In the rapidly evolving landscape of data-driven decision-making, the ability to generate accurate, relevant, and timely reports is paramount for any organization. Yet, the path from a business question to a fully functional report is often fraught with misunderstandings, scope creep, and unmet expectations. Stakeholders envision one thing, analysts interpret another, and developers build something else entirely. This disconnect not only wastes valuable resources but also erodes trust in data insights.
To bridge this crucial gap, a structured approach to defining what a report needs to be is essential. Enter the Report Development Requirements Template – a foundational tool designed to formalize the initial scoping and design phase of any reporting initiative. It acts as a universal translator, ensuring that everyone involved, from the end-user to the technical team, speaks the same language regarding the report’s purpose, content, and delivery. Adopting such a template is not merely a procedural step; it’s a strategic investment in clarity, efficiency, and ultimately, the success of your data analytics projects.
Why Clear Report Requirements Matter
The absence of well-defined requirements is a common pitfall in many report development projects. Without a clear blueprint, teams often find themselves in a reactive cycle, constantly adjusting, redesigning, and troubleshooting. This can lead to significant delays, budget overruns, and reports that ultimately fail to deliver the intended business value. Imagine building a house without architectural plans; the outcome would be chaotic, expensive, and unlikely to meet the homeowner’s vision.
Clear report requirements act as the architectural plans for your data insights. They provide a shared understanding of the report’s objectives, ensuring that the final product directly addresses specific business questions and supports strategic goals. This upfront clarity significantly reduces rework, enhances communication between technical and business teams, and ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, leading to a higher return on your data investments.
The Power of a Structured Requirements Document
A dedicated report development requirements template transforms an abstract idea into a concrete, actionable plan. It moves beyond casual conversations or fragmented emails, consolidating all necessary information into a single, comprehensive document. This structured approach fosters consistency across projects, making it easier to onboard new team members and maintain a historical record of reporting solutions. It serves as the definitive reference point throughout the report’s lifecycle, from initial design to post-implementation review.
By leveraging a robust reporting project requirements document, organizations can standardize their approach to data reporting. This standardization not only streamlines the development process but also ensures that critical aspects, such as data quality, security, and performance, are considered from the outset. It empowers teams to proactively identify potential challenges and make informed decisions, transforming what could be a complex and unpredictable process into a manageable and predictable one.
Key Elements of an Effective Report Requirements Template
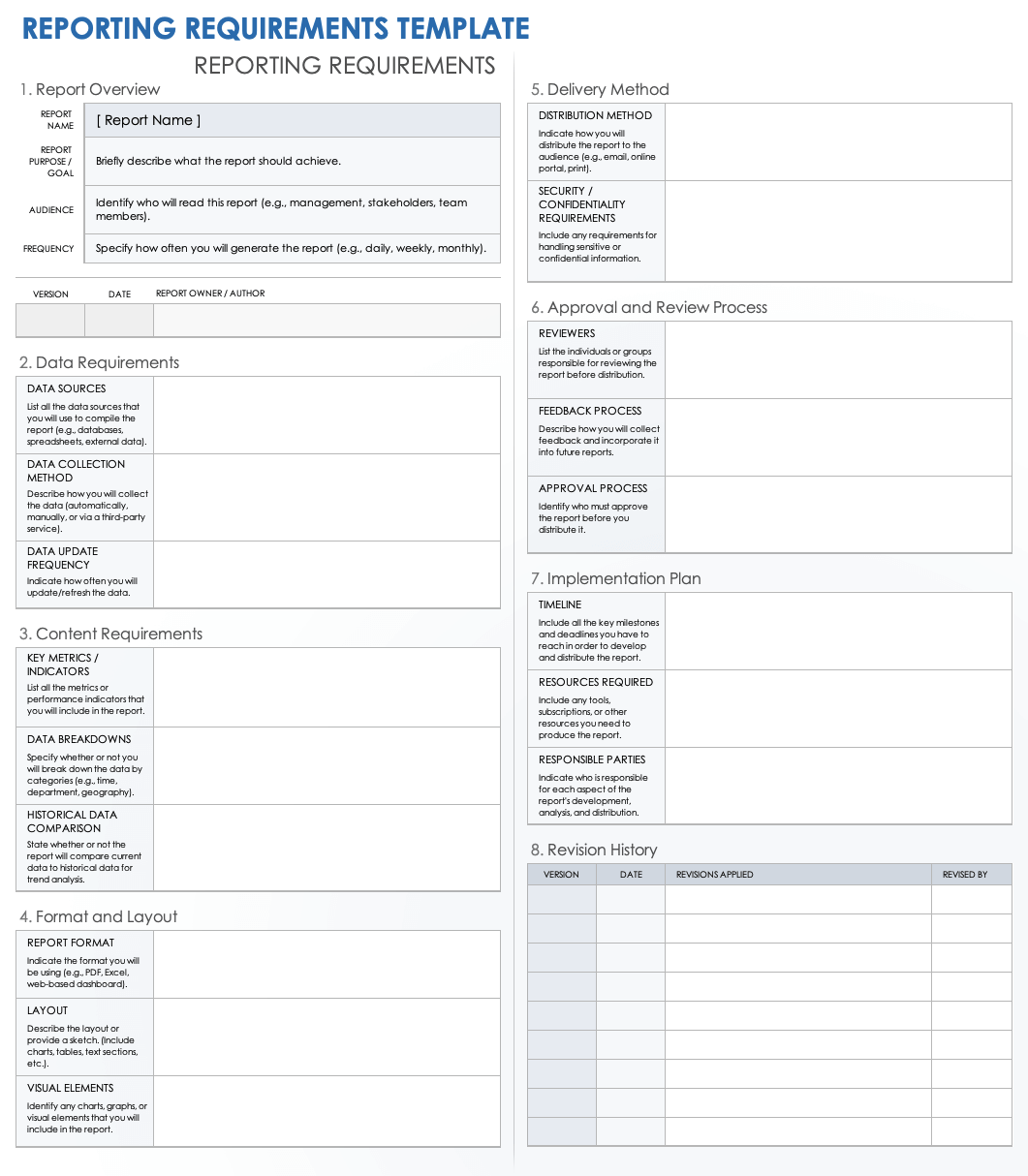
A comprehensive template for defining report needs should cover all critical aspects that contribute to a successful report. While specific sections may vary based on industry or organizational needs, the following elements are fundamental:
- **Report Title and Purpose**: A clear, concise name for the report and a description of its primary objective. What specific business question does it answer, or what decision does it support?
- **Stakeholders and Audience**: Identification of the key individuals or groups who will use the report, along with their roles and what information they expect to gain. Understanding the audience helps tailor the content and presentation.
- **Business Context/Problem**: A detailed explanation of the business scenario or problem that necessitates this report. This provides crucial background for developers and analysts.
- **Key Metrics and Calculations**: Specific data points, key performance indicators (KPIs), and the precise formulas or logic used to derive them. This section is vital for ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- **Data Sources**: Identification of all necessary data sources (e.g., databases, APIs, spreadsheets) and any transformations required to prepare the data for reporting.
- **Visualizations and Layout**: Description of how the data should be presented (e.g., bar charts, line graphs, pivot tables) and the desired layout or dashboard design. Mock-ups or wireframes can be highly beneficial here.
- **Filters and Parameters**: Details on any interactive elements users need, such as date ranges, geographical filters, or product categories, to customize their view of the data.
- **Delivery Method and Frequency**: How and when the report will be accessed or distributed (e.g., web portal, email subscription, scheduled refresh), and how often it needs to be updated.
- **Security and Access Permissions**: Specific requirements for data security and who should have access to the report, and at what level of detail.
- **Performance Expectations**: Any crucial requirements regarding report load times or data refresh rates, especially for high-volume or real-time dashboards.
- **Acceptance Criteria**: Concrete conditions that must be met for the report to be considered complete and successful, serving as the basis for user acceptance testing.
- **Change Management**: A defined process for how future changes or enhancements to the report will be requested, evaluated, and implemented.
Implementing and Customizing Your Requirements Document
Adopting a new report requirements document doesn’t have to be an all-or-nothing proposition. Start by identifying your most pressing needs and gradually integrate the template into your workflow. Many organizations find success by adapting a generic template to fit their specific operational language, data governance policies, and technology stack. The goal is to create a living document that evolves with your business.
Effective implementation hinges on collaboration. Involve stakeholders from across the business—not just IT—in the requirements gathering process. Their input is invaluable for ensuring the report will genuinely meet business needs. Treat the report specification template as a collaborative canvas, where business users articulate their vision and technical teams clarify feasibility and propose solutions. This iterative process of refinement helps to build consensus and ownership, leading to more successful and impactful reporting solutions.
Best Practices for Requirements Gathering
Developing clear and comprehensive data reporting requirements is an art as much as a science. Here are some best practices to ensure your efforts yield the best results:
- **Engage Early and Often**: Involve key stakeholders from the very beginning of the project. Regular check-ins prevent misinterpretations and ensure alignment throughout the development cycle.
- **Ask “Why” Not Just “What”**: Delve deeper than surface-level requests. Understanding the underlying business question or problem helps in designing a report that delivers true value, rather than just data.
- **Define Scope Clearly**: Establish precise boundaries for the report. What will it include, and equally important, what will it explicitly *not* include? This helps prevent scope creep and keeps the project focused.
- **Prioritize Requirements**: Not all requirements are equally critical. Work with stakeholders to categorize needs (e.g., must-have, nice-to-have, future enhancement) to ensure essential functionality is delivered first.
- **Use Visual Aids**: Whenever possible, create mock-ups, wireframes, or sketches of the desired report layout and visualizations. A picture is often worth a thousand words in conveying design intent.
- **Document Assumptions and Constraints**: Clearly state any assumptions made during the requirements gathering process and highlight any technical or business constraints that might impact the report’s design or delivery.
- **Review and Validate Thoroughly**: Circulate the completed `report requirements document` to all key stakeholders for formal review and sign-off. This ensures everyone is on the same page and minimizes surprises later.
- **Manage Expectations**: Be realistic about what can be achieved within given timelines and resources. Communicate potential trade-offs clearly to stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the main benefit of using a report development requirements template?
The primary benefit is achieving clarity and alignment across all project stakeholders, from business users to technical developers. This minimizes misunderstandings, reduces rework, accelerates development cycles, and ensures the final report accurately addresses the business problem it was designed to solve, ultimately saving time and resources.
Who typically uses a report requirements document?
A report requirements document is a collaborative tool used by various roles, including business users who need the reports, data analysts and business intelligence specialists who design them, and developers who build them. Project managers also rely on it for planning, tracking, and managing the scope of reporting initiatives.
Can this template be used for any type of report?
Yes, the fundamental structure of a report specification template is highly adaptable. It can be tailored for a wide range of reports, including operational reports, executive dashboards, financial statements, analytical reports, and even ad-hoc data requests. The core elements remain consistent, while the specifics are customized to the report’s purpose.
How often should report requirements be reviewed?
Report requirements should be reviewed periodically throughout the development lifecycle, especially at key milestones such as design approval, user acceptance testing, and after initial deployment for post-implementation feedback. For reports that are critical to ongoing operations or strategic decisions, an annual or semi-annual review can ensure continued relevance and accuracy as business needs evolve.
Is a report specification template different from a user story?
While related, they serve different purposes. User stories, often used in Agile methodologies (e.g., “As a sales manager, I want to see monthly sales figures by region so I can track team performance”), provide a high-level, user-centric description of a feature. A comprehensive report development requirements template takes these user stories and expands them into detailed technical and functional specifications, outlining every aspect needed for development, from data sources to visualization design and acceptance criteria.
The journey from raw data to actionable insight is often complex, but it doesn’t have to be a gamble. By embracing a structured approach, spearheaded by a well-designed Report Development Requirements Template, organizations can transform their data reporting initiatives into predictable, efficient, and highly valuable endeavors. This systematic framework ensures that every report built is a strategic asset, precisely tuned to meet specific business objectives.
Investing in clear data reporting requirements is an investment in your organization’s future. It fosters a culture of precision, accountability, and data literacy, enabling teams to build reports that not only look good but genuinely drive informed decision-making. Don’t let your valuable data assets remain untapped or mismanaged. Empower your teams with the clarity and structure needed to deliver impactful reports every time.


