In the complex landscape of software development, where features proliferate and user expectations soar, the bedrock of successful testing often lies in the quality and relevance of the data used. Without robust, representative, and well-managed test data, even the most meticulously designed test cases can fall short, leading to missed defects, unreliable results, and ultimately, a compromised product. This critical aspect, however, is frequently an afterthought, leading to frantic data generation, ad-hoc solutions, and a significant drain on project resources.
The challenge isn’t just about having data; it’s about having the right data, at the right time, in the right format, for every test scenario. This is where a structured approach becomes indispensable. Organizations striving for testing excellence recognize that defining, managing, and provisioning test data is a discipline in itself. A dedicated framework for documenting these needs transforms a chaotic scramble into a streamlined, predictable process, benefiting everyone from developers and testers to business analysts and project managers.
Why Test Data Management is Crucial
Effective test data management is no longer a luxury; it’s a fundamental pillar of modern quality assurance and efficient software delivery. In an era of continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), manual data preparation is a bottleneck that cannot be afforded. Outdated or insufficient data can lead to tests that pass falsely, or worse, critical defects that slip into production, eroding user trust and incurring significant remediation costs. Properly managing your test data ensures that your testing accurately reflects real-world scenarios, covers edge cases, and provides reliable feedback on application quality.
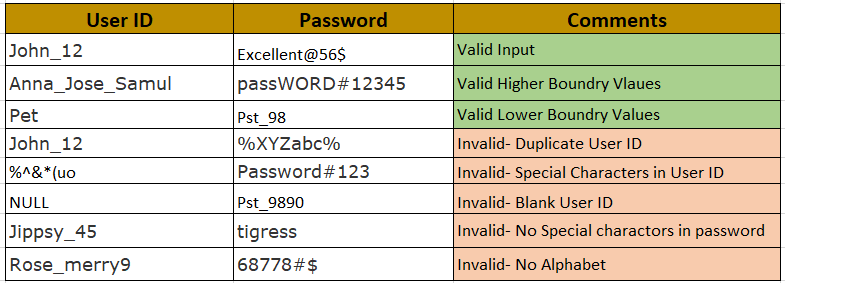
This discipline addresses several pain points: preventing environments from becoming polluted with irrelevant data, safeguarding sensitive information through anonymization or masking, and ensuring that test suites have access to diverse data sets necessary to validate all functional and non-functional requirements. It’s about building a repeatable, scalable process that supports iterative development cycles, allowing teams to deliver high-quality software faster and with greater confidence.
The Power of a Structured Approach
Adopting a standardized Test Data Requirements Template offers a powerful solution to common test data woes. Rather than vague requests or last-minute data generation efforts, this template provides a methodical way to document precisely what data is needed for each test phase and scenario. It transforms the often-informal process of test data specification into a formal, auditable, and collaborative effort. By articulating data needs clearly from the outset, teams can proactively plan for data provisioning, identify dependencies, and mitigate risks associated with data availability or quality.
Such a template serves as a single source of truth, fostering alignment across teams. Testers can clearly articulate their data needs, developers can understand what data conditions to prepare for, and data administrators can efficiently fulfill requests. This level of clarity significantly reduces miscommunication, rework, and delays, ultimately accelerating the testing cycle and improving overall project efficiency. It moves test data from being an obstacle to becoming an enabler of comprehensive and effective testing.
Key Elements of an Effective Test Data Requirements Document
A well-designed document for specifying test data needs provides a comprehensive framework for detailing every aspect of your data requirements. It ensures nothing is overlooked and that all stakeholders have a clear understanding of what’s expected. Here are the essential components:
- Test Case/Scenario Reference: Link data needs directly to specific test cases, user stories, or functional requirements. This establishes traceability and ensures data is purpose-driven.
- Data Type and Format: Clearly specify the kind of data required (e.g., valid, invalid, boundary, null) and its expected format (e.g., date, string, numeric, specific regex pattern).
- Volume and Velocity: Define the quantity of data needed (e.g., 100 unique customer records, a file with 1GB of data) and, for performance testing, the rate at which it should be available.
- Data State and Dependencies: Describe the initial state of the data (e.g., a customer with an active subscription, an order in “pending” status). Note any relationships or dependencies with other data sets or systems.
- Source and Sensitivity: Identify the origin of the data (e.g., production copy, synthetic data, existing test environment). Crucially, categorize its sensitivity (e.g., PII, PCI, HIPAA) to determine necessary masking or anonymization.
- Pre-conditions and Post-conditions: Outline any necessary setup steps before the data can be used (e.g., user account creation) and the expected state of the data or system after the test execution.
- Environment Specifics: Indicate if the data is required for a specific testing environment (e.g., Dev, QA, Staging) or if it needs to be refreshable across multiple environments.
- Creation/Provisioning Method: Suggest or specify how the data should be generated or acquired (e.g., manual entry, database script, data generation tool, API call, production data refresh).
- Approval and Ownership: Designate the owner of the data request and the approver to ensure accountability and validate the data’s fitness for purpose.
Benefits of Adopting a Standardized Framework
Implementing a Test Data Requirements Template across your projects brings a cascade of advantages that reverberate throughout the entire software development lifecycle. Firstly, it significantly **improves test coverage** by ensuring that diverse data sets are considered, thereby identifying more defects earlier. When data needs are explicitly detailed, the chances of missing edge cases or critical business scenarios are dramatically reduced.
Secondly, it leads to faster test execution cycles. With clear data specifications, data provisioning can be planned and automated, eliminating manual bottlenecks and reducing the time testers spend waiting for data. This efficiency directly contributes to faster time-to-market. Thirdly, a structured approach enhances data quality and reliability in testing. By demanding specific attributes and states, teams can ensure the test data accurately reflects production conditions, leading to more trustworthy test results and higher confidence in releases. Furthermore, it significantly reduces costs associated with rework, late-stage defect discovery, and the resources typically wasted on ad-hoc data efforts. Finally, it fosters better collaboration and communication among development, testing, and operations teams, creating a shared understanding of data needs and responsibilities.
Practical Tips for Customizing Your Data Requirements Document
While a standardized Test Data Requirements Template provides a strong foundation, its true power comes from thoughtful customization to fit your organization’s unique context and project needs. Begin by understanding the **specific application architecture** and data models. Different applications will have varying data complexities and dependencies, so tailor the fields in your template to reflect these nuances. For instance, if your application heavily relies on external integrations, ensure there are sections to detail data dependencies with those external systems.
Next, involve key stakeholders early in the customization process. Business analysts, developers, testers, and operations teams should all contribute to shaping the data requirement templates. Their input will ensure the document captures all necessary information from different perspectives. Consider adding fields for data privacy and compliance requirements right from the start, especially if your organization handles sensitive information. This proactive approach ensures data masking or anonymization strategies are built into the data provisioning process. Finally, don’t be afraid to iterate. Start with a version that covers most common scenarios, gather feedback after a few uses, and refine the template over time to make it even more efficient and effective for your specific environment.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Even with a robust Test Data Requirements Template in place, teams may encounter several hurdles. One common challenge is the **difficulty in obtaining realistic production data** due to privacy concerns or data volume. Overcome this by exploring data masking and anonymization tools, or by investing in synthetic data generation tools that can create high-quality, representative data without compromising sensitive information. Another issue is the **management of data dependencies** across multiple systems, especially in complex microservices architectures. Addressing this requires thorough documentation within the data specification document itself, clearly mapping out inter-system data relationships and defining data refresh strategies.
Lack of automation in data provisioning is another frequent bottleneck. While the template defines needs, the next step is automating the fulfillment. Integrate your data requirement templates with test data management tools that can programmatically provision, refresh, and subset data. Finally, resistance to adopting new processes can slow down implementation. Combat this through comprehensive training, demonstrating the tangible benefits of the standardized framework, and showcasing success stories from early adopters. Start small, perhaps with one pilot project, to build momentum and prove the value of a structured approach to defining test data needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of defining test data requirements?
The primary goal is to ensure that testers have access to the right kind, volume, and state of data at the right time, enabling comprehensive and reliable testing that accurately reflects real-world scenarios and uncovers defects effectively.
How does a structured template for test data improve test automation?
A structured template improves test automation by providing clear, unambiguous data specifications. This allows for easier integration with automated data provisioning tools, scripting of data setup and teardown, and ensuring repeatable test results, which is crucial for stable automation suites.
Can this approach be used for non-functional testing, like performance testing?
Absolutely. For non-functional testing, especially performance or load testing, the data specification document is critical for defining the required data volume, variety, and distribution patterns needed to simulate realistic user loads and measure system performance accurately. It ensures the performance tests are valid and representative.
Who is typically responsible for filling out the test data requirements?
While Quality Assurance (QA) engineers or testers are often the primary initiators, the responsibility for accurately filling out the data requirement templates is usually a collaborative effort involving business analysts (for business context), developers (for data structure and dependencies), and product owners (for prioritization).
What’s the difference between test data requirements and test cases?
Test data requirements define *what data* is needed, including its type, state, and volume, to execute a test. Test cases, on the other hand, describe *how to test* specific functionality, including steps, expected results, and the conditions under which the test should run. While distinct, they are intrinsically linked, as test cases often reference specific data requirements.
Implementing a well-designed Test Data Requirements Template is more than just another document; it’s a strategic move towards building a more resilient, efficient, and quality-driven software development pipeline. It instills discipline in a crucial yet often neglected area, transforming reactive data scrambling into proactive, intelligent planning. By making test data a first-class citizen in your development process, you equip your teams with the clarity and resources needed to test effectively, mitigate risks, and deliver exceptional products.
Embrace this structured approach to data requirement templates. It will not only streamline your testing efforts but also elevate the overall quality and reliability of your software, ensuring that every release is a testament to thoroughness and precision. Start today by customizing a data specification document that truly meets the unique demands of your projects and empowers your teams to build with confidence.


