In the complex world of software development and product creation, projects often face a myriad of challenges that can derail even the most promising initiatives. Scope creep, missed deadlines, budget overruns, and features that simply don’t meet user needs are all too common pitfalls. At the heart of many of these issues lies a fundamental problem: unclear, incomplete, or inconsistently communicated requirements. Without a unified understanding of what needs to be built, why it’s important, and how it will function, teams can quickly find themselves working at cross-purposes, leading to frustration and ultimately, failure.
This is where the foundational power of a robust Requirements Engineering Document Template comes into play. Far from being a mere bureaucratic formality, a well-structured requirements document serves as the project’s compass, guiding every decision from initial design to final deployment. It acts as the single source of truth for all stakeholders, from business analysts and product owners to developers, quality assurance testers, and project managers, ensuring everyone is aligned on the vision and specific deliverables. Embracing a standardized approach to documenting requirements is not just about ticking boxes; it’s about embedding clarity, efficiency, and predictability into your development lifecycle, paving the way for successful outcomes.
The Indispensable Role of Clear Requirements
The discipline of requirements engineering is the cornerstone of successful project delivery. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of requirements, from their initial elicitation and analysis to their specification, validation, and ongoing management. When requirements are vague or poorly defined, the ripple effects can be catastrophic. Developers might build the wrong features, testers won’t know what to validate, and ultimately, the end-users receive a product that fails to address their core problems.
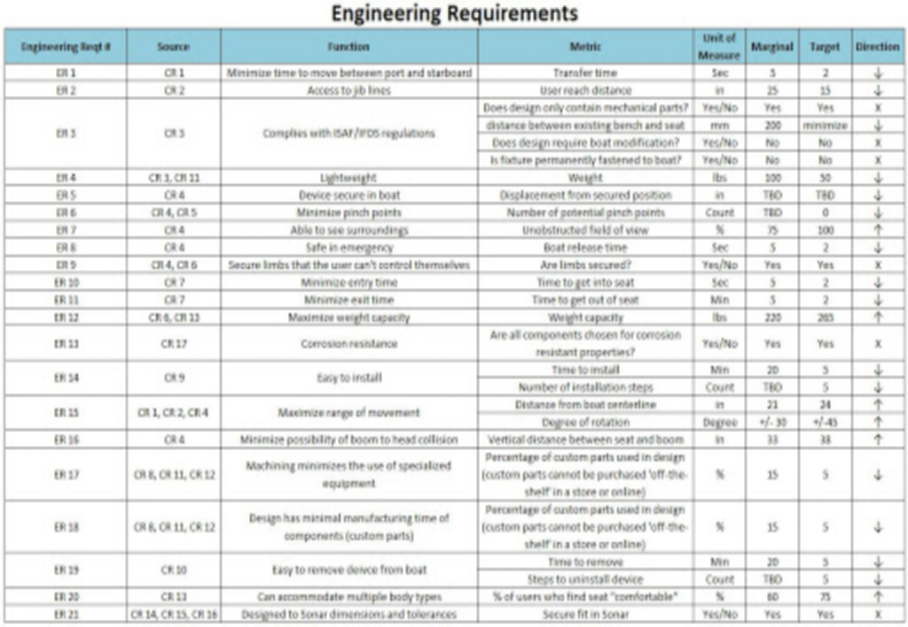
Effective requirements documentation mitigates these risks by providing a precise, unambiguous account of what a system or product is intended to achieve. It bridges the communication gap between technical and non-technical stakeholders, translating abstract business needs into concrete, actionable specifications. By investing time upfront in defining detailed requirements, organizations can prevent costly rework, reduce development cycles, and significantly enhance the quality and relevance of their final product. This proactive approach ensures that every line of code written and every design decision made directly contributes to the overarching project goals.
Why a Standardized Requirements Specification Template is a Game-Changer
In an environment where consistency and clarity are paramount, a standardized requirements engineering document template isn’t just a nicety; it’s a necessity. Imagine the chaos if every project team invented its own way of documenting requirements—critical information could be missed, varying terminologies could lead to misunderstandings, and the effort required to interpret each document would be immense. A consistent specification template eliminates these inefficiencies by providing a predefined structure that guides authors and readers alike.
Adopting a formal requirements documentation framework offers numerous benefits. It ensures that all essential categories of information are consistently captured, from functional capabilities to non-functional attributes like performance and security. This structured approach fosters completeness, making it harder to overlook critical aspects. Moreover, it accelerates the documentation process itself, as teams can focus on content rather than format. Ultimately, a uniform approach to requirements definition enhances project transparency, improves communication across disciplines, and serves as an invaluable reference point throughout the entire project lifecycle, reducing the likelihood of scope creep and facilitating more accurate estimations and planning.
Core Sections of an Effective Requirements Engineering Document
While the specifics might vary based on project type and industry, a robust requirements engineering document typically includes several key sections designed to capture all necessary information comprehensively. Understanding these components is crucial for creating a complete and actionable project requirements document.
- **Introduction:** This section sets the stage, outlining the document’s **purpose**, its intended audience, the **scope** of the system or project being described, and any relevant **definitions** or acronyms used throughout the document to ensure clarity.
- **Overall Description:** Here, you provide a high-level overview. It typically includes the **product perspective** (how it fits into the broader ecosystem), general **user characteristics** (who will use it and their needs), and the **operating environment** (hardware, software, network considerations).
- **Specific Requirements:** This is the heart of the document, detailing the functional and non-functional requirements.
- **Functional Requirements:** Describe **what the system must do**, often broken down into features, use cases, or user stories.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** Define **how the system must perform**, covering aspects like performance (speed, capacity), security, usability, reliability, scalability, and maintainability.
- **External Interface Requirements:** Specify how the system interacts with other systems, users, hardware, and software.
- **Traceability Matrix:** This crucial section links each requirement to its source, related design elements, test cases, and ultimately, to the business objectives it supports. It ensures every requirement is **accounted for** and validated.
- **Appendices:** Used for supplementary information, such as a detailed **glossary** of terms, references to other related documents, or any supporting data that enhances understanding without cluttering the main body.
Leveraging a Project Requirements Document for Success
The true power of a meticulously crafted project requirements document extends far beyond its creation; it’s in its continuous application throughout the project’s journey. This living document becomes the shared blueprint that guides development efforts, informs testing strategies, and serves as a critical reference during quality assurance and deployment. For business stakeholders, it ensures that the final product aligns perfectly with their strategic vision and solves real-world problems. For developers, it provides unambiguous specifications, minimizing guesswork and rework.
Furthermore, a well-defined requirements specification document is indispensable for effective project management. It provides the basis for estimating timelines, allocating resources, and tracking progress. When changes inevitably arise, the document acts as a baseline for assessing the impact of those changes, allowing for informed decision-making and controlled scope management. It fosters a collaborative environment where every team member, from the initial concept phase to the final user acceptance testing, works from a unified understanding, dramatically increasing the likelihood of delivering a high-quality product on time and within budget.
Customizing Your Requirements Documentation Framework
While a standardized template offers immense advantages, it’s vital to remember that it serves as a foundation, not a rigid prison. Every project is unique, varying in size, complexity, methodology (Agile vs. Waterfall), and industry. Therefore, successful implementation of any requirements documentation framework hinges on its thoughtful customization. A template for a small internal tool will differ significantly from one for a large-scale, safety-critical enterprise system.
When adapting your engineering document template, consider the specific needs of your project and stakeholders. For Agile projects, the template might focus more on user stories and epic definitions, linking them to acceptance criteria, while a traditional Waterfall project might demand more granular, highly detailed specifications upfront. Involve key stakeholders in the customization process to ensure the tailored specification template captures all relevant information without introducing unnecessary overhead. The goal is to create a requirements document that is comprehensive enough to prevent ambiguity but agile enough to evolve with the project, ensuring it remains a practical and valuable tool, not a bureaucratic burden.
Best Practices for Robust Requirements Management
Developing a comprehensive requirements document is only the first step; maintaining its relevance and accuracy throughout the project lifecycle is equally critical. Effective requirements management ensures that the document remains a reliable source of truth and continues to support decision-making.
One crucial practice is establishing a clear version control system. As requirements evolve, it’s essential to track changes, document the reasons for those changes, and communicate them to all stakeholders. Regular reviews and updates are also paramount; requirements are rarely static, and iterating on the document ensures it reflects the current understanding and scope. Involving all relevant stakeholders—from end-users to technical architects—early and continuously in the review process helps validate requirements and builds consensus. Furthermore, focusing on making requirements measurable and testable empowers the QA team and provides objective criteria for assessing project success. Finally, consider leveraging specialized requirements management tools to streamline the process, automate traceability, and enhance collaboration, moving beyond static documents to dynamic, interactive specifications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a requirements engineering document?
The primary purpose of a requirements engineering document is to clearly and unambiguously define what a system or product should do, how it should perform, and what constraints it must operate under. It serves as a foundational contract among stakeholders, guiding development, facilitating communication, and providing a basis for validation and testing to ensure the final product meets its intended objectives.
How does a requirements template benefit Agile projects?
While Agile emphasizes flexibility and iterative development, a requirements template still provides significant benefits. It helps structure the capture of user stories and epics, ensuring that comprehensive details, acceptance criteria, and non-functional aspects are consistently considered. It provides a common framework for defining features, promoting clarity and consistency across sprints, and helping to align backlog items with overall strategic goals.
Can one specification template be used for all types of projects?
While a generic base requirements template can provide a good starting point, it’s rarely optimal for all project types without customization. Projects vary significantly in size, complexity, industry, and methodology. A highly detailed template suited for a safety-critical system might be overkill for a small internal application, just as a minimal template wouldn’t suffice for complex regulatory requirements. Adaptability and tailoring are key to its effective use.
Who is typically responsible for filling out a project requirements document?
The responsibility for filling out a project requirements document most often falls to a Business Analyst (BA) or Product Owner. These roles typically serve as the bridge between business needs and technical execution. They work closely with various stakeholders, including end-users, subject matter experts, development teams, and project managers, to elicit, analyze, and document the requirements comprehensively and accurately.
What’s the difference between a business requirements document (BRD) and a system requirements specification (SRS)?
A Business Requirements Document (BRD) focuses on *what* the business needs to achieve and *why* – outlining high-level business goals, objectives, and stakeholder needs. A System Requirements Specification (SRS), on the other hand, details *what* the system will do to meet those business needs, describing functional and non-functional requirements from a technical perspective, often including use cases, data models, and interface specifications. The BRD sets the stage, while the SRS delves into the technical specifics of implementation.
In an increasingly dynamic and competitive landscape, the success of any product or system hinges on its ability to meet precise needs and deliver tangible value. The disciplined use of a requirements engineering document is not an option; it is a strategic imperative. It transforms vague ideas into clear directives, minimizes misunderstandings, and fosters a collaborative environment where every team member is empowered with a unified vision of success.
Embracing a robust requirements specification template is an investment that pays dividends throughout the entire project lifecycle, leading to fewer errors, faster development, and ultimately, products that truly resonate with users. By establishing a culture of clear, comprehensive, and consistent requirements documentation, organizations can navigate complexity with confidence, turning ambitious concepts into successful realities. Make the commitment to clarity today, and empower your teams to build what truly matters.


