In today’s interconnected digital landscape, the human element remains the most significant variable in an organization’s cybersecurity posture. No matter how sophisticated your firewalls or intrusion detection systems, a single click on a phishing email by an unsuspecting employee can render your expensive tech stack vulnerable. This reality underscores the critical need for continuous, engaging, and relevant security education for every member of your team. It’s not just about compliance; it’s about cultivating a culture of vigilance.
Building an effective training regimen from scratch can feel like a daunting task, consuming valuable time and resources. This is where a well-crafted Security Awareness Training Program Template becomes an indispensable asset. It provides a structured starting point, a blueprint that guides you through the complexities of educating your workforce, ensuring consistency, coverage, and efficacy, ultimately transforming your employees from potential liabilities into a robust first line of defense against cyber threats.
The Indispensable Role of Employee Security Education
Modern cyber threats are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and targeted. While technical safeguards are essential, they are not foolproof. Cybercriminals often exploit human psychology through social engineering tactics, recognizing that people are often the easiest entry point into a secured system. A comprehensive employee security education initiative empowers individuals with the knowledge and skills to identify and avoid these common pitfalls.
Beyond simply preventing data breaches, a strong cybersecurity awareness program fosters a proactive security culture. When every employee understands their role in protecting sensitive information and organizational assets, it builds collective resilience. This collective effort not only reduces the likelihood of successful attacks but also helps ensure quicker detection and response should an incident occur, minimizing potential damage and recovery costs.
Key Elements of an Effective Security Awareness Training Program Template
A robust template for security awareness training provides a foundational structure, ensuring all critical areas are addressed. It’s not a rigid document but a flexible framework designed to be adapted to your organization’s specific risks, industry regulations, and operational environment. Think of it as your customizable guide to building a resilient “human firewall.”
At its core, such a template should outline the program’s objectives, target audience, content modules, delivery methods, and evaluation criteria. It standardizes the approach, making it easier to roll out training consistently across different departments or locations. This standardization is crucial for maintaining a uniform level of security understanding throughout the organization, preventing gaps that attackers could exploit.
I. Program Objectives and Scope
Before diving into content, clearly define what you aim to achieve. Your objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). The scope should cover who needs training, what aspects of security will be covered, and any regulatory or compliance requirements that must be met.
An effective security awareness training framework will emphasize reducing specific risks, such as phishing susceptibility or improper data handling. It should also aim to instill best practices that become second nature for employees. This initial clarity sets the stage for a focused and impactful training experience, ensuring that effort translates into tangible security improvements.
II. Core Content Modules and Topics
The heart of any awareness training initiative lies in its content. A comprehensive template will break down the vast subject of cybersecurity into digestible modules. These modules should cover universal threats while also incorporating elements specific to your organization’s digital footprint and data sensitivities.
A general outline of essential topics often includes:
- **Phishing and Social Engineering:** How to recognize and report suspicious emails, texts, and calls.
- **Password Best Practices:** Creating strong, unique passwords and the importance of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- **Data Handling and Classification:** Understanding sensitive data, proper storage, sharing, and disposal.
- **Malware and Ransomware:** Identifying and preventing infections, understanding their impact.
- **Physical Security:** Securing workspaces, devices, and preventing unauthorized access.
- **Mobile Device Security:** Protecting company data on personal and corporate devices.
- **Acceptable Use Policy (AUP):** Understanding organizational rules for internet, email, and device usage.
- **Incident Reporting Procedures:** Knowing when and how to report a security incident.
- **Remote Work Security:** Best practices for securing home networks and remote access.
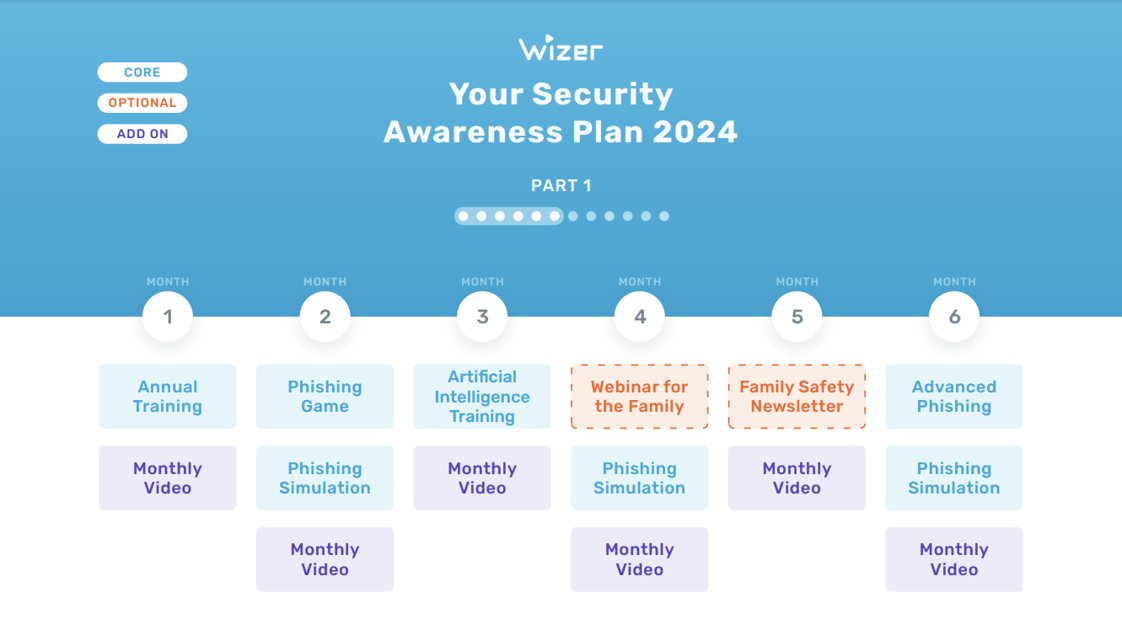
III. Delivery Methods and Schedule
A great training program isn’t just about what you teach, but how you teach it. A template helps you plan a multi-faceted approach to keep employees engaged and learning. Consider a blend of methods to cater to different learning styles and busy schedules.
Typical delivery methods often include:
- **Interactive E-learning Modules:** Self-paced online courses with quizzes and scenarios.
- **Live Webinars/Workshops:** Engaging sessions led by experts, allowing for Q&A.
- **Phishing Simulations:** Controlled exercises to test employee vigilance in a safe environment.
- **Regular Security Tips/Reminders:** Short, digestible communications via email, intranet, or posters.
- **Gamification:** Incorporating challenges, leaderboards, and rewards to boost engagement.
The schedule should also be planned carefully. Annual comprehensive training is a good start, but continuous, shorter “micro-learning” modules throughout the year are often more effective at reinforcing concepts and keeping security top of mind. Regular refreshers are vital as threats evolve rapidly.
IV. Evaluation and Reporting
To prove the effectiveness of your security education plan, you need metrics. The template should include provisions for how you will measure success. This isn’t just about completion rates; it’s about assessing behavioral change and risk reduction.
Metrics might include a reduction in successful phishing clicks, improved scores on knowledge assessments, or an increase in reported suspicious activities. Regular reporting to management demonstrates the value of the program and helps justify continued investment. This data-driven approach allows for continuous improvement, ensuring your training remains relevant and impactful.
Customizing Your Security Awareness Training Program Template for Impact
While a template provides a robust starting point, its true power lies in its adaptability. A generic approach won’t resonate as deeply as one tailored to your specific organizational context. Customization is not merely an option; it’s a necessity for maximum impact and engagement.
Start by identifying your organization’s unique risk profile. Are you in a highly regulated industry like healthcare or finance? Do you handle vast amounts of personally identifiable information (PII)? Your training should reflect these specific vulnerabilities and compliance requirements. For example, a healthcare organization will heavily emphasize HIPAA compliance in its data handling module, whereas a tech company might focus more on intellectual property protection.
Incorporate real-world examples relevant to your employees’ daily tasks. If your team frequently uses collaboration tools, show them how to secure shared documents within those platforms. Use language and scenarios that are familiar, making the training immediately applicable and less abstract. Personalized content helps employees see the direct relevance to their roles, boosting retention and behavioral change.
Consider the varying roles and responsibilities within your organization. Executive leadership might need training focused on protecting high-value targets like their executive assistants, while IT staff might require deeper technical modules. Tailoring the content to different employee groups ensures that everyone receives the most pertinent information without being overwhelmed by irrelevant details. This layered approach to an organizational security training program ensures comprehensive coverage.
Implementing and Sustaining Your Training Initiative
Launching a training program is just the beginning. The long-term success of your employee security education depends on consistent implementation and ongoing engagement. Utilize your chosen awareness training framework to guide these continuous efforts.
Establish a clear communication plan around the training, highlighting its importance and the benefits to both the individual and the organization. Make it mandatory but also emphasize the positive aspects of empowerment and protection. Leadership buy-in is paramount; when executives actively participate and champion the program, it signals its significance to the entire workforce.
Beyond initial rollout, cultivate a culture of ongoing learning. This means regular reinforcement through short, digestible content, periodic phishing simulations, and encouraging an open dialogue about security concerns. A dedicated channel for employees to ask questions or report suspicious activities without fear of reprimand can significantly enhance your security posture.
Feedback mechanisms are also crucial. Regularly solicit input from employees on the training content and delivery methods. Are the modules clear? Is the content engaging? This feedback loop allows you to refine your program over time, ensuring it remains effective, relevant, and well-received. Remember, security awareness is not a one-time event, but a continuous journey.
Measuring Success and Adapting for the Future
A well-defined security awareness training program template should include robust mechanisms for measuring effectiveness. This isn’t just about checking a box; it’s about demonstrating value and identifying areas for improvement. Data-driven insights are invaluable for refining your approach and ensuring your efforts yield tangible results.
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as phishing click-through rates before and after simulations, completion rates of modules, and the number of reported security incidents. Qualitative data, gathered through surveys or focus groups, can also provide valuable insights into employee perceptions and confidence levels regarding cybersecurity. Regularly review this data to understand trends and pinpoint areas where further education or different approaches may be needed.
The cyber threat landscape is dynamic, and your training program must be equally adaptable. As new threats emerge or your organization adopts new technologies, your security awareness content should evolve to address these changes. Treat your template not as a static document, but as a living framework that is regularly reviewed, updated, and enhanced. This iterative process ensures that your workforce remains equipped with the most current knowledge to protect against evolving digital dangers.
Investing in a well-structured **Security Awareness Training Program Template** is more than just good practice; it’s a strategic imperative for any organization operating in today’s digital world. It empowers your most valuable asset—your people—to become an active part of your defense strategy, significantly reducing your overall risk profile. By providing a clear, actionable roadmap, a robust template enables you to build and maintain a vigilant workforce, fostering a culture where security is everyone’s responsibility.
Embrace the power of a comprehensive training program. Leverage a flexible template to customize your approach, engage your employees, and continuously adapt to the ever-changing threat landscape. In doing so, you’re not just complying with regulations; you’re building a formidable human firewall, safeguarding your organization’s future in an increasingly interconnected and perilous digital environment.