In the intricate dance of modern project management, where scope creep looms and stakeholder expectations can shift like sand, a robust framework for managing requirements is not just a luxury—it’s a necessity. Imagine a scenario where every single project requirement, from its inception to its final delivery, is meticulously linked to every phase of development, testing, and deployment. This interconnectedness is precisely what a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) aims to achieve.
The concept of a Requirements Traceability Matrix Template Project Management isn’t just about documenting; it’s about connecting the dots, ensuring that every piece of the puzzle contributes to the final picture, and that no critical element is overlooked. This powerful tool serves as a living document, evolving with the project and offering unparalleled visibility into the project’s adherence to its core objectives. For project managers, business analysts, and development teams, understanding and effectively utilizing such a matrix is paramount to delivering successful outcomes that truly meet user needs and business goals.
Why a Traceability Matrix Matters in Project Management
At its heart, a traceability matrix provides a structured way to track the lifecycle of a requirement, from its origin to the test cases that validate its implementation. This comprehensive view ensures that every requirement is tied to its purpose, design, and validation, making it an indispensable tool for maintaining project integrity. Without proper traceability, projects risk delivering features that don’t align with initial needs or failing to meet regulatory compliance.
One of the primary reasons project teams embrace a strong requirements traceability framework is its ability to mitigate risk. By clearly linking requirements to their source, design specifications, and validation methods, teams can quickly identify the impact of changes, pinpoint areas of potential misunderstanding, and ensure that all agreed-upon functionalities are actually delivered. This transparency fosters a proactive approach to problem-solving, preventing costly rework and delays further down the line.
Furthermore, a well-implemented traceability strategy enhances communication across all project stakeholders. When everyone has access to a centralized, clear document outlining the connections between requirements and project artifacts, it reduces ambiguity and ensures a shared understanding of what needs to be built and why. This clarity is crucial for alignment, especially in complex projects involving multiple teams and external vendors.
Unpacking the Core Benefits of an RTM
Adopting a robust Requirements Traceability Matrix Template Project Management can transform how teams approach complex initiatives. Its advantages extend far beyond mere documentation, offering tangible benefits that improve project quality, efficiency, and stakeholder satisfaction. These benefits collectively contribute to a more predictable and successful project delivery lifecycle.
- Improved Scope Management: A traceability matrix helps keep project scope in check by clearly defining the boundaries of requirements. It makes it easier to identify and prevent **scope creep**, ensuring the team focuses on agreed-upon deliverables.
- Enhanced Quality Assurance: By linking requirements directly to test cases, an RTM ensures that every specified feature is thoroughly tested. This direct mapping improves the **quality and coverage** of testing efforts, leading to a more reliable product.
- Effective Change Impact Analysis: When a requirement changes, a traceability matrix immediately shows all related design elements, code modules, and test cases that might be affected. This capability enables quick and accurate **impact assessments**, simplifying change management.
- Better Risk Management: Identifying and managing risks associated with requirements becomes more straightforward. Unclear or untraceable requirements can signal potential **project risks**, which the RTM helps to highlight and address early.
- Streamlined Communication: A single, shared source of truth about requirements and their connections minimizes misunderstandings and facilitates **clear communication** among developers, testers, business analysts, and stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance and Audit Readiness: For projects in regulated industries, demonstrating that all requirements have been met and verified is crucial. A traceability matrix provides an **auditable trail** of compliance, simplifying regulatory reviews.
Key Components of an Effective Traceability Matrix
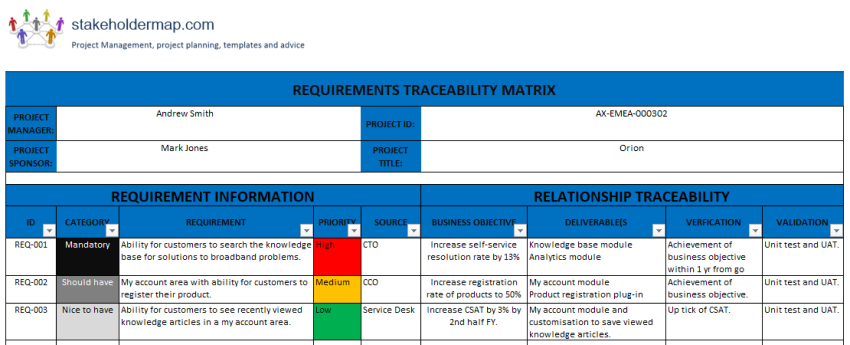
While the specific columns in a requirements traceability matrix can vary based on project needs and organizational standards, certain core elements are almost universally essential. These components ensure that the matrix provides a comprehensive view of a requirement’s journey through the project lifecycle. Understanding these building blocks is the first step toward creating a truly useful and functional matrix.
Typically, an effective traceability matrix will include details that track a requirement from its origin through to its verification. This often involves unique identifiers, descriptive text, and links to various project artifacts. The goal is to establish a clear, verifiable chain of connections that leaves no room for ambiguity.
Here are some common and highly valuable columns you would find in a robust requirements tracking document:
- Requirement ID: A **unique identifier** for each requirement (e.g., REQ-001, FR-015).
- Requirement Description: A **clear and concise** statement of the requirement.
- Requirement Type: Categorization (e.g., **functional**, non-functional, business, user story).
- Source/Origin: Where the requirement came from (e.g., **stakeholder interview**, user story, regulatory document).
- Priority: The **importance** of the requirement (e.g., high, medium, low, mandatory, desirable).
- Status: The current **lifecycle stage** (e.g., proposed, approved, in progress, implemented, tested, deferred).
- Design Specification ID: Links to the **technical design** documents or sections that address this requirement.
- Code Module/Component: The specific **software module** or component where the requirement is implemented.
- Test Case ID(s): Reference to the **test cases** designed to verify the implementation of this requirement.
- Verification Status: Whether the requirement has been **successfully tested** and verified.
- Release/Iteration: The **project release** or agile sprint in which the requirement is targeted for delivery.
- Owner/Analyst: The person **responsible** for the requirement.
Crafting Your Own Requirements Traceability Matrix Template
Creating a customized requirements traceability matrix template doesn’t have to be an arduous task. The key is to start with a clear understanding of your project’s specific needs and the level of detail required for effective tracking. For smaller projects, a simple spreadsheet might suffice, while larger, more complex endeavors may benefit from specialized tools.
Begin by identifying the types of information you need to track. Refer to the "Key Components" section for ideas, but tailor them to your project context. For instance, if you’re in a heavily regulated industry, you might need more granular detail on compliance aspects. If you’re running an agile project, linking to user stories and epics will be more relevant than traditional design documents.
Once you’ve decided on your columns, consider the tools available. Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets are excellent starting points for many teams, offering flexibility and ease of use. For more advanced needs, dedicated requirements management tools or project lifecycle management (PLM) solutions provide integrated features like version control, automated linking, and reporting capabilities. The crucial aspect is to select a tool that your team will actually use consistently.
Best Practices for Implementing Your Traceability Matrix
Implementing a traceability matrix effectively requires more than just filling out a spreadsheet; it demands discipline, consistency, and a clear understanding of its purpose. Following best practices ensures that your requirements management tool becomes a valuable asset rather than a forgotten document. These guidelines help to maximize the benefits of linking requirements to deliverables.
Firstly, start early and maintain regularly. The RTM should be initiated as soon as requirements are gathered and continuously updated throughout the project lifecycle. An outdated matrix is as good as no matrix at all, so bake its maintenance into your regular project activities.
Secondly, ensure team buy-in and clear ownership. Everyone involved in the project, from business analysts to developers and testers, must understand the importance of traceability and their role in maintaining the matrix. Assign a clear owner for the RTM to ensure its consistency and accuracy.
Thirdly, define clear rules and conventions. Establish how requirements will be identified, how changes will be recorded, and what constitutes a "link." Consistency in these definitions prevents confusion and ensures the matrix remains a reliable source of information. Avoid ambiguity in your requirements definitions themselves, as this will inevitably lead to gaps in your traceability.
Lastly, leverage automation where possible. While manual updates are feasible for smaller projects, consider tools that offer automated linking and reporting features as your project scales. This reduces the administrative burden and improves the accuracy of your requirements lifecycle management. Remember, the goal is to facilitate insights, not to create a data entry chore.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, implementing a requirements traceability matrix can fall victim to common pitfalls that undermine its effectiveness. Being aware of these challenges can help project managers and teams navigate them successfully, ensuring the RTM remains a valuable asset for tracking project requirements.
One of the most frequent mistakes is treating the matrix as a one-time activity. An RTM is a living document, and if it’s not regularly updated to reflect changes in requirements, design, or testing status, it quickly becomes irrelevant and misleading. Lack of continuous maintenance renders the entire effort useless.
Another pitfall is over-complication. While it’s tempting to track every conceivable piece of information, an overly complex matrix can become cumbersome to manage, leading to resistance from the team. Focus on tracking only the essential links and information that provide actionable insights. Simplicity often leads to greater adoption and utility.
Furthermore, lack of integration with other project artifacts can severely limit the matrix’s value. If the RTM lives in isolation, disconnected from design documents, test plans, or change requests, its ability to provide a holistic view is compromised. Strive for seamless linking and cross-referencing to maximize its utility as a central project documentation tool.
Finally, insufficient training or understanding among team members can also lead to issues. If the team doesn’t understand why they are maintaining the matrix or how to do it correctly, inconsistencies and errors will proliferate. Invest in proper training and ongoing support to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding the purpose and usage of this vital tracking mechanism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a Requirements Traceability Matrix?
The primary purpose of an RTM is to provide a clear, one-to-one mapping between project requirements and other project artifacts, such as design specifications, code modules, and test cases. It ensures that every requirement is tracked, implemented, and verified, providing an auditable trail of a requirement’s lifecycle.
When should I start building my RTM?
You should ideally start building your traceability matrix as soon as requirements gathering begins and initial requirements are defined. It’s a foundational document that evolves with the project, so integrating it from the outset ensures comprehensive tracking from day one.
Can an RTM be used for agile projects?
Absolutely. For agile projects, the RTM can link user stories and epics to design components, sprint backlog items, and acceptance criteria or automated tests. It helps maintain a clear connection between business value (user stories) and the delivered functionality, ensuring that every piece of work contributes to the overall product vision.
How often should the RTM be updated?
The RTM should be updated regularly, as often as project artifacts or requirements change. In fast-paced environments, this might mean weekly or bi-weekly updates, especially after sprint reviews or major design changes. Consistency is key to keeping the matrix accurate and useful.
What tools are best for creating an RTM?
For basic needs, spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets are highly effective. For more complex projects, dedicated requirements management tools such as Jira, Azure DevOps, DOORS, or homegrown solutions integrated with other PLM tools offer advanced features like automated linking, version control, and comprehensive reporting. The best tool depends on your project’s scale, complexity, and team’s preferences.
The journey from a nascent idea to a fully realized product is often fraught with complexities, but a well-executed requirements traceability strategy can illuminate the path. By meticulously connecting every requirement to its corresponding design, development, and testing efforts, project teams gain an invaluable level of control and insight. This not only mitigates risks and enhances quality but also ensures that the final product truly aligns with its intended purpose.
Embracing the principles of a robust traceability matrix isn’t just about adhering to best practices; it’s about fostering a culture of clarity, accountability, and precision within your project endeavors. Whether you’re navigating regulatory landscapes or striving for agile excellence, the power of a well-maintained requirements tracking framework will undoubtedly set your projects on a stronger, more successful trajectory. Take the step to implement or refine your traceability approach, and witness the transformative impact on your project outcomes.