In the intricate world of project management, where objectives can shift and expectations can diverge, the clear definition and meticulous handling of project requirements stand as the bedrock of success. Many projects falter not due to a lack of effort or resources, but because the foundational elements—what needs to be built or achieved—are ill-defined, poorly communicated, or inadequately managed. This challenge is universal, impacting everything from software development to large-scale infrastructure projects.
Imagine embarking on a journey without a map, or constructing a building without blueprints. The result is chaos, rework, and ultimately, failure to meet the intended goal. This is precisely the scenario projects face without a robust strategy for managing their requirements. Fortunately, a structured approach exists to mitigate these risks and pave the way for predictable outcomes: the Requirements Management Plan Template, a vital tool for any organization aiming for clarity and precision.
Why a Robust Requirements Management Plan is Indispensable
At its core, a requirements management plan is more than just a document; it’s a strategic blueprint that guides how project requirements will be defined, tracked, and controlled throughout the entire project lifecycle. It establishes a common understanding among all stakeholders, from project managers and business analysts to development teams and end-users, ensuring everyone is working towards the same vision. Without such a framework, projects are highly susceptible to scope creep, budget overruns, and missed deadlines, often resulting in solutions that fail to address the true needs of the business.
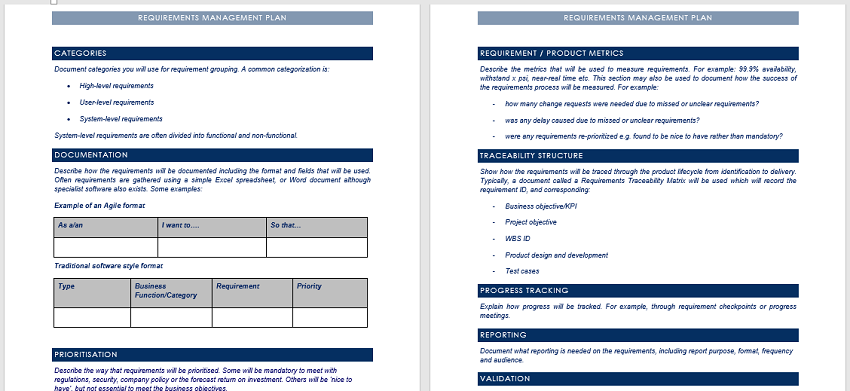
This plan serves as a proactive measure against common project pitfalls. By detailing the processes for requirements elicitation, analysis, documentation, validation, verification, and change management, it provides a structured way to handle the dynamic nature of project needs. It doesn’t just list requirements; it defines the ecosystem in which they will live, evolve, and be delivered, setting the stage for efficient execution and successful project completion.
Key Benefits of Utilizing a Requirements Management Plan
Adopting a formal approach to managing project requirements offers a multitude of tangible benefits that directly contribute to project success and organizational efficiency. These advantages extend beyond mere documentation, fostering a culture of clarity and accountability.
- Enhanced Clarity and Understanding: A well-defined plan ensures that all requirements are unambiguous, consistent, and fully understood by every team member and stakeholder. This eliminates guesswork and reduces misinterpretations, leading to better alignment.
- Effective Scope Control: By detailing how changes to requirements will be managed, the plan provides a robust mechanism to prevent uncontrolled scope creep. It ensures that any proposed changes are properly evaluated, approved, and integrated, protecting project timelines and budgets.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: The plan establishes clear channels and formats for communicating requirements information, fostering better collaboration among diverse teams and stakeholders. Everyone knows where to find the latest information and how to contribute effectively.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying and documenting requirements meticulously early on helps in uncovering potential issues and risks before they escalate. This proactive approach allows teams to address challenges systematically, reducing the likelihood of costly rework later in the project.
- Greater Traceability: A comprehensive requirements management strategy enables end-to-end traceability, linking business needs to functional specifications, design elements, test cases, and ultimately, the delivered solution. This provides transparency and simplifies impact analysis for changes.
- Higher Quality Deliverables: When requirements are clearly understood, consistently managed, and rigorously validated, the resulting product or service is more likely to meet user expectations and business objectives, leading to higher quality and greater user satisfaction.
Core Components of an Effective Requirements Management Plan
A comprehensive requirements management plan typically includes several key sections, each addressing a critical aspect of how requirements will be handled. While the specifics may vary by project, the following elements form the backbone of a robust plan:
- Introduction and Purpose: Clearly states the objective of the plan and its scope within the overall project. It outlines why this requirements management process is necessary.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Defines who is accountable for what throughout the requirements lifecycle. This includes identifying stakeholders, business analysts, project managers, and development leads.
- Requirements Elicitation Process: Describes the methods and techniques to be used for gathering requirements, such as workshops, interviews, surveys, or prototyping. It also details how these activities will be documented.
- Requirements Analysis and Documentation: Explains how raw requirements will be analyzed, refined, prioritized, and documented. This section covers the chosen format (e.g., user stories, use cases, functional specifications) and tools for documentation.
- Requirements Validation and Verification: Outlines the approach for ensuring that requirements are complete, correct, consistent, and meet stakeholder needs. This includes review processes, walkthroughs, and sign-off procedures.
- Requirements Baseline and Change Management: Establishes the process for creating a baseline of approved requirements and, crucially, how any changes to these baselined requirements will be requested, analyzed, approved, and communicated. This is vital for controlling scope.
- Requirements Traceability: Specifies how requirements will be linked to other project artifacts, such as design documents, test cases, and system components, to ensure a complete audit trail.
- Tools and Methods: Identifies any specific software, templates, or techniques that will be used for managing requirements, such as Jira, Azure DevOps, or dedicated RM tools.
- Metrics and Reporting: Defines how the effectiveness of the requirements management activities will be measured and reported, including key performance indicators (KPIs) and status updates.
Customizing Your Requirements Management Plan Template for Success
While a generic requirements management plan template provides an excellent starting point, its true value is realized through thoughtful customization. No two projects are identical, and a one-size-fits-all approach often proves inadequate. Tailoring your requirements management document to the specific context of your project is crucial for its effectiveness.
Consider factors such as the size and complexity of your project. A small, agile project might require a more lightweight approach to handling requirements, focusing on frequent communication and iterative refinement, whereas a large, complex undertaking in a regulated industry might demand extensive formal documentation and stringent change control procedures. Your organizational culture and the experience level of your team also play a significant role. A highly collaborative team might rely more on informal discussions and visual tools, while a distributed team might need more explicit documentation. The key is to adapt the framework to fit your unique circumstances, ensuring it supports, rather than hinders, your project’s progress.
Implementing Your Requirements Management Plan: Best Practices
Having a detailed plan for managing project requirements is only the first step; successful implementation requires adherence to certain best practices. These principles ensure that your strategy for documenting requirements remains a living, useful guide throughout the project lifecycle.
Firstly, start early. Integrate your requirements management strategy into the project planning phase itself, rather than treating it as an afterthought. This ensures that the framework is in place before requirements gathering truly begins. Secondly, involve all key stakeholders from the outset. Their input is invaluable for developing a realistic and comprehensive approach to handling requirements, and their buy-in is critical for adoption.
Regular and transparent communication is paramount. Ensure that all team members understand the established processes for requirements capture, analysis, and change. Conduct regular reviews and updates to the plan, especially during critical project milestones or when significant changes occur. Finally, leverage appropriate tools to support your requirements management efforts. Whether it’s a simple spreadsheet for a small project or a sophisticated requirements management software for a complex program, the right tools can streamline processes, improve traceability, and enhance collaboration, making your overall requirements management more efficient and effective.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of a requirements management plan?
The primary goal is to establish a structured and systematic approach for defining, documenting, tracking, prioritizing, and controlling requirements throughout the entire project lifecycle, ensuring alignment with project objectives and stakeholder needs.
Who is typically responsible for creating and maintaining the plan?
Often, the project manager or a lead business analyst is responsible for drafting the initial plan, with significant input from key stakeholders, development leads, and quality assurance teams. Maintenance is usually a shared responsibility, overseen by the project manager, to ensure it remains current and relevant.
How often should the requirements management plan be reviewed?
The plan should be a living document, reviewed and updated regularly, especially at key project milestones, phase gates, or whenever there are significant changes in project scope, team structure, or organizational processes. Continuous review ensures its continued relevance and effectiveness.
Can a single requirements management strategy work for all projects?
While the core principles remain consistent, a single, rigid strategy for managing requirements is rarely effective for all projects. It’s crucial to tailor the plan’s detail, formality, and tools to the specific project’s size, complexity, industry, team dynamics, and organizational culture.
What is the difference between requirements management and configuration management?
Requirements management focuses specifically on the lifecycle of project requirements, from elicitation to validation and change control. Configuration management, while related, is broader; it involves identifying, tracking, and controlling changes to all project artifacts, including code, documentation, and hardware, throughout the system’s lifecycle to maintain consistency.
The journey from initial concept to a successful product or service is fraught with potential missteps, but many of these can be skillfully navigated with a clear and comprehensive approach to managing requirements. A meticulously crafted requirements management plan is not merely bureaucratic overhead; it is a strategic asset that brings order to complexity, fosters clarity among diverse teams, and ultimately, drives project success.
By investing the time and effort into developing and adhering to a robust framework for handling project requirements, organizations can significantly reduce risks, improve communication, and ensure that the final deliverables truly meet the needs they were designed to address. Embrace the discipline of effective requirements management, and watch your projects transform from ambiguous endeavors into clear, well-executed successes. Utilizing a well-structured Requirements Management Plan Template is your first step towards achieving this critical project excellence.


