competitive edge in a privacy-conscious market. Don’t view this as merely a checkbox exercise; see it as a pivotal investment in your organization’s future integrity and success.


