In the dynamic world of project management and software development, the initial steps often dictate the entire trajectory of success or failure. Too many projects falter not because of execution flaws, but due to a fundamental misunderstanding or miscommunication of what needs to be built or achieved. This critical gap usually stems from an inadequate requirements gathering process, leading to scope creep, budget overruns, and dissatisfied stakeholders.
Imagine embarking on a complex journey without a map, or attempting to construct a skyscraper without blueprints. The outcome would be chaotic, unpredictable, and likely disastrous. Similarly, in project work, a lack of clear, comprehensive, and well-documented requirements can derail even the most promising initiatives. This is precisely where a structured approach, often encapsulated in a robust Requirements Gathering Template Checklist, becomes an indispensable asset for any team aiming for clarity and efficiency.
The Cornerstone of Project Success
Every successful project, regardless of its size or industry, is built on a foundation of clearly defined needs and expectations. Without this clarity, teams often find themselves building the wrong thing, fixing endless bugs, or constantly re-scoping as new information comes to light. Inadequate requirements elicitation is a leading cause of project failure, costing organizations billions annually in wasted resources and lost opportunities.
A systematic approach to defining project needs mitigates these risks significantly. It ensures that all voices are heard, all crucial aspects are considered, and everyone involved operates from a shared understanding of the desired outcome. This proactive method prevents costly rework down the line and fosters a collaborative environment where problems are identified and resolved early, long before they become expensive crises.
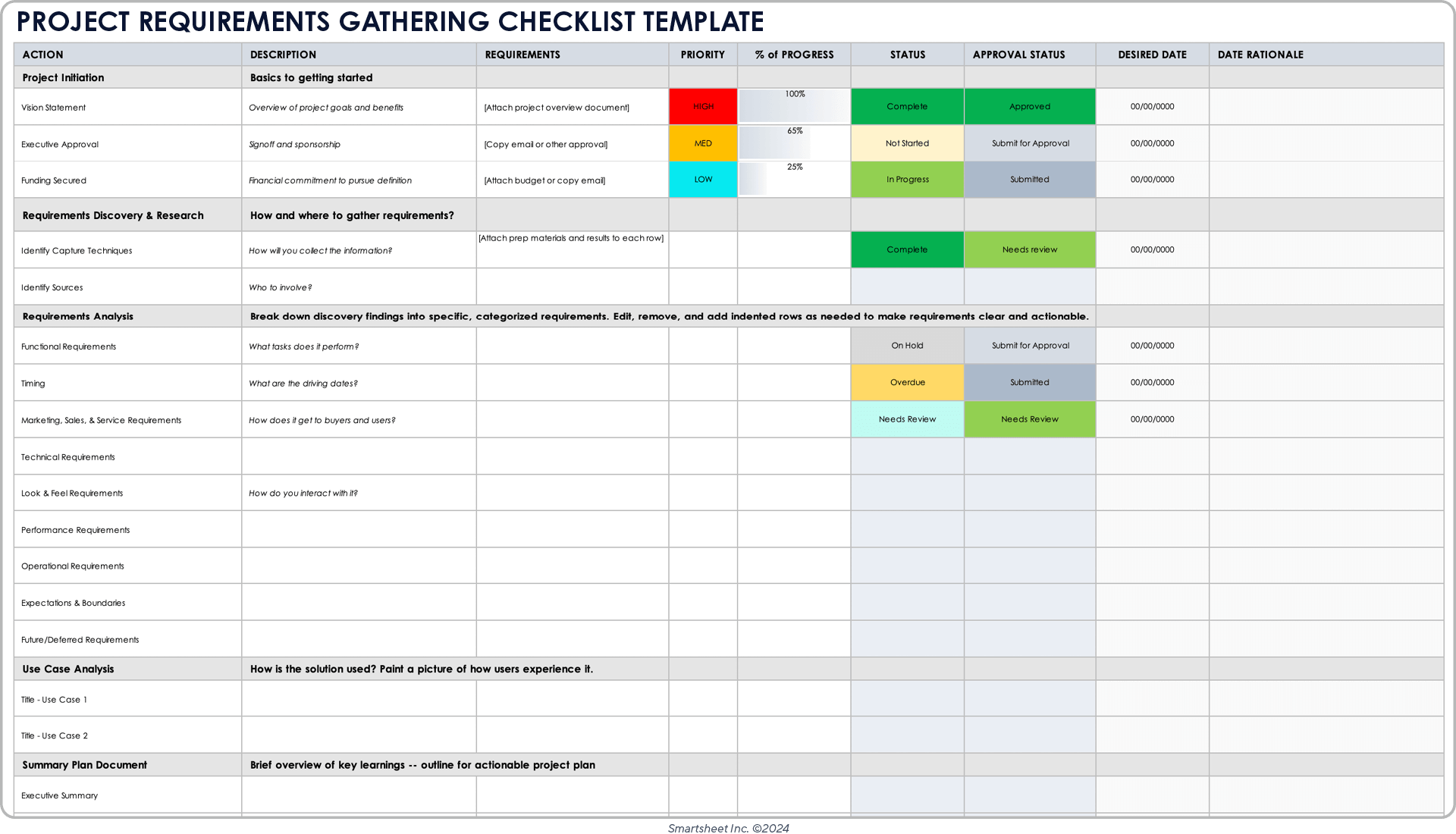
What Exactly Is a Requirements Gathering Template Checklist?
At its heart, a **Requirements Gathering Template Checklist** is a structured document or tool designed to guide project teams through the comprehensive process of identifying, documenting, and validating all necessary information for a project. It’s more than just a list; it’s a strategic framework that ensures no critical detail is overlooked, from high-level business objectives down to granular functional specifications.
This essential tool serves as a comprehensive guide, prompting stakeholders and project managers to ask the right questions at the right time. It acts as an organizational backbone for the elicitation process, helping to categorize and prioritize information systematically. Far from being a rigid, one-size-fits-all solution, a good requirements specification checklist is adaptable, allowing teams to tailor it to the unique demands of each project while maintaining a consistent standard of thoroughness.
Key Benefits of Utilizing a Standardized Approach
Adopting a formalized framework for defining project needs offers a multitude of advantages that extend across the entire project lifecycle. It transforms a potentially chaotic phase into an organized, productive endeavor.
- **Ensures Completeness:** A comprehensive requirements gathering template acts as a safety net, making sure all facets of a project are considered, from user interfaces to data security.
- **Promotes Consistency:** By using a standard format, all requirements are captured in a uniform manner, making them easier to understand, compare, and manage across different teams or project phases.
- **Reduces Rework and Scope Creep:** Clear, agreed-upon requirements minimize changes later in the project, which are typically more expensive and time-consuming to implement.
- **Improves Communication:** It provides a common language and reference point for all stakeholders, fostering better understanding and alignment between business users, developers, and testers.
- **Enhances Stakeholder Alignment:** The structured process facilitates active involvement from all relevant parties, ensuring that diverse perspectives are incorporated and buy-in is secured early on.
- **Facilitates Better Planning and Estimation:** With well-defined requirements, project managers can create more accurate timelines, resource allocations, and budget estimates.
- **Supports Effective Testing:** Clearly articulated requirements translate directly into testable criteria, making the quality assurance process more efficient and effective.
- **Accelerates Time-to-Market:** By streamlining the initial phases and reducing ambiguities, projects can move forward with greater confidence and speed, delivering value sooner.
Core Components of an Effective Requirements Elicitation Guide
An effective requirements elicitation guide doesn’t just list items; it organizes them logically, reflecting the natural progression from high-level vision to detailed implementation. While specific sections may vary based on project type, several components are universally valuable.
- **Project Vision and Scope:** Clearly articulate the overarching goal, business problem being solved, and the boundaries of the project. What is in and out of scope?
- **Stakeholder Identification:** List all individuals or groups affected by or having an interest in the project, including their roles, responsibilities, and level of influence.
- **Business Requirements:** Define the high-level needs of the organization. What business objectives will this project help achieve? What are the key performance indicators (KPIs)?
- **User Requirements (Use Cases/User Stories):** Describe the tasks end-users need to perform with the system. Who are the users, and what do they need to accomplish? User stories typically follow the format “As a [type of user], I want [some goal] so that [some reason].”
- **Functional Requirements:** Detail what the system *must do*. These are the actions, calculations, data manipulations, and specific functionalities that define the system’s behavior.
- **Non-Functional Requirements:** Specify the criteria that judge the operation of a system, rather than specific behaviors. This includes aspects like **performance** (speed, response time), **scalability**, **security** (authentication, data protection), **usability**, **reliability**, and **maintainability**.
- **Data Requirements:** Outline the data elements, their sources, relationships, and any specific validation or storage needs.
- **Interface Requirements:** Describe how the system will interact with other systems, users (UI/UX), and external devices.
- **Reporting Requirements:** Define any necessary reports, their content, frequency, and audience.
- **Constraints:** Identify any limitations or restrictions that must be considered, such as budget, timeline, regulatory compliance, or technical limitations.
- **Assumptions:** Document any factors that are considered to be true for the purpose of planning, but which may not be certain. These need to be monitored.
- **Glossary of Terms:** A shared vocabulary for all project-specific terminology, ensuring everyone understands the jargon.
Strategies for Effective Implementation and Customization
Possessing a comprehensive project requirements template is only half the battle; knowing how to implement and adapt it effectively is crucial. The goal is to make the elicitation process smooth and valuable, not a bureaucratic hurdle.
First, tailor the template to your project’s context. A small internal tool might not need the same level of detail as a large-scale public-facing application. Remove irrelevant sections and add new ones as needed. The best template is a living document, not a static form. Engage stakeholders early and often; their active participation is paramount to capturing accurate needs. Utilize a variety of elicitation techniques, such as interviews, workshops, surveys, prototyping, and observational studies, to gather diverse perspectives and validate findings.
Embrace iterative refinement. Requirements gathering is rarely a one-shot activity; it’s an ongoing process of discovery and clarification. Regularly review and update the requirements document as the project evolves and new information emerges. Implement clear version control to track changes and maintain an audit trail. Finally, consider the tools you use. While a simple document works for many, dedicated requirements management software can offer enhanced collaboration, traceability, and impact analysis capabilities for larger, more complex endeavors.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with the best tools, missteps can occur during the critical process of defining project needs. Being aware of these common pitfalls can help teams navigate the elicitation phase more successfully.
One frequent issue is ambiguity or vagueness in requirements. Phrases like "user-friendly" or "fast performance" are subjective and open to interpretation. Requirements must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Another pitfall is a lack of stakeholder engagement, leading to incomplete or biased information. Ensure all relevant parties, including end-users, management, and technical experts, are actively involved and have opportunities to provide input and review.
Over-specification (getting bogged down in excessive detail too early) or under-specification (leaving too much to interpretation) are both detrimental. Strive for the right level of detail at each stage of the project. Neglecting non-functional requirements can also lead to systems that perform the right functions but are slow, insecure, or difficult to use. Always give performance, security, and usability the attention they deserve. Lastly, failing to prioritize requirements can result in wasted effort on features that deliver minimal value. Implement a clear prioritization scheme (e.g., MoSCoW: Must have, Should have, Could have, Won’t have) to focus efforts on what matters most.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between business and functional requirements?
Business requirements describe the high-level objectives or goals of the organization that the project aims to achieve, focusing on *why* the project is being undertaken. Functional requirements, on the other hand, detail the specific actions or capabilities the system *must perform* to meet those business goals, focusing on *what* the system will do.
Can this checklist be used for Agile projects?
Absolutely. While Agile methodologies often prefer user stories over lengthy traditional documentation, the underlying principles of the requirements gathering template are highly adaptable. Agile teams can use it as a guide for ensuring comprehensive user story identification, covering functional and non-functional aspects, and identifying stakeholders and constraints that inform their backlog grooming and sprint planning.
How often should I update my requirements documentation?
The frequency depends on the project’s methodology and phase. In Agile environments, requirements (user stories) are continuously refined and updated throughout sprints. In more traditional waterfall projects, a major update might occur after each phase (e.g., after initial analysis, design, etc.), with minor clarifications happening as needed. The key is to keep it current and aligned with the evolving understanding of the project.
Who is typically responsible for filling out this type of document?
Typically, a Business Analyst (BA) or Product Owner takes the lead in facilitating and documenting requirements. However, the information itself is gathered collaboratively from a wide array of stakeholders, including project managers, subject matter experts, end-users, developers, and testers. It’s a team effort to ensure completeness and accuracy.
Is a template suitable for all project sizes?
Yes, but with customization. For smaller projects, a simplified version focusing on core elements might suffice. For larger, more complex endeavors, the full range of components detailed in a comprehensive requirements specification guide becomes invaluable. The adaptability of the template is its strength; it should be scaled up or down as appropriate.
Embracing a structured approach to defining project needs, such as leveraging a comprehensive requirements gathering template, is not merely a bureaucratic exercise; it’s a strategic investment in project success. It instills discipline, clarity, and accountability from the very outset, transforming ambiguity into actionable insights. By systematically documenting and validating every facet of a project, teams can significantly reduce the risks of miscommunication and rework.
Ultimately, a well-executed requirements elicitation process powered by an effective checklist empowers organizations to deliver solutions that truly meet user needs and business objectives. It fosters an environment of shared understanding and collaborative effort, leading to higher quality outcomes, happier stakeholders, and projects delivered on time and within budget. Make the commitment to clarity today, and watch your projects thrive.