In the complex landscape of modern project management, navigating the myriad of requirements can feel like charting an unknown ocean. From initial stakeholder requests to final product deployment, every single requirement represents a crucial piece of the puzzle. Losing track of even one can lead to project delays, scope creep, budget overruns, or a product that simply doesn’t meet its intended purpose. This is where a robust framework for managing and tracking these essential elements becomes not just helpful, but absolutely indispensable.
Enter the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) — a powerful tool that serves as the backbone for maintaining clarity and control throughout the project lifecycle. It provides a structured way to link requirements to various project artifacts, ensuring that every design decision, development effort, and test case directly corresponds to a defined need. For anyone involved in bringing a product or system to life, understanding and effectively utilizing a requirements traceability matrix is key to delivering successful outcomes.
Understanding the Essence of a Traceability Matrix
A traceability matrix is essentially a document that maps and traces requirements from their origin through the entire project lifecycle. It creates a comprehensive audit trail, ensuring that every declared need is accounted for and fulfilled. Far from being a mere checklist, this vital document provides a clear, bi-directional link between high-level business objectives, detailed functional specifications, design elements, development tasks, and quality assurance test cases.
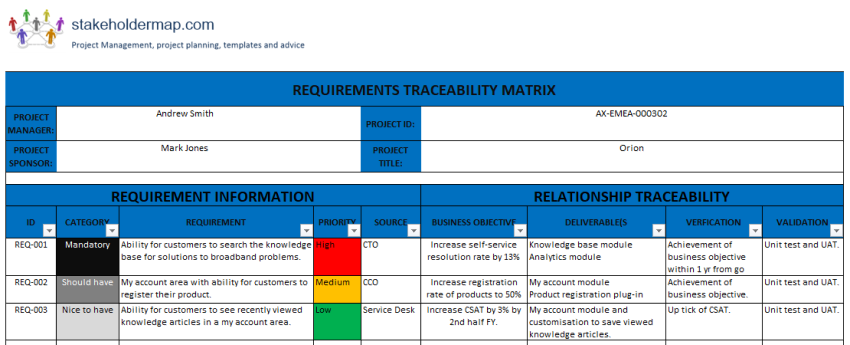
The primary goal of a well-crafted traceability matrix is to establish and maintain a direct relationship between different work products. Imagine being able to instantly see which business requirement led to a specific feature, which design document supports that feature, and which test cases validate its implementation. This level of clarity significantly enhances project visibility, making it easier to manage complexity and respond to changes effectively.
Why a Traceability Matrix Matters for Your Projects
Implementing a comprehensive system for managing requirements offers a multitude of benefits that extend across various project phases and stakeholder groups. It’s a proactive measure that safeguards against common project pitfalls and promotes efficiency.
**Ensuring Complete Coverage:** One of the most significant advantages is the guarantee that no requirement gets overlooked. By systematically linking every project artifact back to its originating requirement, teams can be confident that all specified needs are addressed in the final product. This meticulous approach prevents gaps in functionality and ensures the delivered solution aligns perfectly with initial expectations.
**Facilitating Impact Analysis:** When changes inevitably occur, a robust requirements traceability matrix allows project managers and teams to quickly assess the downstream effects. If a particular requirement needs modification or is removed, the matrix immediately highlights all related design elements, code modules, and test cases that would be impacted, enabling informed decision-making and minimizing unintended consequences.
**Enhancing Risk Management:** Unaddressed or poorly understood requirements are a major source of project risk. By providing a clear view of which requirements are linked to which solutions, and their current status, the matrix helps identify potential issues early. This allows teams to proactively address gaps, mitigate risks, and allocate resources more effectively to critical areas.
**Improving Quality Assurance:** The direct link between requirements and test cases is invaluable for quality assurance teams. It ensures that every requirement is verifiable and that corresponding tests are developed and executed. This not only streamlines the testing process but also guarantees that testing efforts are comprehensive and directly contribute to validating the fulfillment of all specified needs.
**Supporting Compliance and Audit Trails:** For projects in regulated industries (like healthcare, finance, or aerospace), maintaining a clear audit trail is often a legal or regulatory mandate. A well-maintained requirements traceability document provides irrefutable evidence that all requirements, especially those related to compliance, have been thoroughly addressed, tested, and documented.
**Promoting Stakeholder Alignment:** A clear, shared understanding of requirements is crucial for aligning all stakeholders. The matrix serves as a single source of truth, making it transparent how various demands are being met. This reduces miscommunication, fosters collaboration, and ensures everyone is working towards a common goal.
Key Elements of an Effective Traceability Matrix
While the specific columns in a traceability matrix can vary based on project complexity and industry, certain core elements are essential for any effective implementation. A well-designed Requirement Traceability Matrix Template will typically include fields that allow for comprehensive tracking and linking.
- **Requirement ID:** A unique identifier for each requirement, allowing for easy reference. This is crucial for precise tracking.
- **Requirement Description:** A concise summary of the requirement, detailing what needs to be achieved.
- **Requirement Type:** Categorization (e.g., functional, non-functional, business, technical).
- **Source:** Who or what originated the requirement (e.g., stakeholder, regulation, business process).
- **Status:** The current state of the requirement (e.g., **Proposed**, **Approved**, **In Progress**, **Implemented**, **Tested**, **Deferred**, **Rejected**).
- **Priority:** The importance or urgency of the requirement (e.g., **High**, **Medium**, **Low**, **Mandatory**).
- **Parent Requirement ID:** If requirements are hierarchical, this links to the higher-level requirement it supports.
- **Design Specification ID(s):** Links to design documents or specifications that address this requirement.
- **Development Component ID(s):** Links to specific code modules, user stories, or development tasks.
- **Test Case ID(s):** Identifiers for the test cases designed to validate the fulfillment of this requirement.
- **Change Request ID(s):** Links to any change requests that have affected this specific requirement.
- **Verification Method:** How the requirement will be verified (e.g., **Inspection**, **Demonstration**, **Test**, **Analysis**).
Implementing and Customizing Your Traceability Framework
Creating a robust system for linking requirements doesn’t have to be an arduous task. The power of a structured approach, like a good Requirement Traceability Matrix Template, lies in its ability to provide a clear starting point. Whether you opt for a simple spreadsheet or a sophisticated requirements management software, the principles remain the same.
Begin by selecting a tool that fits your project’s scale and your team’s familiarity. For smaller projects, a well-organized spreadsheet can be highly effective. For larger, more complex endeavors, specialized tools offer advanced features like automated linking, version control, and integration with development and testing platforms. The key is to choose a solution that encourages regular updates and seamless collaboration.
Customization is crucial. While a template provides a solid foundation, every project is unique. Tailor the columns and their granularity to match your specific needs. Don’t include fields you won’t use, as this can lead to unnecessary overhead. Conversely, ensure you capture all critical information needed for your project’s success and compliance. For instance, a software project might emphasize links to user stories and code commits, while a construction project might focus on blueprints and build phases.
Tips for successful implementation include:
**Start Early:** Begin populating your requirements traceability matrix as soon as requirements are gathered, even if they are high-level. This prevents a daunting backlog later on.
**Keep it Updated Regularly:** A static matrix is a useless one. Make updating the requirement tracking sheet an integral part of your project’s workflow, especially after any changes, design decisions, or completed development tasks.
**Define Ownership:** Assign clear responsibility for maintaining and updating different sections of the project requirements matrix. This ensures accountability and consistency.
**Integrate with Other Tools:** If possible, integrate your requirements management solution with your project management, development, and testing tools. This can automate linking and reduce manual effort.
**Don’t Overcomplicate:** While comprehensiveness is good, excessive detail can hinder adoption. Strive for a balance that provides sufficient insight without becoming overly burdensome to maintain.
Practical Use Cases Across Industries
The versatility of a requirements traceability matrix means its application extends far beyond just software development. Any project where complex needs must be translated into deliverable solutions can benefit immensely from a structured approach to tracing requirements.
In software development, a traceability matrix is often used to link user stories to functional requirements, design specifications, code components, and automated test scripts. This ensures that every line of code and every feature directly supports a defined user or business need, and that it can be rigorously tested.
For construction projects, a traceability table might connect client specifications for a building (e.g., number of rooms, energy efficiency standards) to architectural blueprints, structural engineering designs, material procurement lists, and inspection checkpoints. This ensures that the final structure adheres to all initial client demands and regulatory codes.
In the healthcare sector, particularly for medical device development or implementing new hospital systems, traceability is paramount for regulatory compliance. A requirement linkage matrix would connect regulatory mandates and patient safety requirements to system features, clinical workflows, validation protocols, and audit documentation, proving adherence to strict standards.
Product development across various industries, from automotive to consumer electronics, also heavily relies on this methodology. Market research insights and customer needs are traced to product features, engineering specifications, manufacturing processes, and quality control checks, ensuring the final product meets market demand and quality benchmarks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the main purpose of a requirements traceability document?
The primary purpose is to establish clear, verifiable links between project requirements and other artifacts like design specifications, code, and test cases. It ensures that all requirements are addressed, provides an audit trail for changes, and helps manage project scope and quality.
Can a small project benefit from using a traceability table?
Absolutely. Even small projects can suffer from scope creep or unmet expectations. A simple traceability table can help maintain focus, ensure all key deliverables align with initial requirements, and make impact analysis easier if any changes arise. It scales down effectively.
How often should a requirement linkage matrix be updated?
It should be updated regularly, ideally as project artifacts are created or modified. This includes after requirements are approved, designs are finalized, code is developed, and tests are executed. Continuous updates ensure the matrix remains a living, accurate reflection of the project’s status.
What’s the difference between forward and backward traceability?
Forward traceability maps requirements to downstream deliverables (e.g., from requirement to design, code, test), ensuring all requirements are implemented. Backward traceability maps deliverables back to requirements (e.g., from a test case to the requirement it validates), ensuring no extraneous work is done and all work aligns with a stated need.
Are there any common pitfalls to avoid when creating a requirement tracking sheet?
Yes, several. A common pitfall is making it overly complex, leading to reluctance in updating it. Another is not keeping it current, rendering it useless. Also, failing to define clear ownership for its maintenance, or not integrating it into the team’s regular workflow, can severely limit its effectiveness.
In the dynamic world of project execution, the ability to clearly define, track, and validate requirements stands as a cornerstone of success. A meticulously maintained system for managing requirements isn’t just a bureaucratic chore; it’s an indispensable strategic asset. It empowers teams to navigate complexities, mitigate risks, and ensure that every delivered component genuinely contributes to the project’s ultimate goals.
Embracing the structured approach offered by a well-designed Requirement Traceability Matrix Template can transform how your organization manages projects. It provides the clarity, control, and confidence needed to move from concept to completion with precision and purpose. By investing in robust requirement tracing practices, you’re not just organizing data; you’re building a foundation for consistent, successful project delivery, ensuring that your vision translates flawlessly into tangible results.


