Navigating the intricate landscape of modern projects often feels like a high-stakes puzzle, where every piece—every requirement—must fit perfectly to achieve success. From software development to aerospace engineering, healthcare product creation to large-scale infrastructure, the sheer volume and complexity of specifications can be overwhelming. Ensuring that every single one of these requirements is not just acknowledged but truly met, tested, and verified is the bedrock of project integrity and stakeholder confidence. Without a systematic approach, critical elements can slip through the cracks, leading to costly reworks, project delays, regulatory non-compliance, and ultimately, project failure.
This is where a robust and thoughtfully designed requirements compliance tool becomes indispensable. It serves as your project’s single source of truth, a living document that systematically maps each requirement to its verification method and actual compliance status. Far more than just a checklist, it’s a strategic asset that provides clarity, mitigates risk, and streamlines communication across diverse teams. For anyone managing a project where adherence to detailed specifications is paramount, understanding and utilizing a comprehensive Requirements Compliance Matrix Template is not merely a best practice—it’s a fundamental necessity for achieving excellence and delivering on promises.
Understanding the “Why”: The Imperative of Requirements Traceability
In any complex endeavor, defining what needs to be built or delivered is just the first step. The real challenge lies in proving that those definitions have been accurately translated into the final product or service. This process, known as traceability, is about establishing a clear, unbroken line from the initial high-level user needs down to the smallest technical specification, and then linking those specifications to tests, design elements, and verification results. A lack of traceability can lead to numerous pitfalls. Features might be developed that don’t align with original needs, critical safety requirements could be overlooked, or regulatory obligations might be missed entirely, opening the door to legal and financial repercussions.
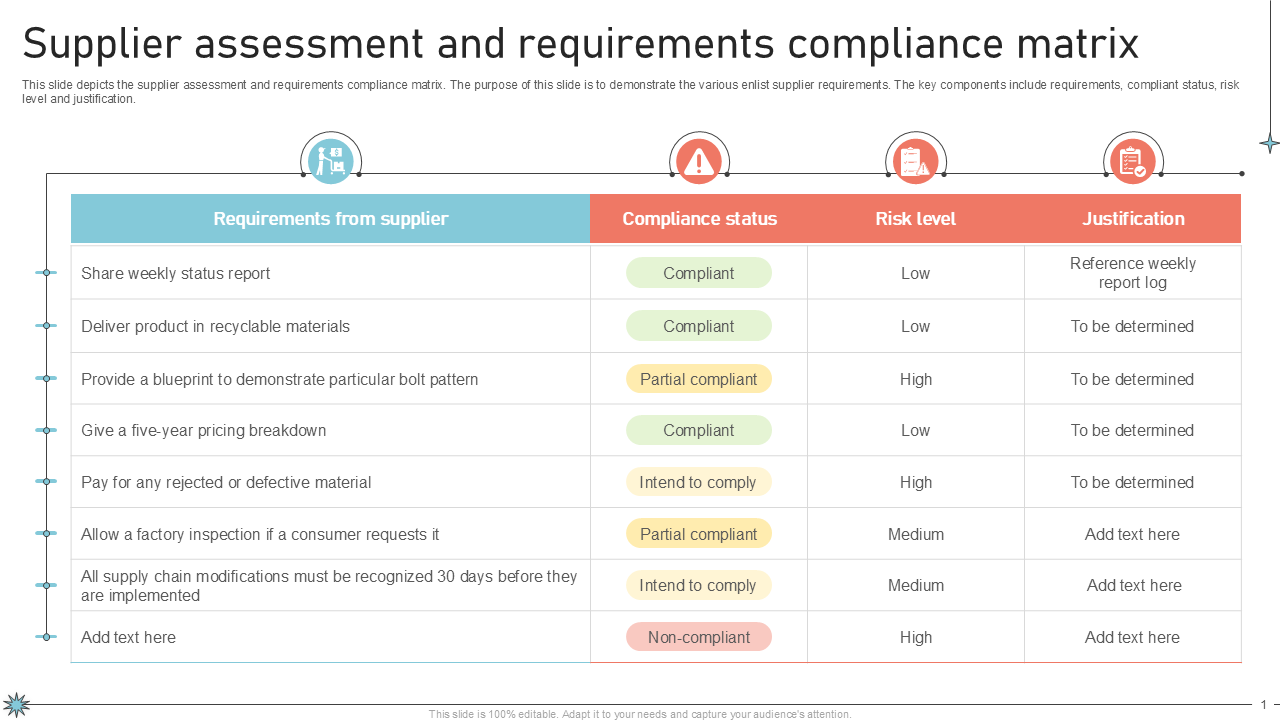
A well-structured compliance matrix directly addresses these challenges by providing a transparent framework for verification. It allows project managers, engineers, and quality assurance teams to track the lifecycle of each requirement, ensuring every item has a defined verification strategy and a documented outcome. This systematic approach is critical for demonstrating due diligence, especially in heavily regulated industries where audits are a routine part of doing business. By making the status of each requirement explicit, a project can proactively identify gaps, address non-compliance early, and maintain a clear path towards successful delivery.
Unpacking the Benefits: More Than Just a Checklist
The strategic advantages of deploying a sophisticated requirements verification matrix extend far beyond mere tracking. It transforms how teams operate, enhance project visibility, and contributes directly to overall success.
One primary benefit is **enhanced clarity and transparency**. All stakeholders gain a clear, consolidated view of project requirements and their current status, eliminating ambiguity and fostering a shared understanding of project goals and progress. This singular source of truth minimizes misinterpretations and ensures everyone is working from the same playbook.
Another significant advantage is **proactive risk mitigation**. By systematically tracking compliance, teams can identify potential areas of non-adherence early in the development cycle. This allows for timely corrective actions, preventing minor issues from escalating into major project impediments and reducing the likelihood of costly rework or delays later on.
The matrix also **improves communication and collaboration** across departments. It provides a common language and reference point for discussions among developers, testers, business analysts, and clients. Everyone can quickly locate information about specific requirements, their history, and their verification outcomes, leading to more efficient meetings and informed decisions.
Furthermore, it drives **efficiency in testing and verification processes**. With clearly defined verification methods and linked test cases, testing teams can work more strategically, ensuring comprehensive coverage and reducing redundant efforts. This focused approach accelerates the verification cycle and improves the quality of testing outcomes.
For projects facing external scrutiny, the matrix offers **audit readiness and regulatory compliance**. It provides irrefutable evidence that all specified requirements, including those mandated by regulatory bodies, have been considered, addressed, and verified. This robust documentation is invaluable during audits, legal reviews, or certification processes.
Finally, by minimizing errors, improving communication, and streamlining verification, a comprehensive compliance tracking sheet ultimately leads to **significant cost savings and improved project predictability**. It helps in allocating resources more effectively, avoiding budget overruns, and delivering projects on time and within scope.
Key Use Cases: Where a Compliance Matrix Shines
The versatility of a requirements compliance tool makes it invaluable across a wide spectrum of industries and project types. Its core function of tracking and verifying adherence to specifications applies universally wherever precision and accountability are paramount.
In **software development**, a compliance matrix is critical for ensuring that every feature, user story, and technical specification outlined in the software requirements specification (SRS) is implemented and thoroughly tested. It bridges the gap between client expectations and developer output, making sure the final product aligns perfectly with initial needs.
For **aerospace and defense** projects, where safety and reliability are non-negotiable, these matrices are fundamental. They track compliance with stringent industry standards (e.g., DO-178C for software, DO-254 for hardware), government regulations, and mission-critical specifications, often for components with extremely long lifespans and complex interdependencies.
**Healthcare and medical device development** heavily rely on these tools to ensure adherence to regulatory bodies like the FDA. From design controls to risk management, every product requirement must be meticulously documented and verified to ensure patient safety and efficacy, making a detailed compliance framework essential for market approval and ongoing quality.
In **construction and infrastructure projects**, the matrix helps manage complex architectural, engineering, and regulatory requirements. It ensures that building codes, structural specifications, material standards, and environmental regulations are all met at every stage of design and construction, mitigating risks and ensuring project integrity.
**Product development** in any industry, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery, benefits immensely from a compliance matrix. It tracks how market requirements, user experience goals, performance specifications, and manufacturing constraints are translated into the final product, ensuring that what is built meets both customer expectations and business objectives.
Finally, for broader **regulatory compliance efforts** (e.g., GDPR, Sarbanes-Oxley, ISO certifications), a compliance matrix can be used to map specific legal or standard requirements to internal policies, procedures, and evidence of adherence. This provides a clear audit trail and demonstrates an organization’s commitment to governance and ethical operations.
Anatomy of a Robust Requirements Compliance Matrix
While the exact columns of a compliance tracking sheet can vary based on project complexity and industry, certain core elements are almost universally present. These components transform a simple list into a powerful project management and verification instrument. A comprehensive matrix typically includes:
- **Unique Requirement ID:** A distinct identifier for each requirement, enabling easy referencing and tracking. This could be a numerical sequence, alphanumeric code, or system-generated ID.
- **Requirement Description:** A clear, concise statement outlining what the requirement entails. This should be unambiguous and testable.
- **Requirement Source:** Where did this requirement come from? (e.g., client, regulatory body, user story, technical specification, design document). Knowing the source helps in understanding its priority and context.
- **Stakeholder Responsible:** The individual or team accountable for ensuring this requirement is met or verified. This clarifies ownership and facilitates communication.
- **Verification Method:** How will this requirement be proven to be met? (e.g., **inspection**, **demonstration**, **test**, **analysis**, **simulation**). Defining this early guides the development and testing phases.
- **Test Case ID/Reference:** A link to the specific test case(s) or procedure(s) designed to verify the requirement. This creates direct traceability between requirements and validation activities.
- **Compliance Status:** The current state of the requirement’s verification (e.g., **Not Started**, **In Progress**, **Verified**, **Failed**, **Waived**, **Not Applicable**). This provides an immediate snapshot of progress.
- **Date Verified:** The date when the requirement was successfully verified, providing a historical record.
- **Verified By:** The name or ID of the person who performed the verification, ensuring accountability.
- **Notes and Comments:** Any additional relevant information, issues encountered during verification, deviations, or justifications for status changes. This provides crucial context.
- **Related Documentation:** Links or references to supporting documents such as design specifications, user manuals, risk assessments, or previous review reports.
By diligently populating and maintaining these fields, teams gain an unparalleled level of control and insight into their project’s adherence to its defined scope. This structured approach not only ensures that all bases are covered but also provides a clear audit trail for every single requirement.
Building Your Own: Practical Steps for Implementation
Creating an effective project requirement tracker doesn’t have to be an arduous task. With a systematic approach, you can tailor a powerful tool that meets your project’s specific needs.
The first step involves **defining your project scope and requirements sources**. Before you even think about the matrix, you need a solid understanding of all the requirements your project must address. Gather requirements from all relevant sources, including contracts, regulatory documents, stakeholder interviews, user stories, and technical specifications. Categorize them logically and ensure they are clear, concise, and testable.
Next, **choose the right tool for your matrix**. For smaller, less complex projects, a spreadsheet program like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets might suffice, offering flexibility and ease of use. For larger, more intricate projects with extensive traceability needs, consider specialized Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) tools such as Jira, IBM DOORS, Jama Connect, or ReqView, which offer advanced features like automated linking, version control, and reporting capabilities.
Once your tool is selected, **populate the matrix with your identified requirements**. Systematically enter each requirement’s unique ID, description, and source into the designated columns. Ensure that every requirement, no matter how small, has its place in the matrix to prevent any omissions.
Then, **define clear verification methods and link test cases**. For each requirement, determine the most appropriate method of verification (e.g., inspection, test, analysis). If applicable, link these to specific test cases or validation procedures that will be executed. This step is crucial for proving compliance and ensuring thorough testing.
Crucially, **assign ownership and responsibilities**. Clearly designate individuals or teams responsible for each requirement’s implementation and verification. This accountability prevents confusion and ensures that progress is consistently tracked and updated. Regular reviews should be scheduled to assess progress and address any emerging issues.
Finally, **establish a review and update process**. A compliance matrix is a living document. It must be regularly reviewed and updated throughout the project lifecycle as requirements evolve, tests are conducted, and statuses change. Define how frequently updates should occur, who is responsible for these updates, and how changes will be communicated to the team. This iterative process ensures the matrix remains accurate and relevant.
Best Practices for Maximizing Your Matrix’s Value
To truly harness the power of your design control document and transform it into a high-value asset, consider these best practices:
**Start Early and Integrate Fully:** Don’t treat the compliance tracking sheet as an afterthought. Begin populating it as soon as requirements are defined, and integrate its use into your daily project management and quality assurance workflows from the outset. Early integration ensures comprehensive coverage and prevents last-minute scrambling.
**Keep it Current and Accurate:** A compliance matrix is only as valuable as its accuracy. Make a habit of regular updates, ensuring that the status of each requirement reflects the current reality of the project. Outdated information can lead to misinformed decisions and significant project risks. Establish a clear process for updates and ensure all team members understand their role in maintaining its integrity.
**Foster Collaboration and Communication:** Encourage all relevant team members—from business analysts and developers to testers and quality assurance—to engage with the matrix. It should serve as a central communication hub, facilitating discussions, clarifying ambiguities, and ensuring everyone is aligned on the status and verification of requirements. Conduct regular walkthroughs of the matrix to address questions and align expectations.
**Tailor to Project Needs, Don’t Over-Engineer:** While comprehensive, your compliance matrix should be pragmatic. Customize the columns and level of detail to suit the size, complexity, and regulatory demands of your specific project. Avoid adding unnecessary fields that create administrative overhead without providing tangible value. Start simple and expand as needed.
**Automate Where Possible:** For larger projects, leverage specialized tools that can automate aspects of the matrix, such as linking requirements to test cases, generating reports, or tracking changes. Automation reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and keeps the matrix up-to-date more efficiently, freeing up valuable team time for critical tasks.
**Provide Training and Support:** Ensure all team members who interact with the matrix understand its purpose, how to use it, and their responsibilities in maintaining it. Offer training sessions and readily available support to address questions and build confidence in using this essential project management tool effectively.
By adhering to these best practices, your system verification plan will evolve from a mere document into a dynamic, indispensable part of your project ecosystem, driving efficiency, accountability, and successful outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a compliance matrix?
The primary purpose of a compliance matrix is to systematically track, manage, and demonstrate that all defined project requirements have been fully met, tested, and verified according to specified criteria and standards. It provides clear visibility into requirement status and adherence.
Who typically creates and maintains a requirements compliance matrix?
While the responsibility is often shared, a project manager, business analyst, systems engineer, or a dedicated quality assurance lead typically initiates and oversees the creation and maintenance of a requirements verification matrix. Input and updates are gathered from the entire project team, including developers, testers, and stakeholders.
Can a compliance matrix be used for agile projects?
Yes, a compliance matrix can be effectively adapted for agile projects. Instead of traditional requirements, it can track user stories, acceptance criteria, and features against their implementation, testing, and acceptance status within sprints. It helps ensure that agile deliverables still meet broader project or regulatory requirements.
What’s the difference between a traceability matrix and a compliance matrix?
A traceability matrix primarily focuses on establishing relationships between various project artifacts (e.g., requirements to design, design to code, code to tests). A compliance matrix, while inherently using traceability, specifically emphasizes the *verification* and *adherence* of requirements to defined standards or objectives, often including a “compliance status” or “verification outcome” field. Essentially, a compliance matrix is a specialized type of traceability matrix focused on proving that requirements have been satisfied.
Are there any specific tools recommended for creating these matrices?
For simpler projects, general spreadsheet applications like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets are excellent starting points due to their flexibility. For more complex projects with extensive requirements and traceability needs, specialized Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) tools such as Jira, IBM DOORS, Jama Connect, Polarion ALM, or Requirements Management (RM) solutions like ReqView offer robust features for managing a detailed project compliance framework.
A carefully constructed and meticulously maintained Requirements Compliance Matrix Template is more than just an administrative chore; it’s a strategic imperative for any project aiming for excellence. It acts as the backbone of your project’s quality assurance, providing an undeniable record of due diligence and a clear roadmap to successful delivery. By systematizing the verification of every single requirement, it transforms potential chaos into structured progress, significantly reducing risks and boosting confidence across your team and with your stakeholders.
Embrace this powerful tool not just as a means to track, but as a catalyst for clearer communication, tighter quality control, and ultimately, greater project success. Whether you’re navigating complex regulatory landscapes or simply ensuring every customer expectation is met, a well-implemented compliance matrix empowers your team to deliver with precision, confidence, and unwavering adherence to your commitments. Start leveraging this essential framework today to elevate your project management to a new standard of accountability and achievement.


