In the intricate world of business analysis, precision and clarity are not just desirable traits; they are absolute necessities. Every project, regardless of its size or complexity, hinges on a clear understanding of what needs to be built or changed. Yet, many organizations still struggle with inconsistent documentation, leading to misunderstandings, rework, and ultimately, project delays and budget overruns. The gap between what stakeholders envision and what developers build often originates from loosely defined or poorly communicated requirements.
This is where a structured approach becomes invaluable, transforming ambiguity into actionable insights. Imagine a scenario where every team member, from the product owner to the quality assurance engineer, speaks the same language, guided by a shared understanding of project scope and details. This level of alignment is not a dream; it’s an achievable reality when you adopt robust tools and methodologies, central among them being a well-designed framework for documenting needs. Such a structured outline provides a consistent blueprint for capturing, organizing, and communicating all essential information, ensuring nothing is missed and everything is understood.
A structured outline offers a consistent blueprint for capturing, organizing, and communicating all essential information, ensuring nothing is missed and everything is understood.
Why a Structured Approach Matters for BAs
Business analysts serve as the crucial link between business stakeholders and technical teams. Their primary role involves eliciting, analyzing, documenting, and validating requirements. Without a standardized method for this critical documentation, BAs risk creating disparate artifacts that are difficult to compare, manage, or even comprehend across different projects or team members. The absence of a uniform template can lead to a “reinventing the wheel” syndrome with each new initiative, wasting valuable time and energy.
Moreover, a lack of consistency impedes effective communication. When requirements are presented in varying formats and levels of detail, it becomes challenging for developers to interpret, for testers to validate, and for stakeholders to review accurately. This often results in a higher error rate, more change requests, and a general erosion of trust in the documentation process. A well-designed BA requirements template serves as a common language, reducing ambiguity and fostering a shared understanding that is paramount for project success.
The Undeniable Benefits of a Standardized Template
Adopting a standardized documentation framework brings a cascade of advantages that streamline the entire project lifecycle. It empowers business analysts to be more efficient, enhances communication across teams, and ultimately contributes to the delivery of solutions that truly meet business needs. The initial effort invested in creating or customizing such a tool pays dividends many times over through improved project outcomes and reduced operational friction.
One of the most significant benefits is the consistency it brings. Every set of requirements, regardless of the project or the individual BA, will follow the same logical flow and include the same fundamental sections. This consistency makes it easier for all stakeholders to navigate and understand the documentation. Furthermore, it significantly reduces the learning curve for new team members or for BAs transitioning between projects, as the structure for documentation remains familiar. This standardization also leads to improved quality and completeness of requirements. A good template acts as a checklist, prompting the BA to consider all necessary aspects, minimizing the chances of overlooking critical details that could later derail development efforts. It also fosters better collaboration by providing a clear framework for discussions and approvals, ensuring everyone is on the same page from the outset.
Key Elements of an Effective Requirements Document
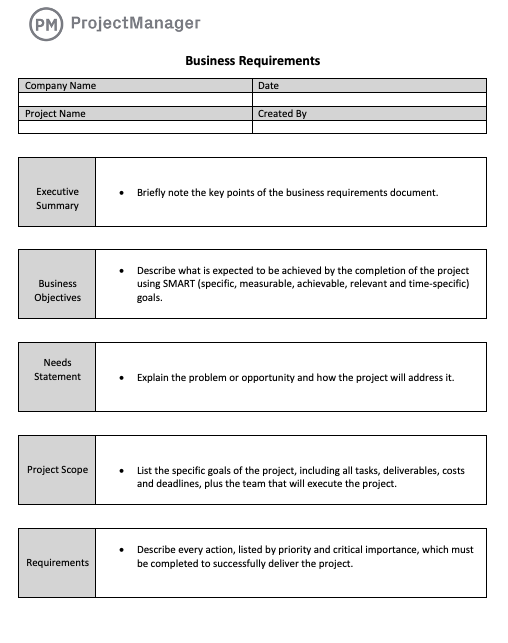
While a specific Requirement Template For Business Analyst will vary based on project type and organizational standards, certain fundamental sections are universally essential for any comprehensive requirements specification framework. These elements ensure that the document covers all critical aspects, from high-level context to granular details, providing a holistic view of the system or solution being developed.
Here are the core components often found in a robust requirements documentation blueprint:
- Introduction and Purpose: Clearly define the document’s objective, target audience, and scope. It sets the stage for the entire document, providing an overview of what will be covered.
- Business Needs and Objectives: Articulate the core problems or opportunities the project aims to address. This section links the requirements directly to strategic business goals, explaining the “why.”
- Scope Definition: Explicitly outline what is **in scope** and, equally important, what is **out of scope**. This prevents scope creep and manages stakeholder expectations effectively.
- Stakeholder Identification: List all key stakeholders involved, along with their roles and responsibilities concerning the project and requirements. Understanding who is affected and who contributes is crucial.
- Assumptions and Constraints: Document any conditions assumed to be true for the project to proceed, as well as any limitations (technical, budgetary, regulatory, etc.) that might impact the solution.
- Functional Requirements: Detail the specific behaviors, functions, or actions the system must perform. These are often described as user stories, use cases, or functional specifications, outlining “what the system does.”
- Non-Functional Requirements: Specify the qualities or characteristics the system must possess, such as performance (speed, response time), security, usability, reliability, scalability, and maintainability. These describe “how well the system performs.”
- User Interface (UI) Requirements: Describe how users will interact with the system, often including wireframes, mockups, or prototypes to illustrate design elements and user flows.
- Data Requirements: Outline the data to be captured, stored, processed, and presented, including data models, data dictionaries, and data migration strategies.
- System Integration Requirements: If the new system interacts with existing systems, detail the interfaces, data exchange formats, and communication protocols.
- Glossary: Define any technical terms, acronyms, or business jargon used within the document to ensure consistent understanding across all readers.
- Approvals and Sign-offs: A section for formal acceptance by key stakeholders, indicating their agreement with the documented requirements.
Crafting Your Template: Customization and Best Practices
While a standardized business analysis template is invaluable, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. The beauty of a template lies in its adaptability. Organizations and projects have unique characteristics that necessitate a tailored approach. Customizing your requirements specification framework to fit your specific context is a critical step in maximizing its utility and ensuring it genuinely serves your team’s needs.
Consider the nature of your projects: Are they primarily Agile, Waterfall, or a hybrid approach? An Agile template might emphasize user stories, acceptance criteria, and lightweight documentation, whereas a Waterfall project might require a more extensive and formal Software Requirements Specification (SRS) outline. The industry you operate in also plays a role; highly regulated industries, for instance, may need to incorporate specific compliance or audit-related sections. When tailoring your BA requirements template, involve key stakeholders, including developers, testers, and project managers, in the design process. Their input will ensure the template addresses their information needs and integrates seamlessly into existing workflows. Regularly review and refine your template based on feedback and lessons learned from completed projects. This iterative improvement ensures it remains relevant and effective.
Regularly review and refine your template based on feedback and lessons learned from completed projects.
Furthermore, establishing best practices for its use is just as important as the template itself. Train your business analysts on how to effectively populate and utilize the documentation tool. Provide clear guidelines on the level of detail expected for different types of requirements. Encourage the use of clear, concise language, avoiding jargon where possible, and employing visual aids like diagrams and flowcharts to enhance understanding. Version control is also paramount; ensure all documents are properly managed, dated, and accessible, with a clear history of changes.
Beyond the Template: Integrating It into Your Workflow
The most meticulously designed documentation framework is only as effective as its integration into the daily workflow of a business analyst and their project team. It should not be seen as a standalone document to be completed once and then filed away, but rather as a living artifact that evolves throughout the project lifecycle. Integrating this structured requirements approach into your operational practices ensures its continuous relevance and value.
This integration involves more than just filling in sections; it’s about making the requirements document a central point of collaboration and decision-making. During requirements elicitation, the template guides the BA’s questioning, ensuring all necessary areas are explored with stakeholders. In the analysis phase, it provides a structured canvas for organizing complex information. For development, it serves as the definitive guide for coding and design. During testing, the acceptance criteria within the template become the basis for test cases. Regular reviews, formal sign-offs, and communication around the documented business needs specification all hinge on the template’s structure. By embedding this standardized structure into every phase, organizations elevate their project management maturity and significantly improve their chances of delivering successful, high-quality solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a Requirement Template For Business Analyst?
The primary purpose of a standardized requirements document template is to provide a consistent, comprehensive, and clear framework for capturing, organizing, and communicating project requirements. It ensures all critical information is included, reduces ambiguity, and improves communication between stakeholders and technical teams, ultimately leading to more successful project outcomes.
Can one universal BA requirements template fit all projects?
While a core requirements specification framework provides a strong foundation, one universal template may not perfectly fit all projects. It’s often beneficial to have a base template that can be customized for different project types (e.g., Agile vs. Waterfall), industry specifics, or the complexity level of the initiative. The key is adaptability while maintaining a consistent core structure.
How often should a requirements specification framework be updated?
A requirements document should be treated as a living document, especially in iterative development environments. It should be updated whenever new information emerges, requirements change, or clarifications are needed. Regular reviews with stakeholders, formal version control, and clear communication of changes are essential practices to maintain its accuracy and relevance throughout the project lifecycle.
Who benefits most from a standardized requirements document template?
Everyone involved in a project benefits from a standardized requirements document. Business analysts gain efficiency and ensure completeness; project managers have better control over scope; developers receive clearer instructions; quality assurance teams have a solid basis for testing; and business stakeholders have a clear understanding of what is being built, leading to better alignment and fewer surprises.
How does a structured requirements approach help prevent scope creep?
A structured approach helps prevent scope creep by clearly defining what is within the project’s boundaries (in-scope) and what is outside them (out-of-scope) from the very beginning. It ensures that all new requests or changes are evaluated against the documented scope and formally managed through a change control process, rather than being informally added, thus maintaining project focus and preventing uncontrolled expansion.
In essence, a well-defined Requirement Template For Business Analyst is more than just a set of headings; it’s a strategic asset. It represents an organizational commitment to clarity, efficiency, and quality in every project. By providing a structured framework for documenting business needs, it elevates the entire requirements process, transforming it from a potential source of chaos into a powerful engine for project success.
Embracing such a standardized requirements structure empowers business analysts to deliver their best work, ensuring that every detail is captured, every stakeholder is informed, and every development effort is aligned with the true needs of the business. It’s an investment that pays dividends in reduced risk, improved communication, and ultimately, the consistent delivery of high-value solutions that propel an organization forward.


